
Copernical Team
SpaceX aims for night crew launch; ailing astronaut now OK
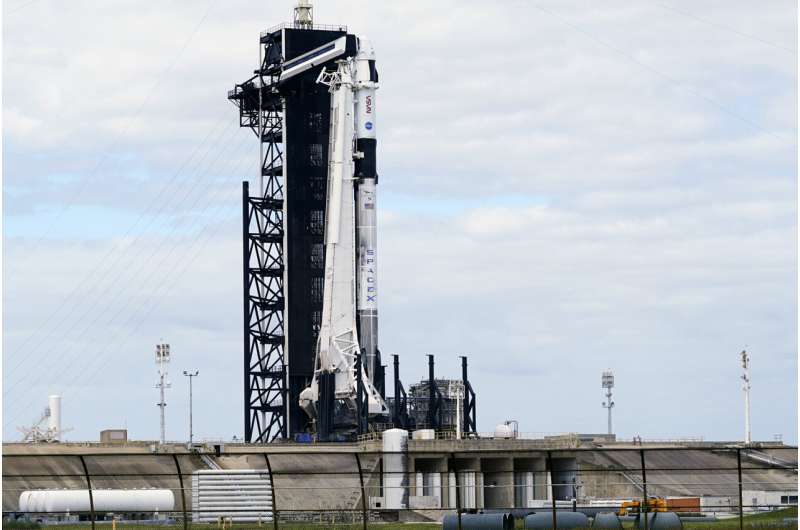

SpaceX counted down Wednesday toward a nighttime launch of four astronauts who have been grounded for nearly two weeks by weather and medical delays.
The Falcon rocket was poised to blast off from NASA's Kennedy Space Center a few hours after sunset. That would put the one German and three U.S. astronauts at the International Space Station by Thursday night to begin a six-month stay.
Alpha: a return to Earth in one minute
 Video:
00:01:28
Video:
00:01:28
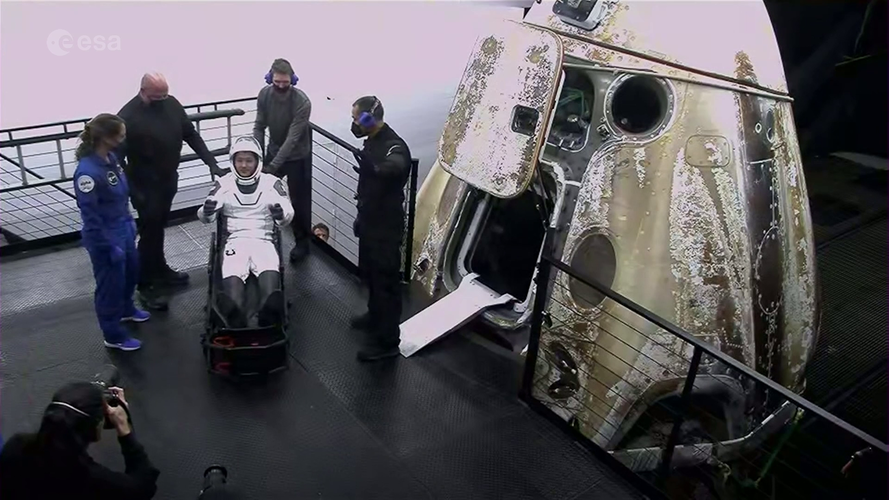
After 199 days in space, ESA astronaut Thomas Pesquet left the International Space Station together with alongside NASA astronauts Shane Kimbrough and Megan McArthur and JAXA astronaut Akihiko Hoshide, marking the end of his second six-month mission known as Alpha.
The return to Earth took ten hours, including a two-hour fly-around of the International Space Station, but this highlight reel shows the key moments of the journey in just a minute. From the Space Station to undocking, fly-around, reentry and splashdown off the coast of Florida, USA.
Thomas and crew splashed down on 9 November 2021 at 03:33 GMT
Weird weather: Metal rain and super-high temperatures on an ultra-hot exoplanet

Ultra-hot Jupiters—named as such because of their physical similarities to the planet Jupiter—are exoplanets that orbit stars other than the sun with temperatures so high that the molecules in their atmospheres are completely torn apart. They are among the most extreme environments in our galaxy.
They also whip around their parent stars in orbits that only last a few days, and astronomers still aren't sure how it's possible for them to form.
While these harsh conditions might sound like they're as extreme as it gets, astronomers are starting to realize they may just be the tip of the (very hot) iceberg. In a recent study published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, my colleagues and I discovered that one of these exotic worlds in particular is even more extreme than we'd ever thought.
Meet VMS: The briefcase-sized chemistry lab headed to Venus
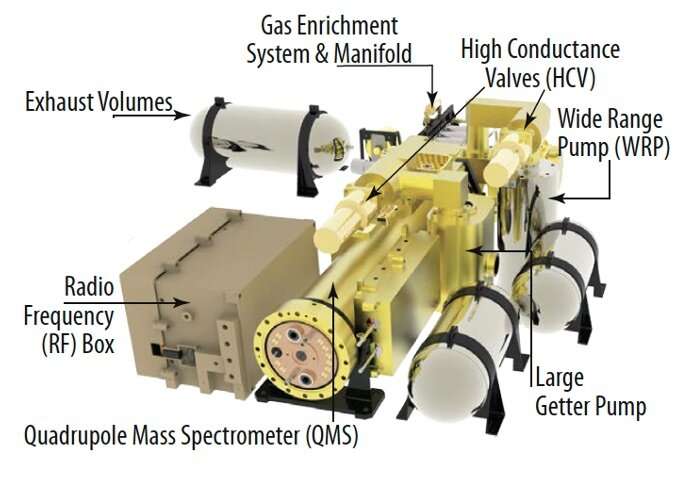
Short for Venus Mass Spectrometer, VMS is one of five instruments aboard the DAVINCI descent probe.
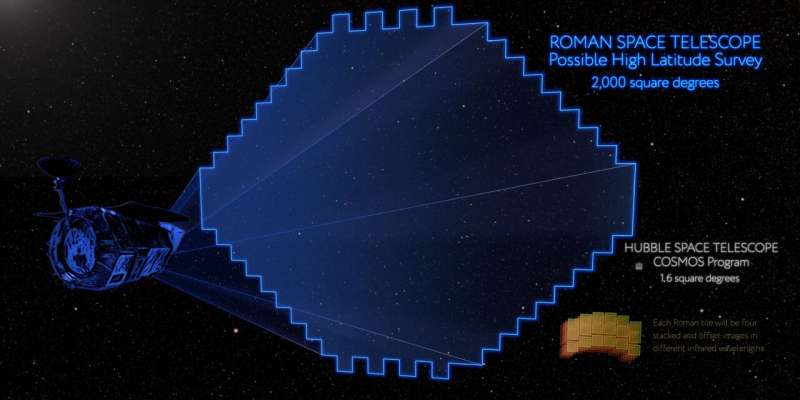
NASA's Roman mission will empower a new era of cosmological discovery

Using blocks dropped from Perseverance and measured by InSight to learn more about Martian surface
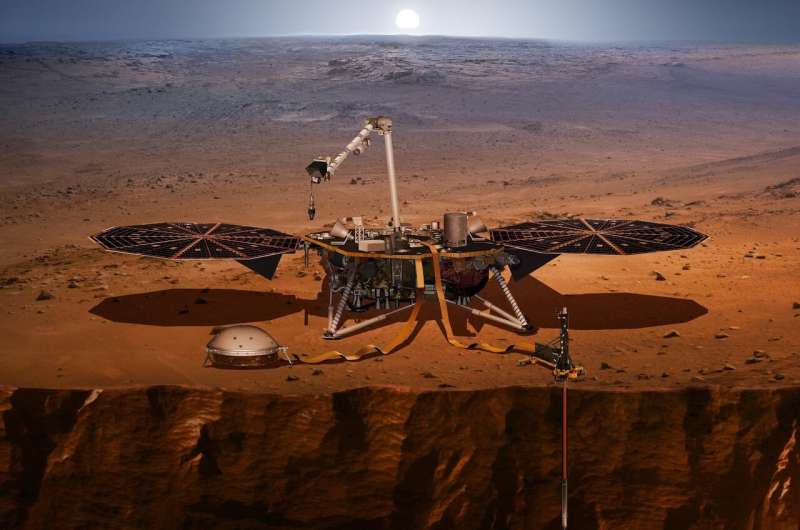

An international team of space researchers has learned more about the density of the Martian surface by analyzing data from the Mars InSight lander that was received during Perseverance's descent. In their paper published in the journal Nature Astronomy, the group describes their study of seismic data from InSight as Perseverance dropped heavy blocks during its descent.
One of the ways that planetary scientists learn more about the makeup of other planets is by studying seismic activity—waves from such activity can provide clues to the density of different parts of a planet. In this new effort, the researchers noted that gathering seismic data from extraterrestrial events such as asteroids striking the surface of a planet is difficult as they are so random. But they also noted that the Perseverance mission offered a unique opportunity—as part of its descent earlier this year, the rover's landing craft dropped two tungsten blocks—each weighing approximately 77.5kg to the surface below.
Satellites for safer seas… and a safer world!
 Video:
00:02:43
Video:
00:02:43
What if the Titanic had help from satellites? Its journey would likely have ended completely differently.
We live in an ever-changing world; the shipping industry still faces the old dangers, but today also encounters risks due to climate change as well as incentives to become greener.
Fortunately ships today have satellite support. Satellites designed for science, weather monitoring, Earth observation, navigation and communication serve our security needs on a daily basis. Not only in the ocean, but worldwide, in any situation.
From fighting organised crime to monitoring climate change. From establishing worldwide food security to ensuring aviation safety. Global challenges
European software-defined satellite starts service
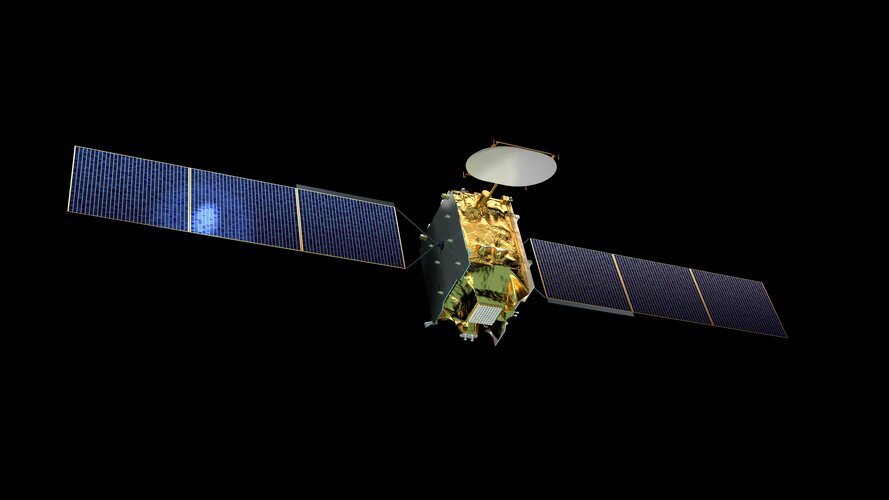

A telecommunications satellite that can be reprogrammed in-orbit, offering unprecedented mission reconfiguration capacity, has successfully passed its in-orbit acceptance review.
Carbon dioxide monitoring satellite given the shakes
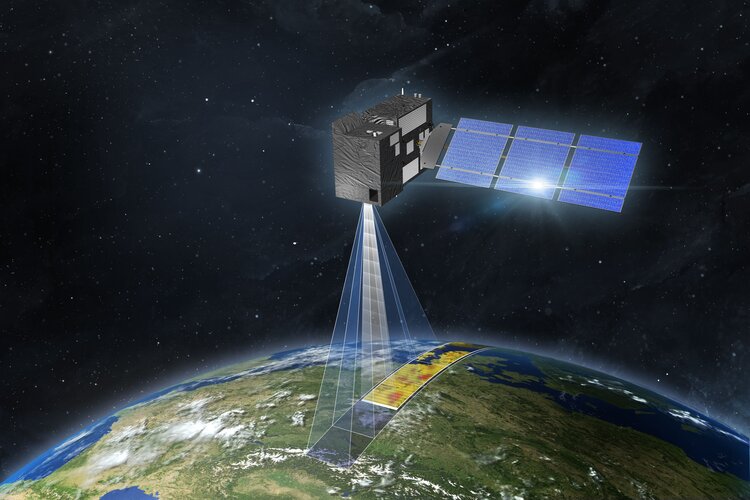

A new satellite destined to be Europe’s prime mission for monitoring and tracking carbon dioxide emissions from human activity is being put through its paces at ESA’s Test Centre in the Netherlands. With nations at COP26 pledging net-zero emissions by 2050, the pressure is on to reduce the amount of greenhouse gases we pump into the atmosphere – but the race is also on to support the monitoring that shows targets are being met. ESA, the European Commission, Eumetsat and industrial partners are therefore working extremely hard to get the Copernicus Anthropogenic Carbon Dioxide Monitoring mission ready for liftoff
Astronaut training in the land of volcanoes
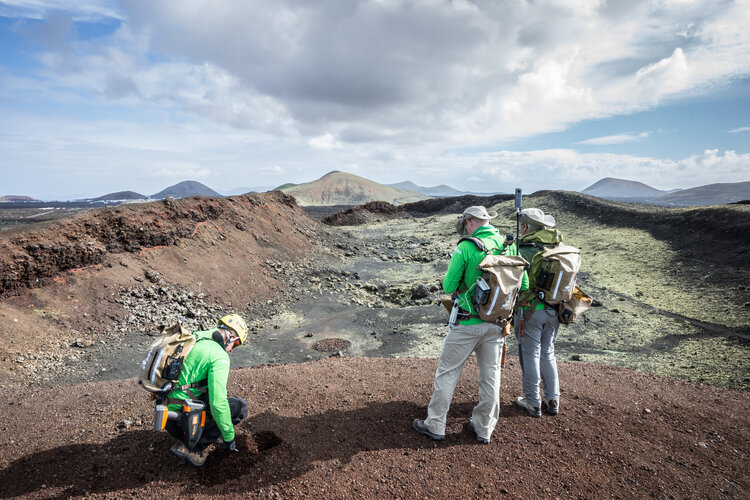

A team of astronauts, engineers and geologists is travelling to Spain’s Canary Islands, one of Europe’s volcanic hot spots, to learn how to best explore the Moon and Mars during ESA’s Pangaea geological training course.

