
Copernical Team
NASA plans crashing spacecraft into asteroid to study Earth-impact defense
 NASA plans to launch a spacecraft as early as Nov. 23 and crash it into an asteroid next year so scientists can try to understand how to redirect dangerous space objects away from potential catastrophic Earth collisions.
The mission is NASA's first flight demonstration for planetary defense, space agency officials said.
The Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, is scheduled for
NASA plans to launch a spacecraft as early as Nov. 23 and crash it into an asteroid next year so scientists can try to understand how to redirect dangerous space objects away from potential catastrophic Earth collisions.
The mission is NASA's first flight demonstration for planetary defense, space agency officials said.
The Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, is scheduled for Tidying up planetary nurseries
 A group of astronomers, led by scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, propose and have tested a mechanism that explains most of the properties observed in dispersing planet-forming disks around newborn stars for the first time. The key ingredients to this new physical concept are X-ray emissions from the central star and a calm inner disk, well shielded from the incident radiati
A group of astronomers, led by scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, propose and have tested a mechanism that explains most of the properties observed in dispersing planet-forming disks around newborn stars for the first time. The key ingredients to this new physical concept are X-ray emissions from the central star and a calm inner disk, well shielded from the incident radiati NASA takes additional steps to investigate Hubble in safe mode
 NASA is continuing work to resolve an issue that has suspended science operations on the Hubble Space Telescope. The science instruments entered a safe mode configuration on Oct. 25 after detecting a loss of specific data synchronization messages.
The Hubble team is focusing its efforts to isolate the problem on hardware that commands the instruments and is part of the Science Instrument C
NASA is continuing work to resolve an issue that has suspended science operations on the Hubble Space Telescope. The science instruments entered a safe mode configuration on Oct. 25 after detecting a loss of specific data synchronization messages.
The Hubble team is focusing its efforts to isolate the problem on hardware that commands the instruments and is part of the Science Instrument C New dates for Crew-2 return and Crew-3 launch

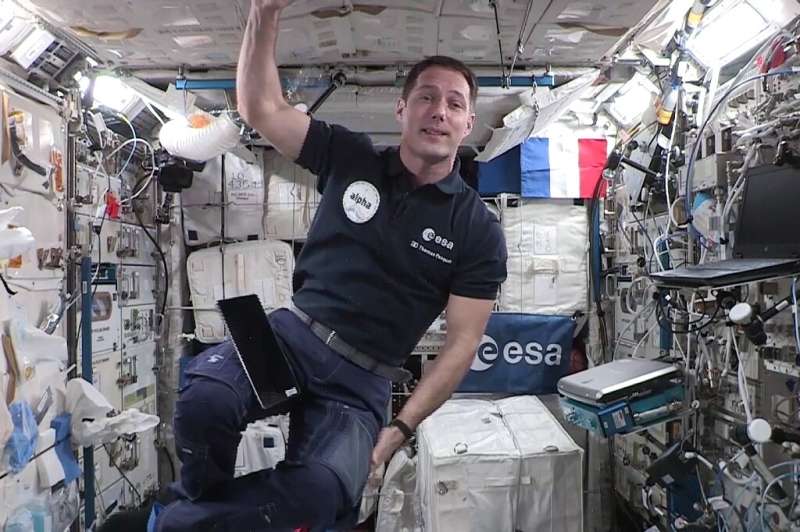
Update: Undocking of Crew-2 with Thomas Pesquet now planned for Sunday, 7 November, 18:05 GMT/19:05 CET for a splashdown on Monday, around 12:14 GMT/13:14 CET. Next launch opportunity for Crew-3 with Matthias Maurer is planned for Thursday, 11 November, 02:03 GMT/03:03 CET.
No toilet for returning SpaceX crew, stuck using diapers
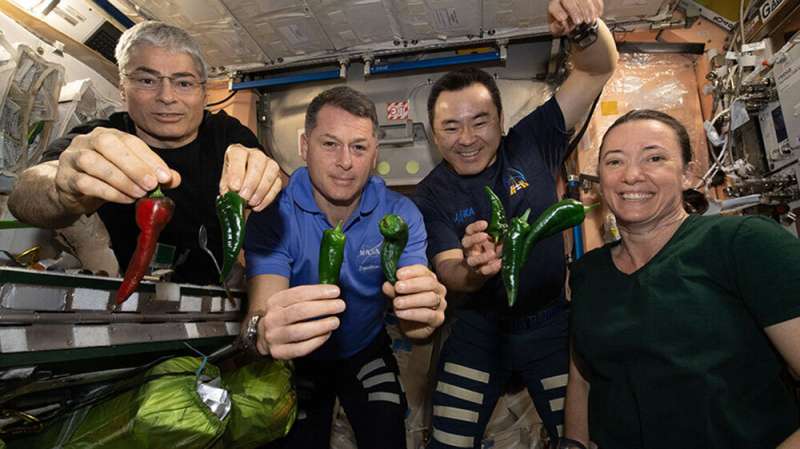

The astronauts who will depart the International Space Station on Sunday will be stuck using diapers on the way home because of their capsule's broken toilet.
NASA astronaut Megan McArthur described the situation Friday as "suboptimal" but manageable. She and her three crewmates will spend 20 hours in their SpaceX capsule, from the time the hatches are closed until Monday morning's planned splashdown.
"Spaceflight is full of lots of little challenges," she said during a news conference from orbit.
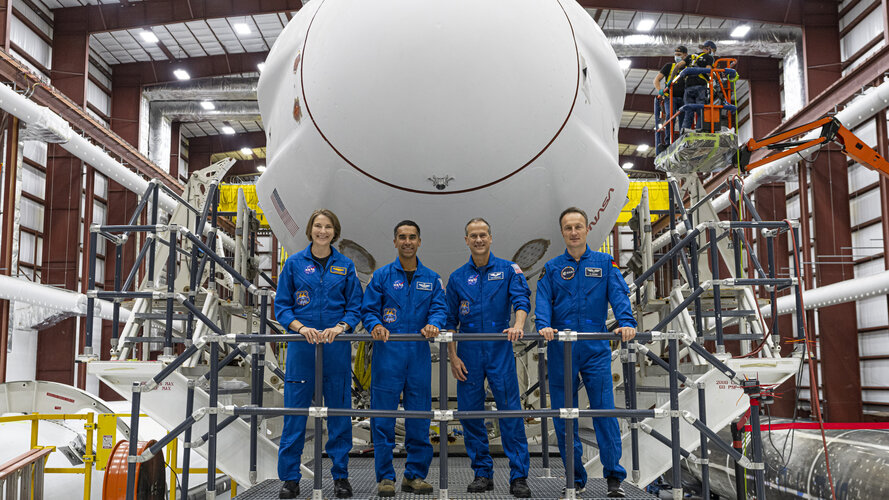
Astronauts to return from space station next week: NASA

Four astronauts are scheduled to return to Earth from the International Space Station early Monday after spending more than six months in space, NASA announced.
The four members of the Crew-2 mission, including a French and a Japanese astronaut, will therefore return to Earth before the arrival of a replacement crew, whose take-off was delayed several times due to unfavorable weather conditions.
NASA said in a statement late Friday that Crew-2 members are due to return to Earth "no earlier than 7:14 am EST (1214 GMT) Monday, Nov. 8, with a splashdown off the coast of Florida."
"As we're preparing to leave, it's kind of a bittersweet feeling, we might never come back to see the ISS, and it's really a magical place," French astronaut Thomas Pesquet said earlier Friday during a press conference from the space station.
New great observatories, including Lynx, recommended as a national priority by decadal survey
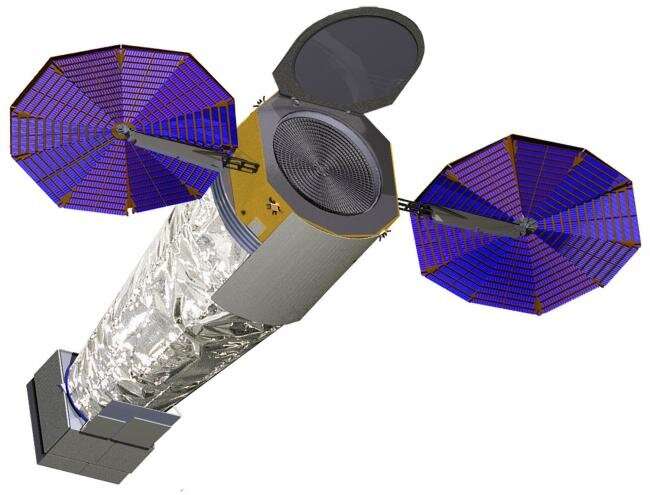
The 2020 Decadal Survey for Astronomy and Astrophysics has recommended a new series of three Great Observatories—or space-based telescopes—as a top national priority for the future of space astrophysics.
The Lynx X-Ray Observatory is included as part of this vision. Dozens of scientists and engineers at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian teamed with colleagues around the world to define the observatory's scientific objectives, conceptualize its design and work on key technologies.
Known as the Decadal Survey, the report evaluates astrophysics and astronomy programs and prioritizes them for the next decade of transformative science. Findings from the survey are submitted as recommendations to NASA, the National Science Foundation and the Department of Energy to guide funding requests and allocations for astrophysics over the next 10 years.
"I am pleased to hear that the scientific community endorses a vision for the New Great Observatories that includes Lynx," says Charles Alcock, director of the Center for Astrophysics (CfA). "Lynx will transform our understanding of the cosmos by providing by far the most sensitive X-ray vision into the otherwise invisible universe.
To find life on other planets, NASA rocket team looks to the stars
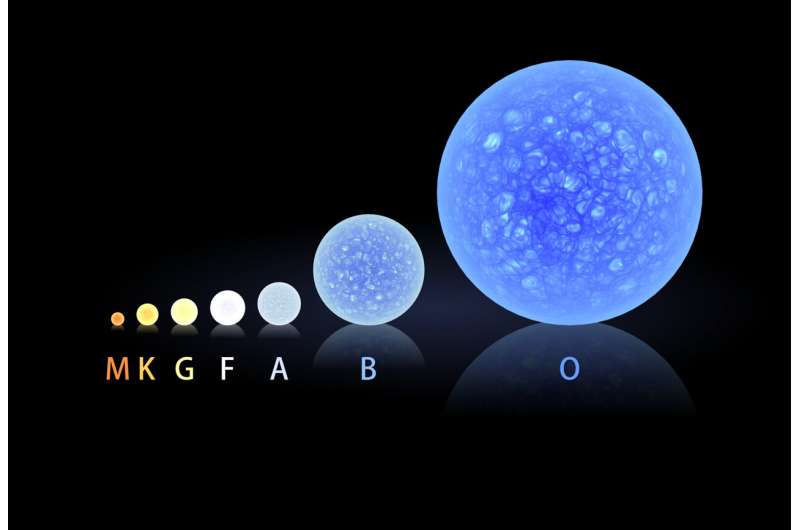
A NASA sounding rocket will observe a nearby star to learn how starlight affects the atmospheres of exoplanets—key information in the hunt for life outside our solar system.
Last call: fly your payload on first Ariane 6 launch

ESA offers an opportunity for payloads and experiments to ride on board the first flight of Ariane 6 planned in 2022. Notice of interest should reach ESA by 15 November.
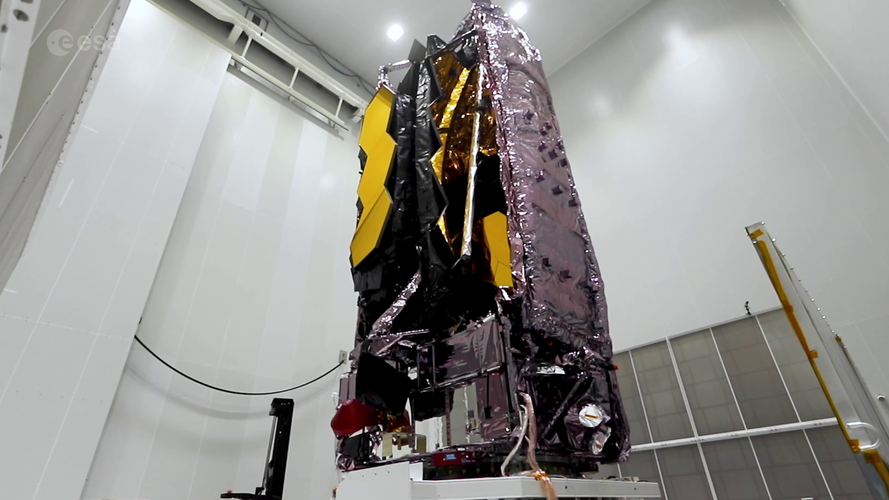
Webb unboxed in cleanroom at Europe’s Spaceport
 Video:
00:01:19
Video:
00:01:19
After its arrival at Pariacabo harbour in French Guiana on 12 October 2021, the James Webb Space Telescope was transported to Europe’s Spaceport and unboxed in the cleanroom. It is now being prepared for its launch on an Ariane 5 rocket in December.
Though the telescope weighs only six tonnes, it is more than 10.5 m high and almost 4.5 m wide when folded. It was shipped in its folded position in a 30 m long container which, with auxiliary equipment, weighed more than 70 tonnes.
After arriving in the harbour, the telescope inside its container

