
Copernical Team
SpaceX to test-fire rocket ahead of Axiom-1 private astronaut mission
 SpaceX plans to test-fire a Falcon 9 rocket on Monday ahead of its first private astronaut mission, Axiom-1, to the International Space Station.
The test, dubbed a static fire test, is a routine part of prelaunch procedures.
All nine of the Falcon's Merlin 1D engines will briefly fire up as the rocket is held firmly to the launch pad. The ignition will enable engineers to ensure
SpaceX plans to test-fire a Falcon 9 rocket on Monday ahead of its first private astronaut mission, Axiom-1, to the International Space Station.
The test, dubbed a static fire test, is a routine part of prelaunch procedures.
All nine of the Falcon's Merlin 1D engines will briefly fire up as the rocket is held firmly to the launch pad. The ignition will enable engineers to ensure Mars' thin atmosphere means quieter sounds, new data shows
 Data from NASA's Perseverance Rover has given scientists their first clear picture of how sound travels on Mars' surface.
The Red Planet's thin, cold atmosphere, made of mostly carbon dioxide, causes sound to move slower and carry for shorter distances compared to those on Earth. An international team of scientists led by Sylvestre Maurice, an astrophysicist at the University of Toulous
Data from NASA's Perseverance Rover has given scientists their first clear picture of how sound travels on Mars' surface.
The Red Planet's thin, cold atmosphere, made of mostly carbon dioxide, causes sound to move slower and carry for shorter distances compared to those on Earth. An international team of scientists led by Sylvestre Maurice, an astrophysicist at the University of Toulous SpaceX launches Transporter-4 rideshare mission from Florida
 SpaceX launched its 12th rocket of the year Friday afternoon, in spite of gloomy weather.
The two-stage Falcon 9 rocket blasted off on time at 12:25 p.m. EDT from Space Launch Complex 40 Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Fla., carrying dozens of small satellites into space as part of the company's fourth dedicated rideshare mission.
About 9 minutes after the rocket launched, th
SpaceX launched its 12th rocket of the year Friday afternoon, in spite of gloomy weather.
The two-stage Falcon 9 rocket blasted off on time at 12:25 p.m. EDT from Space Launch Complex 40 Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Fla., carrying dozens of small satellites into space as part of the company's fourth dedicated rideshare mission.
About 9 minutes after the rocket launched, th Miniaturized laser systems to seek out traces of life in space
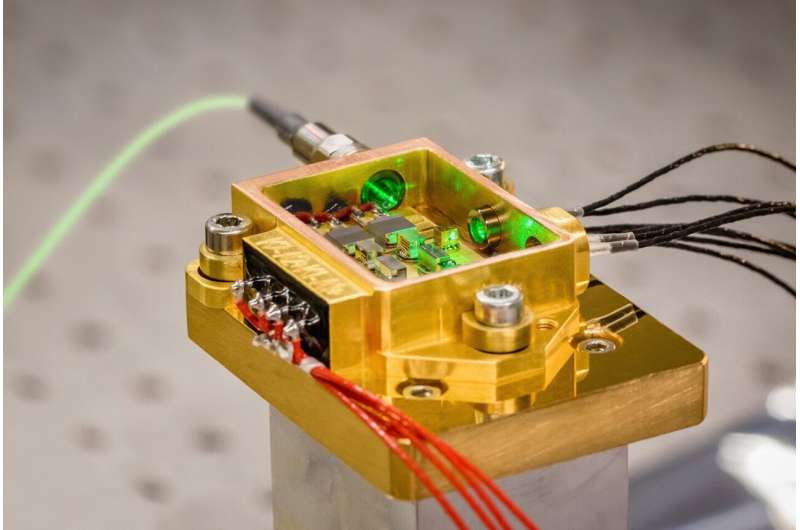

Was there life on Mars? This is the question that the European Space Agency (ESA) is setting out to answer with its ExoMars mission. The mission, in which Russia is a participant, is scheduled to launch this fall, although recent political developments have raised questions as to whether this will be possible. Part of the mission is an exciting analytical system that was designed to operate in space and was created as part of the research work conducted at the Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Optics and Precision Engineering IOF. The Jena-based researchers developed the miniaturized laser module for the ExoMars Rover's mobile laboratory. The institute will present this Raman spectrometer, which is fitted with a diode-pumped solid-state laser and is the size of a 50-cent coin, at the Laser World of Photonics in Munich from April 26 to 29.
NASA begins critical final test on mega Moon rocket
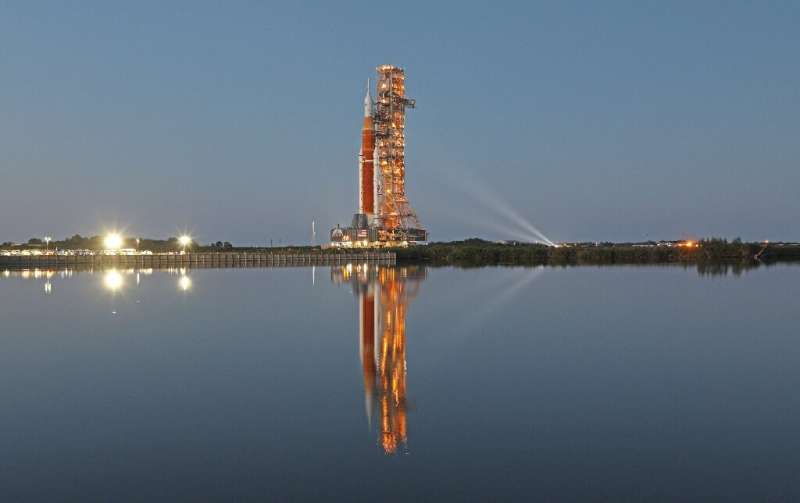

NASA on Friday begins a critical two-day-long test of its giant Space Launch System (SLS) rocket complete with a mock countdown, as the agency gears up to return humans to the Moon.
Known as the "wet dress rehearsal," it is the final major test before the Artemis-1 mission this summer: an uncrewed lunar flight that will eventually be followed by boots on the ground, likely no sooner than 2026.
"It is our last design verification prior to our launch," senior NASA official Tom Whitmeyer said in a call with reporters this week.
First audio recorded on Mars reveals two speeds of sound
 The first audio recordings on Mars reveal a quiet planet with occasional gusts of wind where two different speeds of sound would have a strange delayed effect on hearing, scientists said Friday.
After NASA's Perseverance rover landed on Mars in February last year, its two microphones started recording, allowing scientists to hear what it is like on the Red Planet for the first time.
In a
The first audio recordings on Mars reveal a quiet planet with occasional gusts of wind where two different speeds of sound would have a strange delayed effect on hearing, scientists said Friday.
After NASA's Perseverance rover landed on Mars in February last year, its two microphones started recording, allowing scientists to hear what it is like on the Red Planet for the first time.
In a Week in images: 28 March - 1 April 2022

Week in images: 28 March - 1 April 2022
Discover our week through the lens
Earth from Space: Barranquilla, Colombia

Barranquilla, the capital of the Atlántico department in northwest Colombia, is featured in this image taken by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission.


 Image:
Solar power down
Image:
Solar power down 





























