
Copernical Team
Mining the moon's water will require a massive infrastructure investment, but should we?
We live in a world in which momentous decisions are made by people often without forethought. But some things are predictable, including that if you continually consume a finite resource without recycling, it will eventually run out.
Yet, as we set our sights on embarking back to the moon, we will be bringing with us all our bad habits, including our urge for unrestrained consumption.
Since the 1994 discovery of water ice on the moon by the Clementine spacecraft, excitement has reigned at the prospect of a return to the moon. This followed two decades of the doldrums after the end of Apollo, a malaise that was symptomatic of an underlying lack of incentive to return.
That water changed everything. The water ice deposits are located at the poles of the moon hidden in the depths of craters that are forever devoid of sunlight.
ESA moves forward with Destination Earth
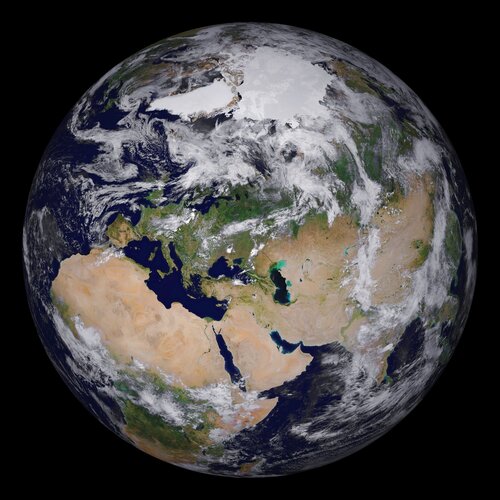

Earth observation provides a wealth of information to benefit our daily lives. As the demand for satellite data grows to address the challenges of climate change and a growing population, ESA, under the leadership of the European Commission, along with its key European partners, are developing high precision digital models of Earth to monitor and simulate both natural and human activity, to enable more sustainable development and support European environmental policies.
Today, at the ESA Council, Member States approved a ‘Contribution Agreement', which paves the way for cooperation with the European Commission on the Destination Earth initiative, in the context of the Digital
Information Session from 300th ESA Council
 Video:
00:40:56
Video:
00:40:56
Watch the replay of this media event to hear about the outcome of the 300th ESA Council.
Delegations from Member States are meeting in Paris on 20 and 21 October 2021. Panelists, including ESA Director General Josef Aschbacher, provide live updates on the Intermediate Ministerial Meeting that will take place in Portugal in November 2021. The High-Level Advisory Group Report will also be presented and new ESA directors will be announced.
South Korea launches first domestic space rocket but mission fails
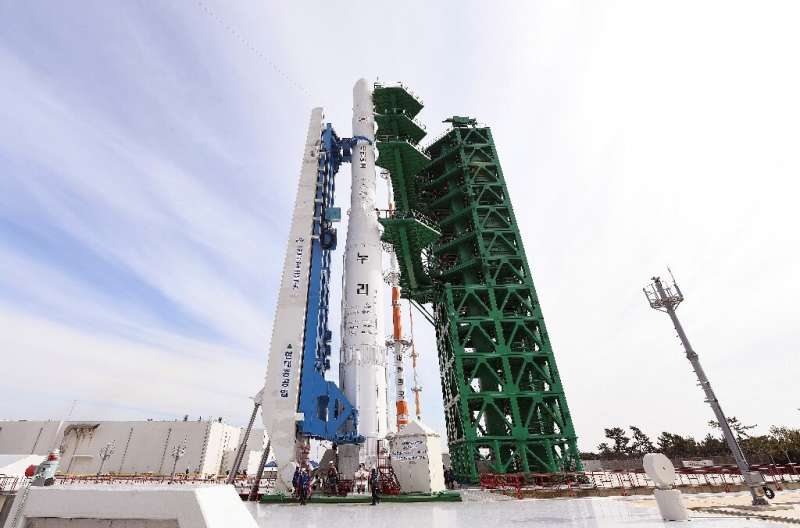

South Korea launched its first domestically developed space rocket on Thursday but failed to put its dummy payload into orbit, a setback in the country's attempts to join the ranks of advanced space-faring nations.
The Korea Space Launch Vehicle II, informally called Nuri and emblazoned with a South Korean flag, rose upwards from Goheung on the southern coast trailing a column of flame.
All three stages of the rocket worked, taking it to an altitude of 700 kilometres, and the 1.5-tonne payload separated successfully, President Moon Jae-in said after watching the launch at the control centre.
But "putting a dummy satellite into orbit remains an unfinished mission", he announced.
"Though it fell short of achieving its goals perfectly, we have achieved very good feats with our first launch."
Another attempt will be made in May, he added.
"Countries that lead in space technology will lead the future. And we are not too late to do it."
The mission failed because the third-stage engine stopped burning 46 seconds earlier than scheduled, science minister Lim Hye-sook told reporters.
Galileo: the first ten years
 Video:
00:01:25
Video:
00:01:25
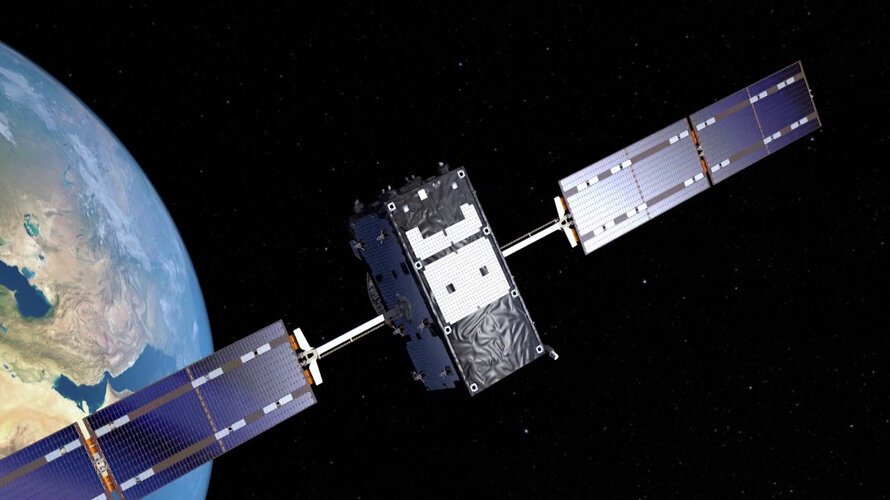
Europe’s own satellite navigation system, Galileo, has become the world’s most precise, delivering metre-level accuracy, available anywhere on Earth. It is also saving lives, relaying distress calls for search and rescue. Today there are 26 Galileo satellites in orbit 23 222 km over our heads; the first of them were launched on 21 October 2011, with nine more launches in the following years. The satellites in space are supported by a globe-spanning ground segment. The system as a whole is set to grow, with the first of 12 ‘Batch 3’ about to join the current satellites in
From Polar Bears to Polar Orbits
 Alaska is known for its polar bears, rugged landscapes, expansive areas and remoteness. Alaska is not the first place people envision when they think of rocket launches. However, Alaska is one of four locations in the United States that allow a rocket launch into polar orbit.
In fact, the Pacific Spaceport Complex-Alaska ("PSCA") operated by Alaska Aerospace Corporation has been launching
Alaska is known for its polar bears, rugged landscapes, expansive areas and remoteness. Alaska is not the first place people envision when they think of rocket launches. However, Alaska is one of four locations in the United States that allow a rocket launch into polar orbit.
In fact, the Pacific Spaceport Complex-Alaska ("PSCA") operated by Alaska Aerospace Corporation has been launching China may boost accuracy of its hypersonic weapons via AI technology
 Chinese PLA researchers are reportedly seeking to improve the accuracy of the country's hypersonic delivery systems via artificial intelligence, according to the South China Morning Post.
Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesman Zhao Lijian on Monday refuted a report by the Financial Times saying that the country conducted a hypersonic missile test in August. First, it was not a missile but a sp
Chinese PLA researchers are reportedly seeking to improve the accuracy of the country's hypersonic delivery systems via artificial intelligence, according to the South China Morning Post.
Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesman Zhao Lijian on Monday refuted a report by the Financial Times saying that the country conducted a hypersonic missile test in August. First, it was not a missile but a sp NEID Spectrometer Lights Up Path to Exoplanet Exploration
 As NASA expands its quest to discover exoplanets - planets beyond our solar system - it also grows its toolbox. Over the summer, a new tool called NEID (pronounced NOO-id) delivered its first batch of data on the nearest and best-studied star, our Sun.
The NEID spectrometer, which will help locate and characterize new worlds, observes the sky from Kitt Peak National Observatory in Arizona.
As NASA expands its quest to discover exoplanets - planets beyond our solar system - it also grows its toolbox. Over the summer, a new tool called NEID (pronounced NOO-id) delivered its first batch of data on the nearest and best-studied star, our Sun.
The NEID spectrometer, which will help locate and characterize new worlds, observes the sky from Kitt Peak National Observatory in Arizona. China's Chang'e-5 mission offers new insights into evolution of Moon
 Chinese researchers have studied the lunar samples brought back by the Chang'e-5 mission and dated the youngest rock on the Moon at around 2 billion years in age, extending the "life" of lunar volcanism 800-900 million years longer than previously known.
The study, conducted mainly by a research team at the Institute of Geology and Geophysics (IGG), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), was p
Chinese researchers have studied the lunar samples brought back by the Chang'e-5 mission and dated the youngest rock on the Moon at around 2 billion years in age, extending the "life" of lunar volcanism 800-900 million years longer than previously known.
The study, conducted mainly by a research team at the Institute of Geology and Geophysics (IGG), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), was p China's lunar samples reveal new type of basalt
 An analysis of moon rocks brought back to Earth by China's Chang'e-5 mission suggests the samples are a new type of lunar basalt, different from those collected during previous Apollo and Luna missions.
Researchers from the National Astronomical Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC) analyzed rock particles 10 to 500 microns (a quarter the thickness of a credit card) in si
An analysis of moon rocks brought back to Earth by China's Chang'e-5 mission suggests the samples are a new type of lunar basalt, different from those collected during previous Apollo and Luna missions.
Researchers from the National Astronomical Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC) analyzed rock particles 10 to 500 microns (a quarter the thickness of a credit card) in si 
