
Copernical Team
NASA wants your help designing a starshade to observe exoplanets
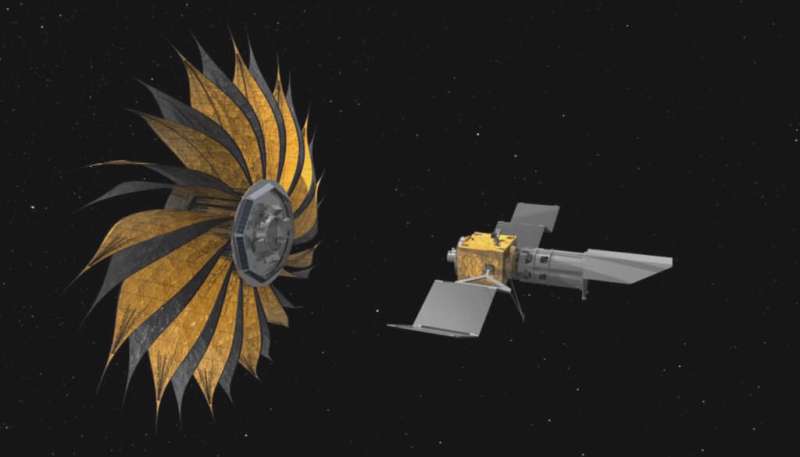

The field of exoplanet study has come a long way in recent decades. To date, 5,063 exoplanets have been confirmed in 3,794 systems beyond our own, with another 8,819 candidates awaiting confirmation. In the coming years, tens of thousands of more planets are expected to be found, thanks to next-generation observatories. The ultimate goal in this search is to find planets that are "Earth-like," meaning they have a good chance of supporting life. This is no easy task, as rocky planets located within their parent star's habitable zones (HZs) tend to orbit closely, making them harder to see.
To make this process easier, NASA is designing a hybrid observatory consisting of a "Starshade" that will block out a star's light so that a ground-based telescope can directly image planets orbiting it.
Explosive volcanic eruption produced rare mineral on Mars

Planetary scientists from Rice University, NASA's Johnson Space Center and the California Institute of Technology have an answer to a mystery that's puzzled the Mars research community since NASA's Curiosity rover discovered a mineral called tridymite in Gale Crater in 2016.
Tridymite is a high-temperature, low-pressure form of quartz that is extremely rare on Earth, and it wasn't immediately clear how a concentrated chunk of it ended up in the crater. Gale Crater was chosen as Curiosity's landing site due to the likelihood that it once held liquid water, and Curiosity found evidence that confirmed Gale Crater was a lake as recently as 1 billion years ago.
Greece battles wildfires on Lesbos island
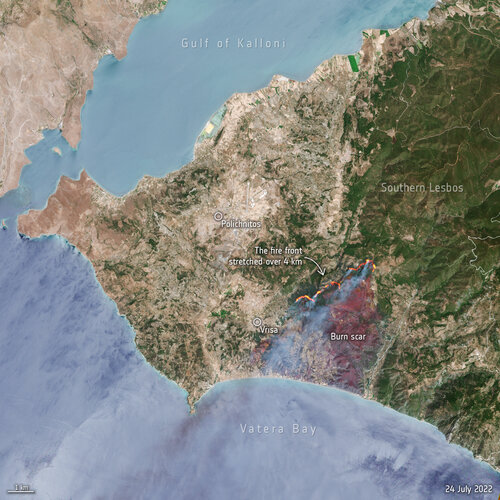 Image:
Hundreds of residents and tourists have been evacuated from the Greek island of Lesbos after a wildfire broke out on the morning of 23 July. This image, captured by Sentinel-2, shows the active fire front which stretches for more than four km.
Image:
Hundreds of residents and tourists have been evacuated from the Greek island of Lesbos after a wildfire broke out on the morning of 23 July. This image, captured by Sentinel-2, shows the active fire front which stretches for more than four km. Sumitomo invests in TAE Technologies for Fusion Reactor development
 Sumitomo Corporation of Americas ("SCOA") has announced its investment in TAE Technologies ("TAE"), a fusion power company and world leader in hydrogen-boron fusion research. The investment will help fund the construction of TAE's next research reactor, "Copernicus" and accelerate SCOA's implementation of fusion power in Japan and Asia as part of the company's strategy to help realize a carbon-n
Sumitomo Corporation of Americas ("SCOA") has announced its investment in TAE Technologies ("TAE"), a fusion power company and world leader in hydrogen-boron fusion research. The investment will help fund the construction of TAE's next research reactor, "Copernicus" and accelerate SCOA's implementation of fusion power in Japan and Asia as part of the company's strategy to help realize a carbon-n Maxar's hi-res Vivid Basemaps enhances Esri ArcGIS Living Atlas of the World
 Maxar Technologies (NYSE:MAXR) (TSX:MAXR), provider of comprehensive space solutions and secure, precise, geospatial intelligence, has announced that Esri, the global leader in geographic systems (GIS) and location intelligence, will enhance the World Imagery layer with higher resolution Maxar Vivid basemaps in the Living Atlas.
With the new, multiyear agreement, Esri will use Maxar's Vivi
Maxar Technologies (NYSE:MAXR) (TSX:MAXR), provider of comprehensive space solutions and secure, precise, geospatial intelligence, has announced that Esri, the global leader in geographic systems (GIS) and location intelligence, will enhance the World Imagery layer with higher resolution Maxar Vivid basemaps in the Living Atlas.
With the new, multiyear agreement, Esri will use Maxar's Vivi China's space station expanding nation technology base
 The Wentian space lab will help to greatly advance scientific research and the development of technology in China, providing a unique platform for experiments that are difficult or impossible to be done on Earth, a senior scientist said.
Zhang Wei, director of the Chinese Academy of Sciences' Technology and Engineering Center for Space Utilization, said on Sunday in Wenchang, Hainan provin
The Wentian space lab will help to greatly advance scientific research and the development of technology in China, providing a unique platform for experiments that are difficult or impossible to be done on Earth, a senior scientist said.
Zhang Wei, director of the Chinese Academy of Sciences' Technology and Engineering Center for Space Utilization, said on Sunday in Wenchang, Hainan provin Metaspectral and HySpeed Computing to develop earth observation payload for ISS
 Metaspectral, a company delivering the next generation of computer vision, and HySpeed Computing, a remote sensing data access and analysis company, have been selected to deploy an Earth Observation (EO) payload on the International Space Station (ISS). The payload is known as Onboard Programmable Technology for Image Classification and Analysis (OPTICA) and will enable real-time compression, st
Metaspectral, a company delivering the next generation of computer vision, and HySpeed Computing, a remote sensing data access and analysis company, have been selected to deploy an Earth Observation (EO) payload on the International Space Station (ISS). The payload is known as Onboard Programmable Technology for Image Classification and Analysis (OPTICA) and will enable real-time compression, st Satellite operators Eutelsat and OneWeb eye possible merger
 French satellite operator Eutelsat said Monday it is in talks with British counterpart OneWeb for a possible tie-up to become a global champion in broadband internet, rivalling US operators such as SpaceX's Starlink.
"Following recent market rumours, Eutelsat Communications confirms that it has engaged in discussions with its co-shareholders in OneWeb regarding a potential all-share combina
French satellite operator Eutelsat said Monday it is in talks with British counterpart OneWeb for a possible tie-up to become a global champion in broadband internet, rivalling US operators such as SpaceX's Starlink.
"Following recent market rumours, Eutelsat Communications confirms that it has engaged in discussions with its co-shareholders in OneWeb regarding a potential all-share combina Hawkeye 360 opens new satellite manufacturing facility
 HawkEye 360 has opened its Advanced Technology and Development Center in Herndon, Virginia. The 19,000 square-foot data processing, software development, and satellite manufacturing facility continues HawkEye 360's investment in Fairfax County to support U.S. government and allied government needs.
The facility enables HawkEye 360 to have end-to-end responsibility to manufacture its commer
HawkEye 360 has opened its Advanced Technology and Development Center in Herndon, Virginia. The 19,000 square-foot data processing, software development, and satellite manufacturing facility continues HawkEye 360's investment in Fairfax County to support U.S. government and allied government needs.
The facility enables HawkEye 360 to have end-to-end responsibility to manufacture its commer China to put large telescope in orbit next year
 China plans to launch a large space telescope next year to fly alongside the Tiangong space station, according to the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology.
The academy said a Long March 5B heavy-lift carrier rocket will deploy the Xuntian space telescope in a low-Earth orbit similar to the track of the Tiangong station as they both circle Earth. The telescope will carry out deep-spac
China plans to launch a large space telescope next year to fly alongside the Tiangong space station, according to the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology.
The academy said a Long March 5B heavy-lift carrier rocket will deploy the Xuntian space telescope in a low-Earth orbit similar to the track of the Tiangong station as they both circle Earth. The telescope will carry out deep-spac 
