Copernical Team
DARPA focusing on biomanufacturing to B-SURE
 The DoD has a role in orbital and lunar missions as defined by the US Space Force (USSF) Space Capstone Publication. In this document, USSF notes the "inherent value of the space domain and the tremendous influence space has on U.S. prosperity and security." There is a critical DoD need for the continued development and future expansion of orbital manufacturing to enable and ensure supply chain
The DoD has a role in orbital and lunar missions as defined by the US Space Force (USSF) Space Capstone Publication. In this document, USSF notes the "inherent value of the space domain and the tremendous influence space has on U.S. prosperity and security." There is a critical DoD need for the continued development and future expansion of orbital manufacturing to enable and ensure supply chain Russia creates debris field near ISS
NASA's DART asteroid collision mission nears launch
 NASA is set to launch a spacecraft from California on Tuesday night to smack head on into an asteroid next fall in an effort to understand how humanity could prevent such a space body from colliding with Earth.
Elon Musk's SpaceX plans to launch the DART mission, or Double Asteroid Redirection Test, on a Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg Space Force Base at 10:20 p.m. PST.
The spac
NASA is set to launch a spacecraft from California on Tuesday night to smack head on into an asteroid next fall in an effort to understand how humanity could prevent such a space body from colliding with Earth.
Elon Musk's SpaceX plans to launch the DART mission, or Double Asteroid Redirection Test, on a Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg Space Force Base at 10:20 p.m. PST.
The spac Mars helicopter Ingenuity completes 16th flight
 NASA's Mars helicopter Ingenuity completed its 16th flight over the weekend, the space agency announced Monday.
The NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory said the helicopter captured color images of Mars' surface during the flight, which saw it travel 116 meters northeast for 109 seconds.
"Mars helicopter continues to thrive!" the lab wrote on Twitter.
The 16th flight over seven
NASA's Mars helicopter Ingenuity completed its 16th flight over the weekend, the space agency announced Monday.
The NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory said the helicopter captured color images of Mars' surface during the flight, which saw it travel 116 meters northeast for 109 seconds.
"Mars helicopter continues to thrive!" the lab wrote on Twitter.
The 16th flight over seven ESA Boost! contract for flight demonstration of Spectrum launch vehicle
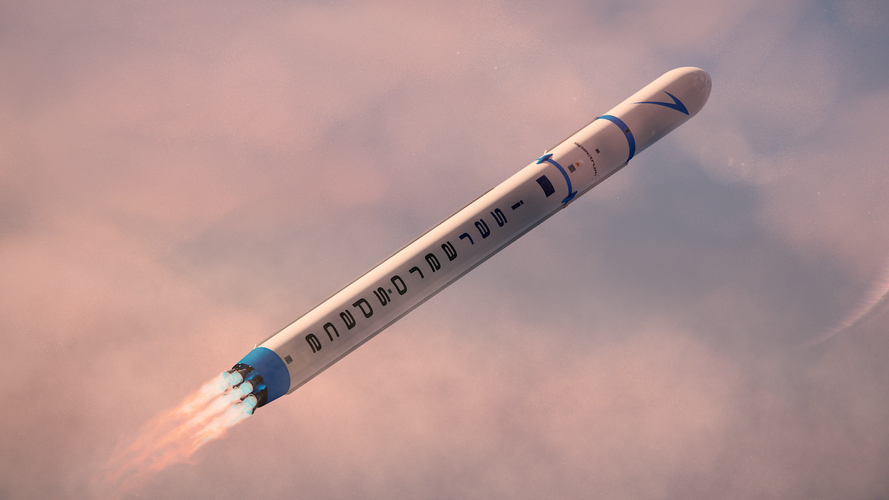
Small and medium satellites can expect new launch opportunities on the Spectrum launch vehicle thanks to an ESA Boost! co-funding contract worth €11 m with Isar Aerospace Technologies in Germany.
Double Asteroid Redirection Test launch could be key step forward in planetary defense

NASA's latest launch into outer space is going to make an impact. In fact, that's its entire mission.
DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test), which is scheduled to launch at 10:20 p.m. PST on Nov. 23 out of Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, is NASA's first planetary defense mission. This mission will demonstrate asteroid deflection via kinetic impact. The goal is to collide with the target to see how the orbit changes. It's a test run to see if such a plan is feasible should we find an asteroid on a collision course with Earth one day.
Cristina Thomas, an assistant professor of astronomy and planetary sciences at Northern Arizona University and lead of the DART Observations Working Group, is excited to see the effects of the impact. She and her international team have been working for years to obtain a precise pre-impact orbit of Dimorphos, the satellite asteroid, around Didymos, the primary asteroid in a near-Earth asteroid system.
Near-Earth, of course, is relative; the planet is in no danger from Didymos. However, an asteroid heading toward Earth is possible, and scientists throughout the world are working on ways to identify these potential threats and how to mitigate them.
An absolutely bonkers plan to give Mars an artificial magnetosphere
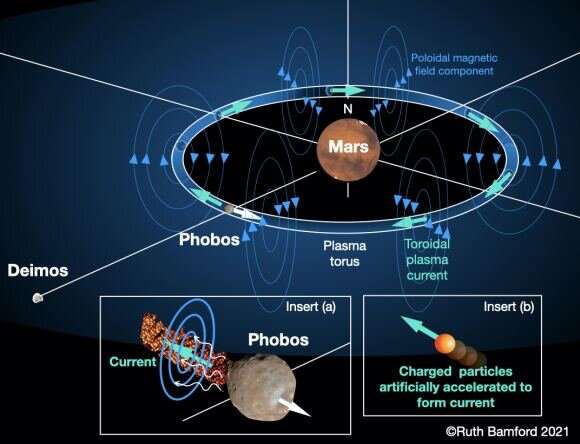
Terraforming Mars is one of the great dreams of humanity. Mars has a lot going for it. Its day is about the same length as Earth's, it has plenty of frozen water just under its surface, and it likely could be given a reasonably breathable atmosphere in time. But one of the things it lacks is a strong magnetic field. So if we want to make Mars a second Earth, we'll have to give it an artificial one.
The reason magnetic fields are so important is that they shield a planet from solar wind and ionizing particles. Earth's magnetic field prevents most high-energy charged particles from reaching the surface. Instead, they are deflected from Earth, keeping us safe. The magnetic field also prevents solar winds from stripping Earth's atmosphere over time. Early Mars had a thick, water-rich atmosphere, but it was gradually depleted without the protection of a strong magnetic field.
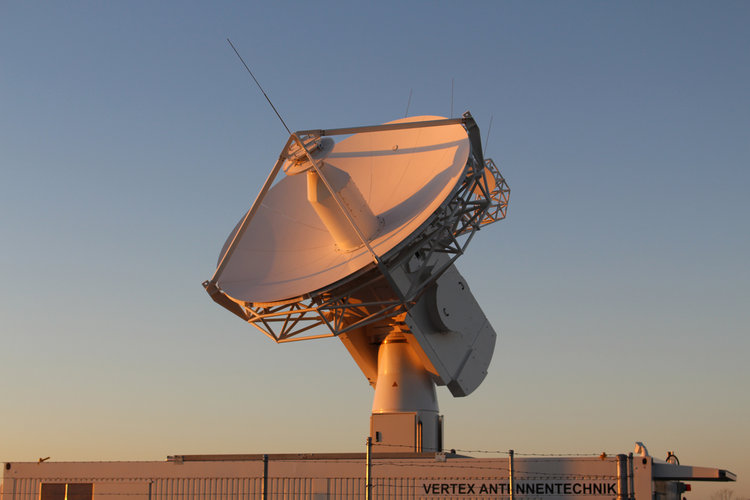
ESA antenna to catch DART's first words
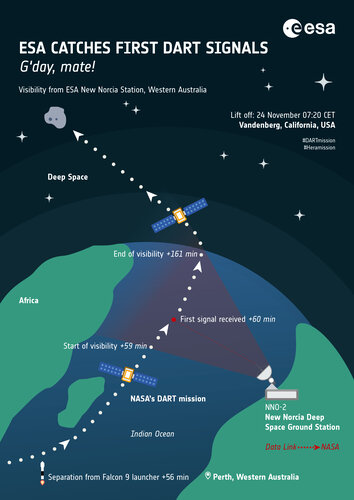 Image:
ESA's Australian ground station to catch DART's first words
Image:
ESA's Australian ground station to catch DART's first words ESA's Australian ground station to catch DART's first words
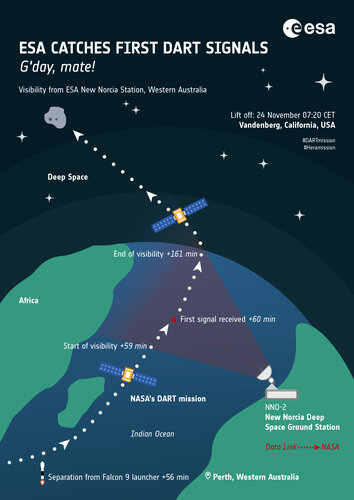 Image:
ESA's Australian ground station to catch DART's first words
Image:
ESA's Australian ground station to catch DART's first words Catching asteroid deflection mission's first words


