Copernical Team
Hubble Reaches New Milestone in Mystery of Universe's Expansion Rate
 Completing a nearly 30-year marathon, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has calibrated more than 40 "milepost markers" of space and time to help scientists precisely measure the expansion rate of the universe - a quest with a plot twist.
Pursuit of the universe's expansion rate began in the 1920s with measurements by astronomers Edwin P. Hubble and Georges Lemaitre. In 1998, this led to the di
Completing a nearly 30-year marathon, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has calibrated more than 40 "milepost markers" of space and time to help scientists precisely measure the expansion rate of the universe - a quest with a plot twist.
Pursuit of the universe's expansion rate began in the 1920s with measurements by astronomers Edwin P. Hubble and Georges Lemaitre. In 1998, this led to the di Airbus to further develop LISA gravitational wave observatory mission
 Airbus has been awarded a contract from the European Space Agency (ESA) to further develop the implementation of LISA (Laser Interferometer Space Antenna), one of the most ambitious science missions ESA has planned to date. With Phase B1 now underway, the detailed mission design and final technology development activities for the gravitational wave observatory are due to be completed by 2024, wi
Airbus has been awarded a contract from the European Space Agency (ESA) to further develop the implementation of LISA (Laser Interferometer Space Antenna), one of the most ambitious science missions ESA has planned to date. With Phase B1 now underway, the detailed mission design and final technology development activities for the gravitational wave observatory are due to be completed by 2024, wi China's Zhurong rover switches to dormant mode in severe Martian dust storm
 Mars rover Zhurong has been switched to dormant mode while waiting out a dust storm on the surface of the planet, the China National Space Administration said on Friday.
The latest images taken by cameras onboard China's Tianwen-1 Mars orbiter show a dust storm passing over the patrol area of Zhurong. Scientists compared them with photos taken in the last two months and analyzed recent pow
Mars rover Zhurong has been switched to dormant mode while waiting out a dust storm on the surface of the planet, the China National Space Administration said on Friday.
The latest images taken by cameras onboard China's Tianwen-1 Mars orbiter show a dust storm passing over the patrol area of Zhurong. Scientists compared them with photos taken in the last two months and analyzed recent pow Sampling Strategy for the Delta Front Campaign
 The past few weeks have been exciting ones for Perseverance's science team. At the "Enchanted Lake" site, we took our first look at what appear to be some of the bottommost sedimentary layers that make up the Jezero crater delta.
Since then, we've re-traced our steps back towards "Three Forks" and have begun the ascent of the delta near "Hawksbill Gap." It's along this Hawksbill Gap route
The past few weeks have been exciting ones for Perseverance's science team. At the "Enchanted Lake" site, we took our first look at what appear to be some of the bottommost sedimentary layers that make up the Jezero crater delta.
Since then, we've re-traced our steps back towards "Three Forks" and have begun the ascent of the delta near "Hawksbill Gap." It's along this Hawksbill Gap route Artemis I Moon Rocket to Return to Launch Pad 39B in Early June
 The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft are slated to return to launch pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida in early June for the next wet dress rehearsal attempt.
Engineers successfully completed work on a number of items observed during the previous wet dress rehearsal test. This includes addressing the liquid hydrogen system leak at the tail service mast u
The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft are slated to return to launch pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida in early June for the next wet dress rehearsal attempt.
Engineers successfully completed work on a number of items observed during the previous wet dress rehearsal test. This includes addressing the liquid hydrogen system leak at the tail service mast u Terran Orbital announces DARPA award
 Terran Orbital Corporation (NYSE: LLAP), a global leader in small satellite solutions, primarily serving the United States aerospace and defense industry, has announced that its subsidiary, PredaSAR Corporation, received a contract award from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) under an Other Transaction Authority for Prototype Agreement. Specific terms of the Agreement were no
Terran Orbital Corporation (NYSE: LLAP), a global leader in small satellite solutions, primarily serving the United States aerospace and defense industry, has announced that its subsidiary, PredaSAR Corporation, received a contract award from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) under an Other Transaction Authority for Prototype Agreement. Specific terms of the Agreement were no Boeing docks crew capsule to space station in test do-over
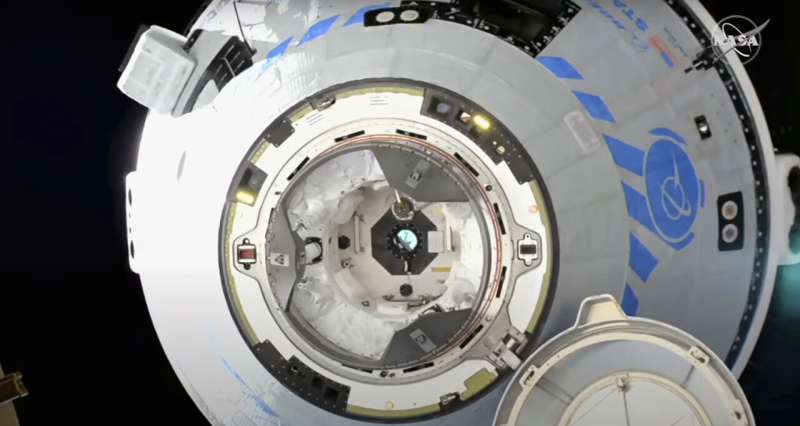

Boeing's Starliner spaceship docks with ISS in high-stakes test mission
 Boeing's Starliner capsule docked with the International Space Station Friday, a major milestone in a high-stakes uncrewed test flight as the US aerospace giant seeks to restore its reputation following past failures.
The spaceship made contact at 8:28 pm Eastern time (0028 GMT Saturday), a little over 24 hours after it blasted off from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on a mission to pro
Boeing's Starliner capsule docked with the International Space Station Friday, a major milestone in a high-stakes uncrewed test flight as the US aerospace giant seeks to restore its reputation following past failures.
The spaceship made contact at 8:28 pm Eastern time (0028 GMT Saturday), a little over 24 hours after it blasted off from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on a mission to pro Boeing's Starliner approaching ISS in high-stakes test mission
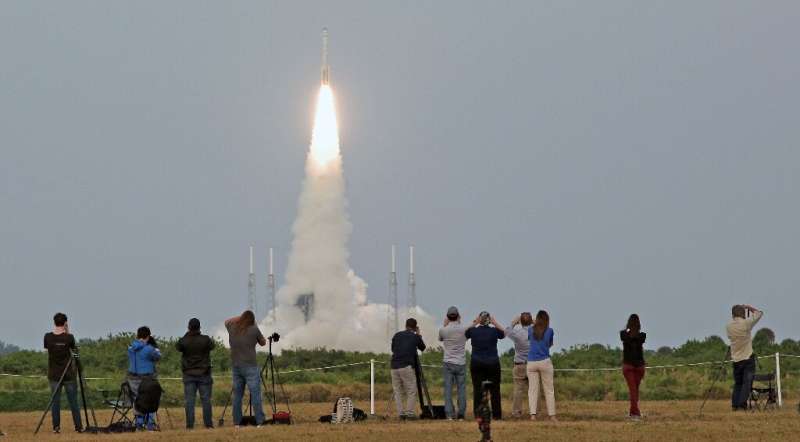

Boeing's Starliner capsule was preparing to dock with the International Space Station Friday, in a high-stakes uncrewed test flight key to reviving the US aerospace giant's reputation after a series of failures.
The spaceship blasted off from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday evening, and is now set to rendezvous with the ISS at 7:10 pm Eastern Time (2310 GMT), as part of a mission to prove it is capable of providing safe rides for NASA astronauts.
Where do "Hawaiian box jellies" come from?

An insightful cross-disciplinary team of University of Hawai'i (UH) at Mānoa researchers, working for over a decade, published a study recently revealing that a key number of hours of darkness during the lunar cycle triggers mature "Hawaiian box jellyfish" (Alatina alata) to swim to leeward O'ahu shores to spawn.
Led by Angel Yanagihara, associate research professor at the UH Mānoa School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST) and the John A. Burns School of Medicine, researchers at the UH at Mānoa have been carefully tracking local box jellies for over 20 years. While the monthly shoreline aggregations are understood to occur like clockwork 8-10 days after each full moon, with jelly forecasts included on the local news, mysteries have remained: Why are they appearing at this particular part of the lunar cycle? Where do these box jellies come from and where are they found the rest of the lunar cycle? Why has this become a monthly problem in only the last 30 years?