
Copernical Team
Glasgow Prestwick Spaceport announces Launch Partner
 Prestwick Spaceport has secured a launch partner for its spaceport development in a landmark deal that will boost Scotland's space industry ambitions and create an important strategic asset for the UK.
The spaceport, represented by Glasgow Prestwick Airport and South Ayrs0hire Council, yesterday signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Astraius, the leading UK based, commercially op
Prestwick Spaceport has secured a launch partner for its spaceport development in a landmark deal that will boost Scotland's space industry ambitions and create an important strategic asset for the UK.
The spaceport, represented by Glasgow Prestwick Airport and South Ayrs0hire Council, yesterday signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Astraius, the leading UK based, commercially op US Space Force to take over SATCOM operations from Army, Navy
 The U.S. Space Force will take over satellite communications billets, funding and mission responsibility from the U.S. Army and Navy, the Department of Defense announced Wednesday.
The transfer, which includes a total of 15 global units with 319 military and 259 civilian billets, is scheduled to be effective Oct. 1, if the Defense Department budget is passed and signed.
"We're on
The U.S. Space Force will take over satellite communications billets, funding and mission responsibility from the U.S. Army and Navy, the Department of Defense announced Wednesday.
The transfer, which includes a total of 15 global units with 319 military and 259 civilian billets, is scheduled to be effective Oct. 1, if the Defense Department budget is passed and signed.
"We're on Delta-X helps with disaster response in wake of Hurricane Ida
 Charged with studying the Mississippi River Delta, NASA's Delta-X project was gearing up to collect data on Louisiana's coastal wetlands when Hurricane Ida barreled ashore in late August. The storm - a high-end Category 4 when it made landfall near Port Fourchon, Louisiana, on Aug. 29 - damaged buildings and infrastructure alike, resulting in power outages, flooding, and oil slicks in the Gulf o
Charged with studying the Mississippi River Delta, NASA's Delta-X project was gearing up to collect data on Louisiana's coastal wetlands when Hurricane Ida barreled ashore in late August. The storm - a high-end Category 4 when it made landfall near Port Fourchon, Louisiana, on Aug. 29 - damaged buildings and infrastructure alike, resulting in power outages, flooding, and oil slicks in the Gulf o Raymond describes Space Force achievements, plans, challenges ahead
 Chief of Space Operations, Gen. John W. "Jay" Raymond used a list of "firsts" and achievements across the Space Force's brief history Sept. 21 to illustrate how the nation's newest military service is "purpose built" for success at a time when the nation "can no longer take space for granted."
"Space is clearly a warfighting domain and we're convinced that if deterrence were to fail, we're
Chief of Space Operations, Gen. John W. "Jay" Raymond used a list of "firsts" and achievements across the Space Force's brief history Sept. 21 to illustrate how the nation's newest military service is "purpose built" for success at a time when the nation "can no longer take space for granted."
"Space is clearly a warfighting domain and we're convinced that if deterrence were to fail, we're Xplore receives $2M contract from NSIC to accelerate Xcraft Platform Development
 Xplore Inc., a commercial space company providing Space as a Service, has announced it has received a $2M contract from National Security Innovation Capital (NSIC) within the Defense Innovation Unit (DIU) of the Department of Defense (DoD). This funding will accelerate the development of the Xcraft spacecraft platform, culminating with launch in 2023.
Lisa Rich, Founder and COO of Xplore s
Xplore Inc., a commercial space company providing Space as a Service, has announced it has received a $2M contract from National Security Innovation Capital (NSIC) within the Defense Innovation Unit (DIU) of the Department of Defense (DoD). This funding will accelerate the development of the Xcraft spacecraft platform, culminating with launch in 2023.
Lisa Rich, Founder and COO of Xplore s All-female crew in water-tank spaceflight study

This week 20 women are tucking themselves in a waterbed for five days as part of a dry immersion study to recreate some of the effects of spaceflight on the body. The campaign kicked off yesterday with the first two subjects at the Medes space clinic in Toulouse, France.
Node 1 | Space Station 360 (in French with English subtitles available)
 Video:
00:02:40
Video:
00:02:40
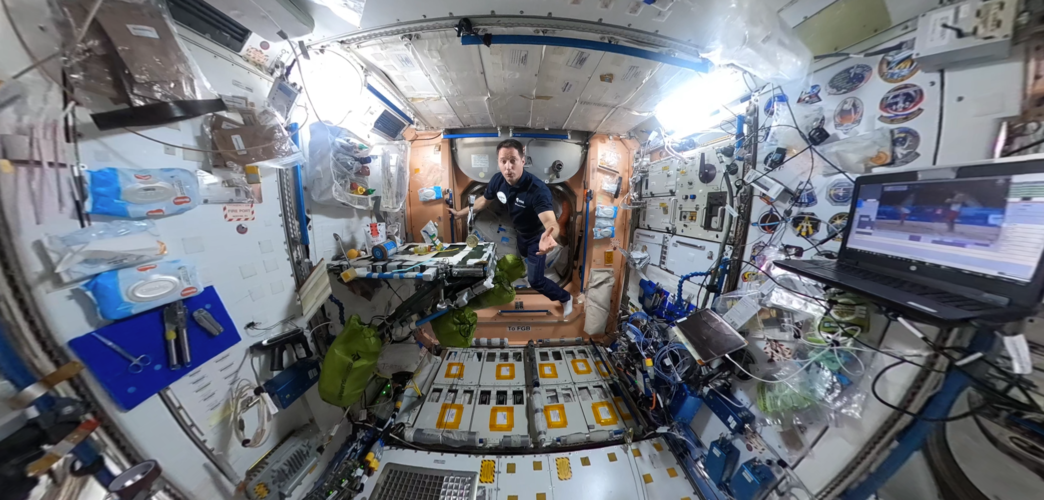
ESA astronaut Thomas Pesquet takes you on a tour of the International Space Station like no other. Filmed with a 360 camera, the Space Station 360 series lets you explore for yourself alongside Thomas’s explanation – episode five is NASA’s Node-1, also known as Unity.
Unity is the module that connects the Russian segment of the International Space Station to the other modules. Launched on 4 December 1998 inside Space Shuttle Endeavour, it was joined to the Russian Zarya module two days later, forming the basis of the International Space Station. The cylindrical module has six docking ports
Image: Gloomy moonscape created for rover test
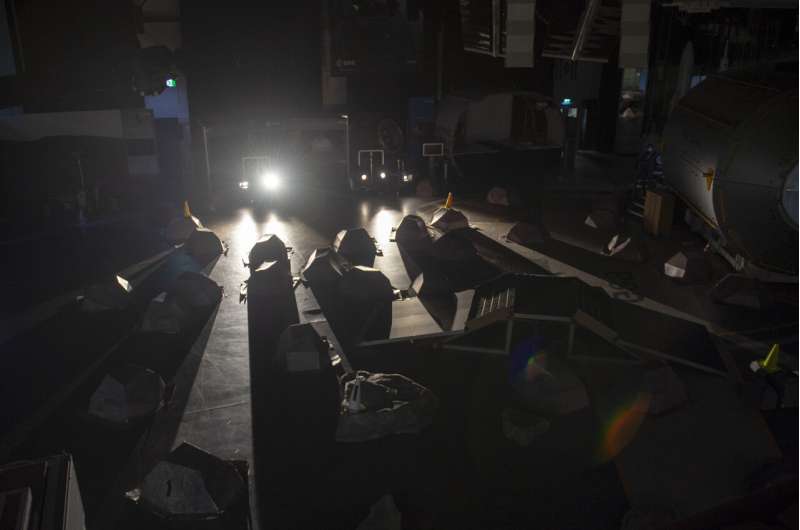

A sun barely peeking over a cratered horizon, casting long shadows across a rocky moonscape: ESA's Erasmus Innovation Center was transformed into an analog of the moon's polar regions, in a dress rehearsal for an international rover competition.
The Space Resources Challenge—supported by ESA and the European Space Resources Innovation Center (ESRIC) in Luxembourg- is asking European (and Canadian) researchers and institutions to develop and demonstrate a system of one or more vehicles capable of prospecting resources on the moon in the near future.
Some 13 teams have been selected to participate in the Challenge's first field test in November, with €375 000 in ESA contracts to be awarded to the five winners, with a larger prize pool on offer after a follow-on field test next year.
"The focus here is really on prospecting—pinpointing promising resources within a difficult lunar environment then characterizing them in as much detail as possible, such as through spectral analysis," comments Massimo Sabbatini, managing the Erasmus Center, part of ESA's ESTEC technical center in the Netherlands.
"We're preparing for the first rover field test in November, which will take place in a larger location, still to be disclosed, but we decided to try out the challenge for ourselves first, here at Erasmus.
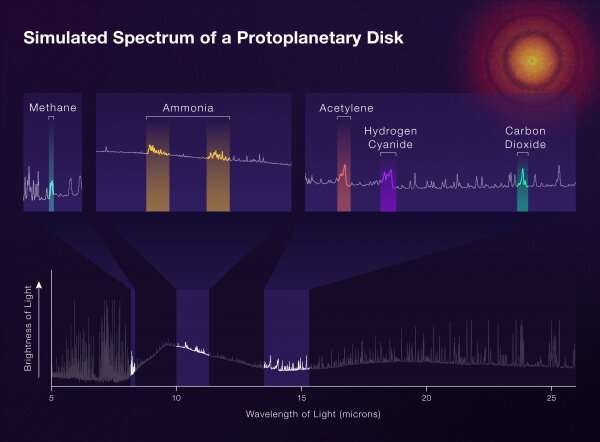
Webb telescope to explore forming planetary systems
NASA Invites Media to Webb Telescope Prelaunch Events in French Guiana
 NASA invites members of the media to register their interest in attending events in French Guiana ahead of the launch of the James Webb Space Telescope, a mission led by NASA in partnership with the European and Canadian space agencies.
NASA invites members of the media to register their interest in attending events in French Guiana ahead of the launch of the James Webb Space Telescope, a mission led by NASA in partnership with the European and Canadian space agencies. 
