
Copernical Team
Methane levels surged in 2020 despite lockdowns
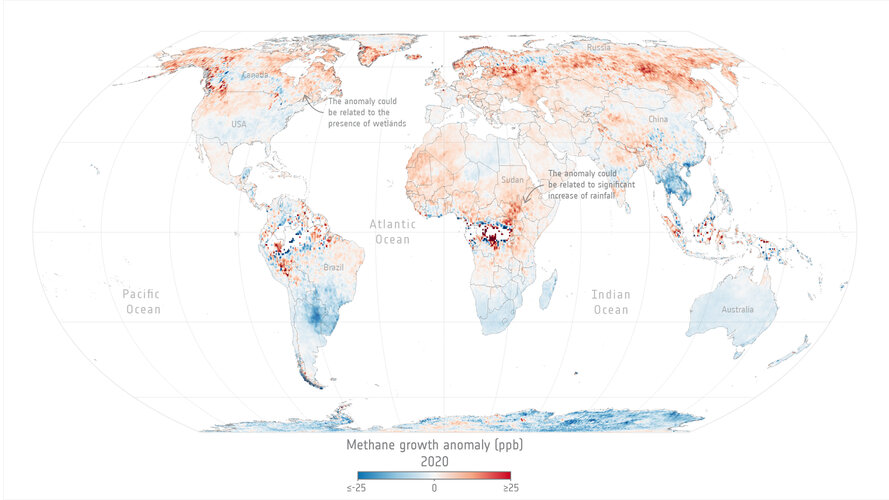
Levels of methane, the second most important greenhouse gas in our atmosphere, continued their unrelenting rise in 2020 despite the economic slowdown caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
A team of scientists, from the University of Leeds, have used data from the Copernicus Sentinel-5P satellite to pinpoint locations with large surges of methane emissions. These findings were presented during ESA’s Living Planet Symposium which took place last month in Bonn, Germany.
Lunar science stirring on Mount Etna
 Image:
Lunar science stirring on Mount Etna
Image:
Lunar science stirring on Mount Etna Exploring globular clusters with the lens of asteroseismology
 Asteroseismology - one of the most fascinating and sophisticated methods for measuring the mass of stars, and by extension, their age - can also be successfully used to reveal the characteristics of the stars within globular clusters: very large groups of stars (in the order of hundreds of thousands) condensed in a relatively small space and all at approximately the same distance from us.
Asteroseismology - one of the most fascinating and sophisticated methods for measuring the mass of stars, and by extension, their age - can also be successfully used to reveal the characteristics of the stars within globular clusters: very large groups of stars (in the order of hundreds of thousands) condensed in a relatively small space and all at approximately the same distance from us. You can help scientists study the atmosphere on Jupiter
 A new citizen science project, led by researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities with support from NASA, allows volunteers to play an important role in helping scientists learn more about the atmosphere on Jupiter. Citizen scientists can help astrophysicists categorize tens of thousands of stunning images taken from the Juno spacecraft with just a web browser.
The planet Jupite
A new citizen science project, led by researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities with support from NASA, allows volunteers to play an important role in helping scientists learn more about the atmosphere on Jupiter. Citizen scientists can help astrophysicists categorize tens of thousands of stunning images taken from the Juno spacecraft with just a web browser.
The planet Jupite NASA's Webb to Uncover Riches of the Early Universe
 For decades, telescopes have helped us capture light from galaxies that formed as far back as 400 million years after the big bang - incredibly early in the context of the universe's 13.8-billion-year history. But what were galaxies like that existed even earlier, when the universe was semi-transparent at the beginning of a period known as the Era of Reionization?
NASA's next flagship obse
For decades, telescopes have helped us capture light from galaxies that formed as far back as 400 million years after the big bang - incredibly early in the context of the universe's 13.8-billion-year history. But what were galaxies like that existed even earlier, when the universe was semi-transparent at the beginning of a period known as the Era of Reionization?
NASA's next flagship obse China launches new test satellite
 China on Wednesday sent a new satellite into space from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in northwest China.
The Tianxing-1 test satellite was launched by a Kuaizhou-1A carrier rocket at 10:08 a.m. (Beijing Time) and entered the planned orbit.
The satellite is mainly used for experiments such as space environment detection.
It was the 15th flight mission of the Kuaizhou-1A r
China on Wednesday sent a new satellite into space from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in northwest China.
The Tianxing-1 test satellite was launched by a Kuaizhou-1A carrier rocket at 10:08 a.m. (Beijing Time) and entered the planned orbit.
The satellite is mainly used for experiments such as space environment detection.
It was the 15th flight mission of the Kuaizhou-1A r Key milestones achieved in Manned-Unmanned Teaming for future air power
 The ability to task unmanned systems from a manned aircraft is an important force multiplier in Airbus' vision for future air power, with a wide range of applications extending to combat scenarios and beyond.
As a pioneer in the realm of Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T), Airbus has developed an ambitious technological roadmap to make this innovative concept - which boosts the effectiveness
The ability to task unmanned systems from a manned aircraft is an important force multiplier in Airbus' vision for future air power, with a wide range of applications extending to combat scenarios and beyond.
As a pioneer in the realm of Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T), Airbus has developed an ambitious technological roadmap to make this innovative concept - which boosts the effectiveness Globalstar announces successful launch of spare satellite
 Globalstar, Inc. (NYSE American: GSAT), a leading provider of satellite-powered innovation, has announced the successful launch of the FM-15 spare satellite from Cape Canaveral's Kennedy Space Center. FM-15 is the 25th and final satellite of Globalstar's second-generation constellation, which was manufactured and stored by Thales Alenia Space.
The satellite is expected to remain as an in-o
Globalstar, Inc. (NYSE American: GSAT), a leading provider of satellite-powered innovation, has announced the successful launch of the FM-15 spare satellite from Cape Canaveral's Kennedy Space Center. FM-15 is the 25th and final satellite of Globalstar's second-generation constellation, which was manufactured and stored by Thales Alenia Space.
The satellite is expected to remain as an in-o Lockheed Martin partners with US Indo-Pacific Command in Multi-Domain Experiments
 Lockheed Martin paired its DIAMONDShield battle management system with four Virtualized Aegis Weapon System (VAWS) nodes deployed across hundreds of miles to successfully demonstrate multi-domain operations during a recent U.S. military exercise.
The exercise, called Valiant Shield 2022, is a biennial training activity involving thousands of U.S. military personnel and more than 200 ships,
Lockheed Martin paired its DIAMONDShield battle management system with four Virtualized Aegis Weapon System (VAWS) nodes deployed across hundreds of miles to successfully demonstrate multi-domain operations during a recent U.S. military exercise.
The exercise, called Valiant Shield 2022, is a biennial training activity involving thousands of U.S. military personnel and more than 200 ships, First Ariane 5 launch of 2022 is a success for Malaysia and India clients
 On Wednesday, June 22, 2022 at 06:50 pm local time, an Ariane 5 launcher lifted off from the Guiana Space Center, Europe's Spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana (South America), successfully orbiting two geostationary telecommunication satellites, MEASAT-3d and GSAT-24.
"With this Ariane 5 mission, Arianespace is honored to support the ambitions of two key actors in the Asia-Pacific region: M
On Wednesday, June 22, 2022 at 06:50 pm local time, an Ariane 5 launcher lifted off from the Guiana Space Center, Europe's Spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana (South America), successfully orbiting two geostationary telecommunication satellites, MEASAT-3d and GSAT-24.
"With this Ariane 5 mission, Arianespace is honored to support the ambitions of two key actors in the Asia-Pacific region: M 






























