Europa clipper could help discover if Jupiter's moon is habitable
Tuesday, 05 December 2023 18:28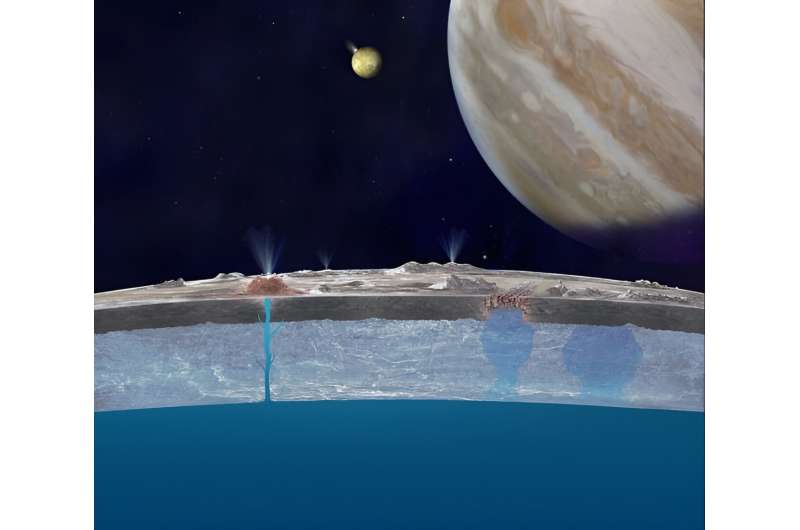
Since 1979, when the Voyager probes flew past Jupiter and its system of moons, scientists have speculated about the possibility of life within Europa. Based on planetary modeling, Europa is believed to be differentiated between a rocky and metallic core, an icy crust and mantle, and a liquid-water ocean that could be 100 to 200 km (62 to 124 mi) deep. Scientists theorize that this ocean is maintained by tidal flexing, where interaction with Jupiter's powerful gravitational field leads to geological activity in Europa's core and hydrothermal vents at the core-mantle boundary.
Investigating the potential habitability of Europa is the main purpose of NASA's Europa Clipper mission, which will launch on October 10th, 2024, and arrive around Jupiter in April 2030. However, this presents a challenge for astrobiologists since the habitability of Europa is dependent on many interrelated parameters that require collaborative investigation.
SETI: How we're searching for alien life at previously unexplored frequencies
Tuesday, 05 December 2023 16:37
Is there life beyond Earth? The question has turned out to be one of the hardest to answer in science. Despite the seemingly boundless expanse of the universe, which implies there's potential for abundant life, the vast distances between stars render the search akin to locating a needle in a cosmic haystack.
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) constitutes a branch of astronomy dedicated to finding extraterrestrial life by searching for unusual signals, dubbed technosignatures. The identification of a technosignature wouldn't just signify the existence of life, but specifically point to the presence of intelligent life using advanced technology.
That said, 60 years of searches have so far come up short. But now my colleagues and I have started investigating a previously unexplored range of frequencies.
SETI makes the assumption that extraterrestrial civilizations might rely on technology in a similar way to people on Earth, such as using cell phones, satellites or radar.
Since a significant portion of such technology generates signals that are prominently detectable in radio frequencies, focusing on these wavelengths serves as a logical starting point in the quest for potential extraterrestrial intelligence.
Was going to space a good idea?
Tuesday, 05 December 2023 16:26
In 1963, six years after the first satellite was launched, editors from the Encyclopedia Britannica posed a question to five eminent thinkers of the day: "Has man's conquest of space increased or diminished his stature?" The respondents were philosopher Hannah Arendt, writer Aldous Huxley, theologian Paul Tillich, nuclear scientist Harrison Brown and historian Herbert J. Muller.
Sixty years later, as the rush to space accelerates, what can we learn from these 20th-century luminaries writing at the dawn of the space age?
The state of space 60 years on
Much has happened since. Spacecraft have landed on planets, moons, comets, and asteroids across the solar system. The two Voyager deep space probes, launched in 1977, are in interstellar space.
A handful of people are living in two Earth-orbiting space stations. Humans are getting ready to return to the moon after more than 50 years, this time to establish a permanent base and mine the deep ice lakes at the south pole.
There were only 57 satellites in Earth orbit in 1963. Now there are around 10,000, with tens of thousands more planned.
NAVISP Industry 2023 @ ESTEC
Tuesday, 05 December 2023 16:00 Video:
00:02:04
Video:
00:02:04
In November 2023, ESA hosted its annual NAVISP Industry Days event. This year, more than 200 positioning, navigation and timing (PNT) professionals from across Europe gathered at ESA’s Space Research and Technology Centre (ESTEC) in the Netherlands to explore together opportunities for innovation, commercialisation and collaboration via ESA’s Navigation Innovation and Support Programme (NAVISP).
For more information: visit https://navisp.esa.int
Orbit Fab and Australia’s Space Machines Company cooperate on in-orbit servicing
Tuesday, 05 December 2023 12:00

Data rights limitations affecting NASA technology development
Tuesday, 05 December 2023 11:41

Galileo Second Generation satellites take shape
Tuesday, 05 December 2023 11:10
To make the future of Galileo a reality, ESA and European industry are hard at work developing ultra-precise atomic clocks, system testbeds, ground mission and ground control segments and, of course, the satellites. Airbus Defence and Space, who is building six of the Galileo Second Generation constellation satellites, presented their first flight model structure to the programme’s stakeholders last week.
Delve into the new CEOS Earth Observation Handbook
Tuesday, 05 December 2023 08:15
Delve into the new CEOS Earth Observation Handbook
Chandrayaan-3 Propulsion Module Successfully Transitions from Lunar to Earth Orbit
Tuesday, 05 December 2023 05:42 In a striking demonstration of space mission versatility, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully maneuvered the Propulsion Module (PM) of its Chandrayaan-3 mission from an orbit around the Moon to an orbit around Earth. This maneuver is not just a technical achievement but also a strategic move to enhance the utility of the mission's assets.
Launched on July 14, 202
In a striking demonstration of space mission versatility, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully maneuvered the Propulsion Module (PM) of its Chandrayaan-3 mission from an orbit around the Moon to an orbit around Earth. This maneuver is not just a technical achievement but also a strategic move to enhance the utility of the mission's assets.
Launched on July 14, 202 CAS Space expands into Guangdong with new rocket engine testing complex
Tuesday, 05 December 2023 05:42 CAS Space, a prominent Beijing-based rocket company under the Chinese Academy of Sciences, marked a significant milestone on Saturday with the commencement of construction on a new rocket engine testing facility in Guangdong province. This facility, the first of its kind in this economically vibrant region, represents a crucial step in the expansion of China's space capabilities.
Situated
CAS Space, a prominent Beijing-based rocket company under the Chinese Academy of Sciences, marked a significant milestone on Saturday with the commencement of construction on a new rocket engine testing facility in Guangdong province. This facility, the first of its kind in this economically vibrant region, represents a crucial step in the expansion of China's space capabilities.
Situated CityU develops universal metasurface antenna, advancing 6G communications
Tuesday, 05 December 2023 05:42 Researchers at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) have achieved a significant breakthrough in antenna technology, creating the world's first universal metasurface antenna that can control all five fundamental properties of electromagnetic waves through software. This novel technology holds immense potential for the future of 6G wireless communication systems, offering advanced waveform manipul
Researchers at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) have achieved a significant breakthrough in antenna technology, creating the world's first universal metasurface antenna that can control all five fundamental properties of electromagnetic waves through software. This novel technology holds immense potential for the future of 6G wireless communication systems, offering advanced waveform manipul D-Orbit advancing space logistics with Beyond mission
Tuesday, 05 December 2023 05:42 On December 1st, D-Orbit, a leader in the realm of space logistics and orbital transportation, achieved a significant milestone by successfully launching its 13th commercial mission, named Beyond. This mission utilized the company's innovative Orbital Transfer Vehicle (OTV), the ION Satellite Carrier, showcasing its versatility and advanced capabilities in the industry.
The launch occurred
On December 1st, D-Orbit, a leader in the realm of space logistics and orbital transportation, achieved a significant milestone by successfully launching its 13th commercial mission, named Beyond. This mission utilized the company's innovative Orbital Transfer Vehicle (OTV), the ION Satellite Carrier, showcasing its versatility and advanced capabilities in the industry.
The launch occurred