
Copernical Team
Spacemanic startup wins Pierre Cardin Prix Bulles prize
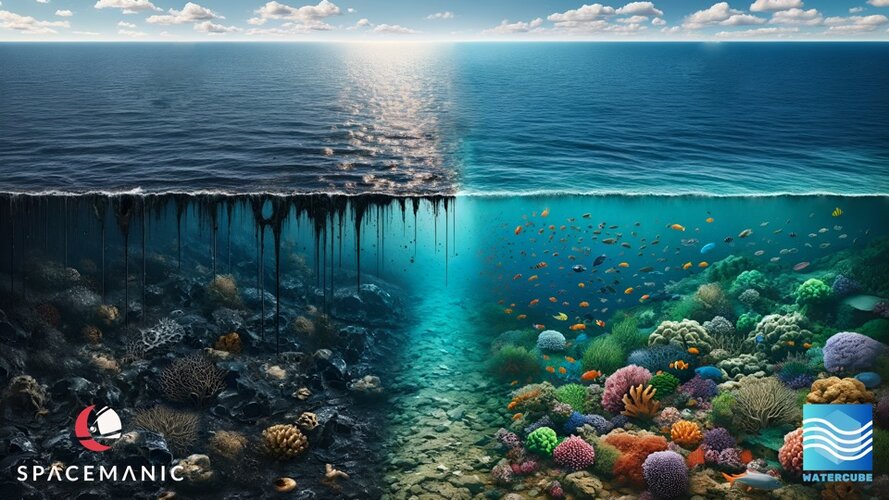

Spacemanic, a Slovak and Czech startup company, won this year’s Prix Bulles Cardin award of €20 000 on 17 May for its ocean WaterCube.
This device, which is based on space hardware, has sensors which measure pollution levels in sea water allowing the identification of pollution hotspots. With this data, action can be taken to safeguard habitats and species critical for the long-term sustainability of marine ecosystems and fisheries.
'Planetary parade' to start in June

First came a rare solar eclipse, followed by the northern lights, fueled by a solar storm. The next celestial phenomenon will come next month, when skygazers can look forward to an alignment known as a "planetary parade."
The parade will start June 3, when Mercury, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune will be aligned, according to Star Walk Astronomical News, a planetarium phone app.
During such events, multiple planets can be seen across the sky. A "mini planetary alignment" is when three are aligned; a large alignment comprises five or six, according to the outlet.
But don't expect to see them all.
Preston Dyches of NASA's "Skywatching Tips" video series explained that only two planets will be visible to the naked eye June 3, if any.
"Contrary to many reports and social media postings, there will not be a string of naked-eye planets visible on June 3," he said via email. "Mercury and Jupiter will be far too low in the sky at sunrise. Even under ideal conditions (a dark sky, free from light pollution) Uranus is very dim and challenging to spot.
Space Force training HQ gets official nod to come to Space Coast

The decision has been a year in the making, but the Space Coast will officially become the home of STARCOM, the training headquarters for Space Force.
Patrick Space Force Base and Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, both former Air Force facilities, were named in May 2023 the presumptive home for STARCOM, which stands for Space Training and Readiness Command. It's one of three Space Force field command units, similar to an Air Force air command.
Sen. Marco Rubio confirmed the decision was made final posting congratulations on X.
"Great news for Florida! Patrick Space Force Base has received final approval to become the permanent headquarters for STARCOM, bolstering Florida's growing leadership in space," Rubio posted May 21.
The Space Coast lost out on getting the Department of Defense's U.S. Space Command headquarters in 2022, but STARCOM would bring a major addition to Space Force's already sizable presence as the launch capital of the world.
STARCOM is "responsible for the deliberate development, education and training of space professionals in addition to the development of space warfighting doctrine, tactics, techniques and procedures, and the operational test and evaluation of Space Force systems," according to an Air Force press release.
Ariane 6 launches: Replicator – 3D printing in open space

Watch EarthCARE launch live
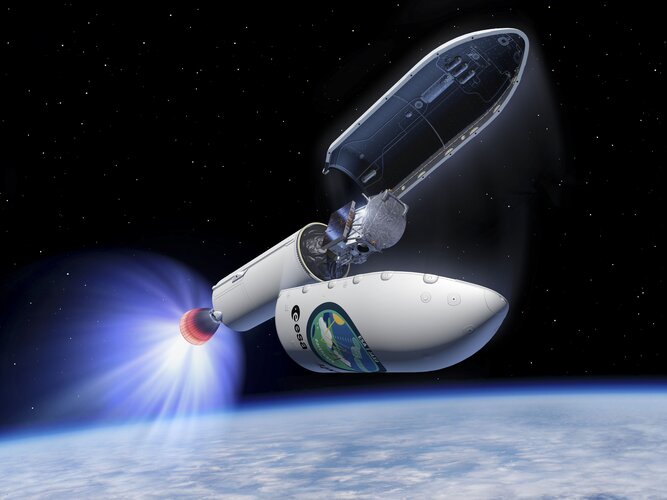

ESA’s Earth Cloud Aerosol and Radiation Explorer (EarthCARE) mission is getting ready for lift-off on a SpaceX Falcon 9 from Vandenberg, California, with a target launch date of no earlier than 28 May 2024. Save the date and watch the launch live on ESA WebTV or ESA YouTube.
Cool by design 3D printing
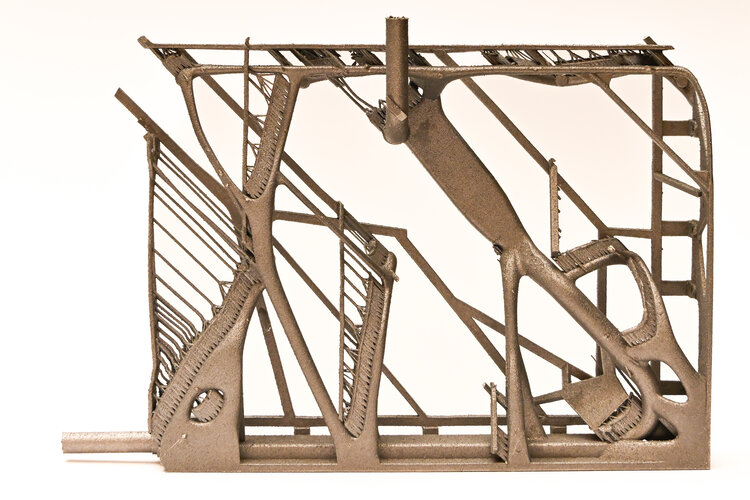 Image:
Cool by design 3D printing
Image:
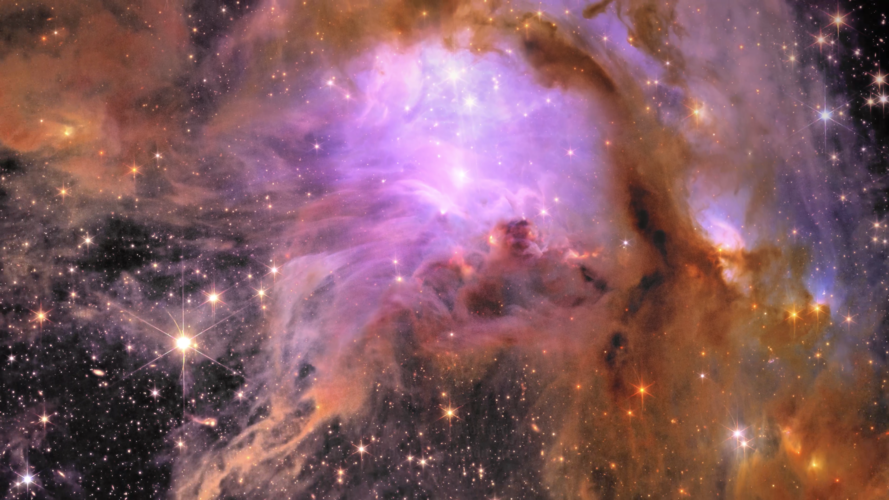
Cool by design 3D printing Euclid celebrates first science with sparkling new images
 Video:
00:01:01
Video:
00:01:01
Today, ESA’s Euclid space mission releases five unprecedented new views of the Universe. The never-before-seen images demonstrate Euclid’s ability to unravel the secrets of the cosmos and enable scientists to hunt for rogue planets, use lensed galaxies to study mysterious matter, and explore the evolution of the Universe.
Read more about Euclid's first images and download the individual images here.
Pentagon says Russia launched space weapon in path of US satellite
 Russia has launched a likely space weapon and deployed it in the same orbit as a US government satellite, the Pentagon said.
"Russia launched a satellite into low Earth orbit that we assess is likely a counter-space weapon presumably capable of attacking other satellites in low Earth orbit," Pentagon spokesman Air Force Major General Pat Ryder told a press briefing late Tuesday.
The Russ
Russia has launched a likely space weapon and deployed it in the same orbit as a US government satellite, the Pentagon said.
"Russia launched a satellite into low Earth orbit that we assess is likely a counter-space weapon presumably capable of attacking other satellites in low Earth orbit," Pentagon spokesman Air Force Major General Pat Ryder told a press briefing late Tuesday.
The Russ Euclid space telescope unveils new images of the cosmos
 A mind-boggling number of shining galaxies, a purple and orange star nursery and a spiral galaxy similar to our Milky Way: new images were revealed from Europe's Euclid space telescope on Thursday.
It is the second set of images released by the European Space Agency since Euclid launched last year on the first-ever mission to investigate the mysteries of dark matter and dark energy.
Scie
A mind-boggling number of shining galaxies, a purple and orange star nursery and a spiral galaxy similar to our Milky Way: new images were revealed from Europe's Euclid space telescope on Thursday.
It is the second set of images released by the European Space Agency since Euclid launched last year on the first-ever mission to investigate the mysteries of dark matter and dark energy.
Scie Yahsat and Eutelsat Partner to Expand Satellite Broadband in Africa
 Eutelsat Group (ISIN: FR0010221234 - Euronext Paris / London Stock Exchange: ETL) and YahClick, the data solutions arm of Al Yah Satellite Communications Company PJSC (Yahsat), the UAE's flagship satellite solutions (ADX: YAHSAT, ISIN: AEA007501017), have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU). This agreement allows YahClick to use capacity on Eutelsat's geostationary satellite, EUTELSAT KON
Eutelsat Group (ISIN: FR0010221234 - Euronext Paris / London Stock Exchange: ETL) and YahClick, the data solutions arm of Al Yah Satellite Communications Company PJSC (Yahsat), the UAE's flagship satellite solutions (ADX: YAHSAT, ISIN: AEA007501017), have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU). This agreement allows YahClick to use capacity on Eutelsat's geostationary satellite, EUTELSAT KON 
