Copernical Team
Two teams report on study of Hayabusa2 asteroid samples

Two teams of researchers are publishing their findings thus far after initial study of samples collected from the asteroid Ryugu and returned to Earth last year by the Japanese space probe Hayabusa2. Both teams are large and both are made up mostly of researchers from institutions in Japan. Both teams have also published their findings in Nature Astronomy.
Engineers test an idea for a new hovering rover
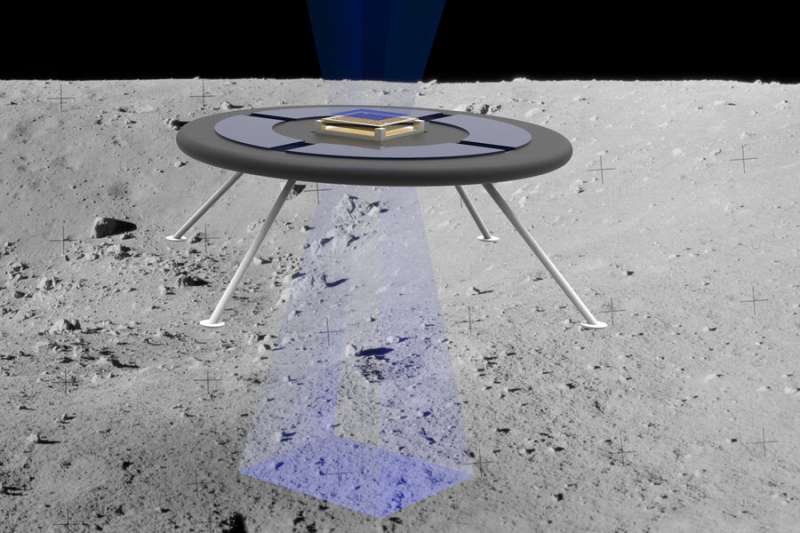

Aerospace engineers at MIT are testing a new concept for a hovering rover that levitates by harnessing the moon's natural charge.
Because they lack an atmosphere, the moon and other airless bodies such as asteroids can build up an electric field through direct exposure to the sun and surrounding plasma. On the moon, this surface charge is strong enough to levitate dust more than 1 meter above the ground, much the way static electricity can cause a person's hair to stand on end.
Engineers at NASA and elsewhere have recently proposed harnessing this natural surface charge to levitate a glider with wings made of Mylar, a material that naturally holds the same charge as surfaces on airless bodies.
SpaceX launches Christmas presents, supplies to station
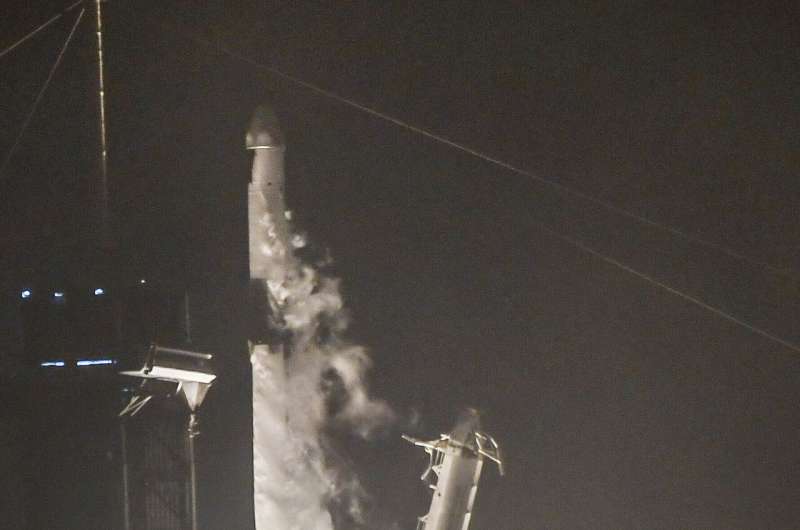

SpaceX launched Christmas gifts, goodies and supplies to the International Space Station on Tuesday and got a present in return: the company's 100th successful rocket landing.
The predawn liftoff from NASA's Kennedy Space Center was barely visible in the fog and clouds, as the Falcon rocket hoisted a Dragon capsule loaded with more than 6,500 pounds (2,950 kilograms) of gear for the station's seven astronauts. Several minutes later, the first-stage booster landed upright on an ocean platform, six years to the day that Elon Musk's company accomplished its first booster touchdown in 2015.
LUNA is taking shape
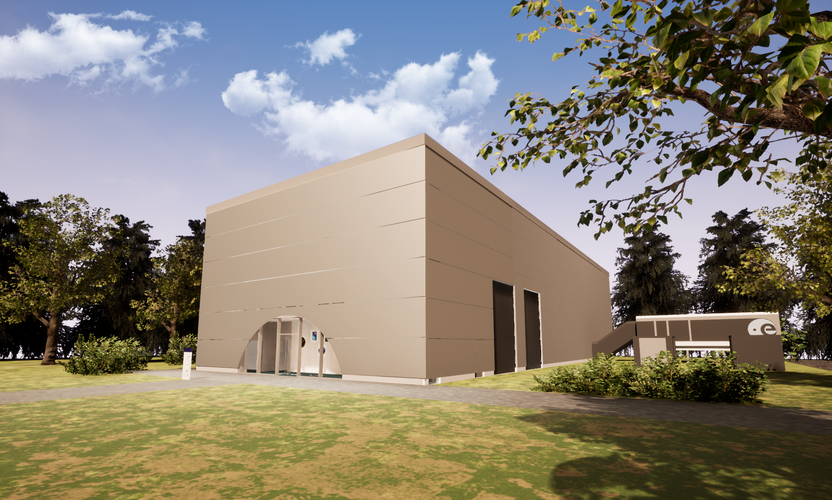

The Moon is in sight at ESA’s European Astronaut Centre (EAC) in Cologne, Germany, where a facility designed to recreate the lunar surface will soon be built. Known as ESA-DLR LUNA, the collaborative project between the European Space Agency ESA and the German Aerospace Centre DLR will provide a training ground for astronauts and a test centre for technology, equipping partners and users with the knowledge to go forward to the Moon.
Webb flies Ariane 5: watch the launch live
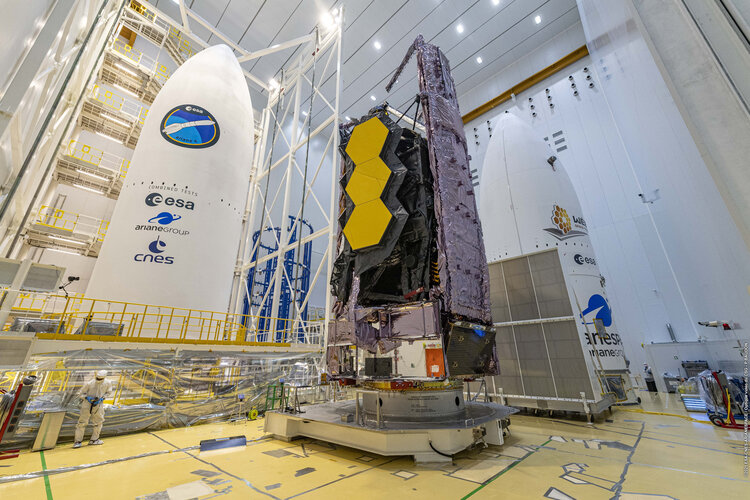

ESA and NASA will be broadcasting live as the James Webb Space Telescope is launched to space on ESA’s Ariane 5 from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana at 12:20 GMT / 13:20 CET on Friday 24 December.
A Christmas comet for Solar Orbiter
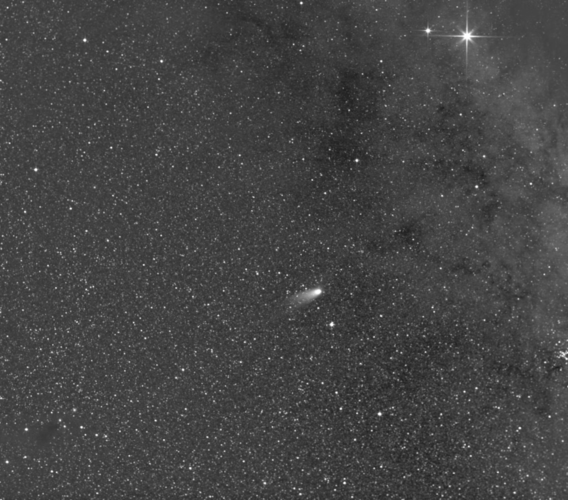

Comet Leonard, a mass of space dust, rock and ice about a kilometre across is heading for a close pass of the Sun on 3 January, and the ESA/NASA Solar Orbiter spacecraft has been watching its evolution over the last days.
2022 Copernicus Sentinels calendar

Download the 2022 Copernicus Sentinels calendar
Deep Mantle Krypton Reveals Earth's Outer Solar System Ancestry
 Krypton from the Earth's mantle, collected from geologic hot spots in Iceland and the Galapagos Islands, reveals a clearer picture of how our planet formed, according to new research from the University of California, Davis.
The different isotopes of krypton are chemical fingerprints for scientists sleuthing out the ingredients that made the Earth, such as solar wind particles and meteorit
Krypton from the Earth's mantle, collected from geologic hot spots in Iceland and the Galapagos Islands, reveals a clearer picture of how our planet formed, according to new research from the University of California, Davis.
The different isotopes of krypton are chemical fingerprints for scientists sleuthing out the ingredients that made the Earth, such as solar wind particles and meteorit New technologies make Chinese astronauts' in-orbit lives easier
 Chinese astronauts live and work more conveniently and comfortably in orbit with the application of advanced information technology, said the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC).
There are smart home systems in China's space station core module Tianhe, Bai Linhou, deputy chief designer of the space station at the China Academy of Space Technology (CAST) under the CASC
Chinese astronauts live and work more conveniently and comfortably in orbit with the application of advanced information technology, said the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC).
There are smart home systems in China's space station core module Tianhe, Bai Linhou, deputy chief designer of the space station at the China Academy of Space Technology (CAST) under the CASC Fugro's remote space operations complex to be located in Perth, Australia
 Fugro confirms the Australian Space Automation, Artificial Intelligence and Robotics Control Complex (SpAARC) will be located in the heart of downtown Perth's central business district (CBD). Housed in Western Australia's (WA's) largest telecommunications exchange, and thanks to an ongoing partnership with Telstra, Fugro's world-class facility will manage robotics and remote operations in Austra
Fugro confirms the Australian Space Automation, Artificial Intelligence and Robotics Control Complex (SpAARC) will be located in the heart of downtown Perth's central business district (CBD). Housed in Western Australia's (WA's) largest telecommunications exchange, and thanks to an ongoing partnership with Telstra, Fugro's world-class facility will manage robotics and remote operations in Austra