
Copernical Team
Space Force General Admits That US Lagging Behind Russia, China in Hypersonic Weapons
 Last month, the US military botched its own hypersonic missile testing, while China reportedly conducted a test of a missile capable of sending nuclear weapons around the globe this summer. Russia also successfully test-fired its "Zircon" hypersonic missile in the arctic on 18 November.
US Space Force General David Thompson on Saturday warned that American hypersonic missile capabilities a
Last month, the US military botched its own hypersonic missile testing, while China reportedly conducted a test of a missile capable of sending nuclear weapons around the globe this summer. Russia also successfully test-fired its "Zircon" hypersonic missile in the arctic on 18 November.
US Space Force General David Thompson on Saturday warned that American hypersonic missile capabilities a China's Hypersonic test leaves Pentagon officials 'Baffled' by Beijing's advance
 The alleged July test of a hypersonic Chinese missile has sparked concerns in the United States over how Washington seems to lag behind Beijing in the field of hypersonic weapons' capabilities.
The US military and intelligence officials were caught off-guard by China's reported hypersonic missile test carried out in July at five times the speed of sound - an unprecedented feat, The Financi
The alleged July test of a hypersonic Chinese missile has sparked concerns in the United States over how Washington seems to lag behind Beijing in the field of hypersonic weapons' capabilities.
The US military and intelligence officials were caught off-guard by China's reported hypersonic missile test carried out in July at five times the speed of sound - an unprecedented feat, The Financi Nanoracks to deploy first 0.3U CubeSat from Space Station
 Nanoracks Europe is on track to set a new record as the company prepares to deploy the first-ever 0.3U CubeSat from the International Space Station (ISS). The satellite, named FEES2, was developed by the Italian company GP Advanced Projects and is approximately the thickness of a cherry. It will be one of the smallest trackable objects deployed directly from the Space Station.
FEES2 (Flexi
Nanoracks Europe is on track to set a new record as the company prepares to deploy the first-ever 0.3U CubeSat from the International Space Station (ISS). The satellite, named FEES2, was developed by the Italian company GP Advanced Projects and is approximately the thickness of a cherry. It will be one of the smallest trackable objects deployed directly from the Space Station.
FEES2 (Flexi Mining tech heads for the stars as IMDEX backs lunar rover project
 Mining-tech leaders IMDEX - the company behind breakthrough drill and blast technology BLASTDOG TM - is backing development of an Australian-made lunar rover that NASA could send to the moon by 2026.
IMDEX is part of a group of companies supporting Australian Remote Operations for Space and Earth (AROSE) that is looking to leverage autonomous technology prevalent in the mining sector for u
Mining-tech leaders IMDEX - the company behind breakthrough drill and blast technology BLASTDOG TM - is backing development of an Australian-made lunar rover that NASA could send to the moon by 2026.
IMDEX is part of a group of companies supporting Australian Remote Operations for Space and Earth (AROSE) that is looking to leverage autonomous technology prevalent in the mining sector for u Russia's Prichal module docks at ISS
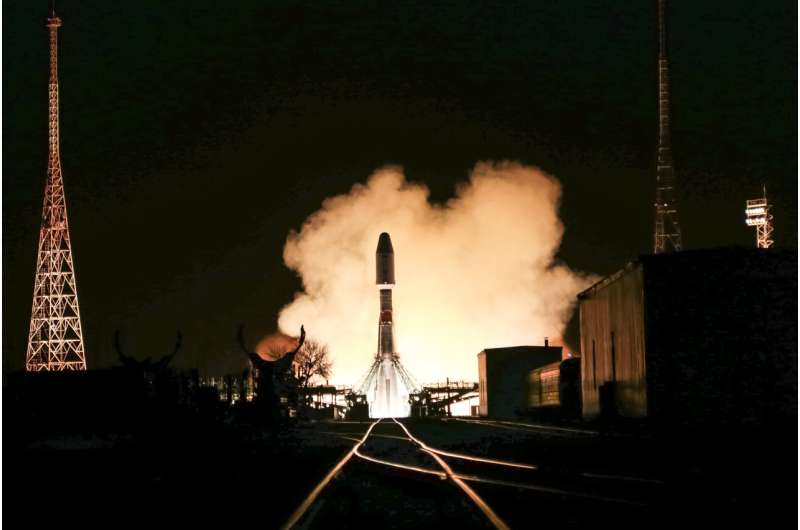
 Russia's new docking module Prichal on Friday successfully docked with the International Space Station (ISS), the Russian space agency Roscosmos said.
The new addition to the ISS completed an automated docking with the nadir (Earth-facing) port of Russia's Nauka lab module at 1519 GMT, it said.
Roscosmos chief Dmitry Rogozin congratulated the Russian crew members of the ISS on the "suc
Russia's new docking module Prichal on Friday successfully docked with the International Space Station (ISS), the Russian space agency Roscosmos said.
The new addition to the ISS completed an automated docking with the nadir (Earth-facing) port of Russia's Nauka lab module at 1519 GMT, it said.
Roscosmos chief Dmitry Rogozin congratulated the Russian crew members of the ISS on the "suc NASA, INL take next step toward developing dynamic radioisotope power system
 Idaho National Laboratory (INL) has selected Aerojet Rocketdyne as the lead subcontractor for the first of three phases toward the development of a dynamic radioisotope power system for a lunar demonstration mission by the late 2020s as outlined in Space Policy Directive-6.
The goal of this technology demonstration is to develop and demonstrate performance of a system that is three times m
Idaho National Laboratory (INL) has selected Aerojet Rocketdyne as the lead subcontractor for the first of three phases toward the development of a dynamic radioisotope power system for a lunar demonstration mission by the late 2020s as outlined in Space Policy Directive-6.
The goal of this technology demonstration is to develop and demonstrate performance of a system that is three times m Rocket Lab confirms helicopter capture attempt for next recovery mission
 Rocket Lab has confirmed it will attempt to catch a returning rocket booster mid-air with a helicopter during the company's next recovery mission. The confirmation follows the successful demonstration of helicopter shadow operations for the first time during the company's 22nd Electron launch last week in the company's latest effort to make Electron the world's first reusable, orbital-class comm
Rocket Lab has confirmed it will attempt to catch a returning rocket booster mid-air with a helicopter during the company's next recovery mission. The confirmation follows the successful demonstration of helicopter shadow operations for the first time during the company's 22nd Electron launch last week in the company's latest effort to make Electron the world's first reusable, orbital-class comm New Russian module docks with International Space Station

Testing confirms Webb Telescope on track for targeted Dec. 22 launch
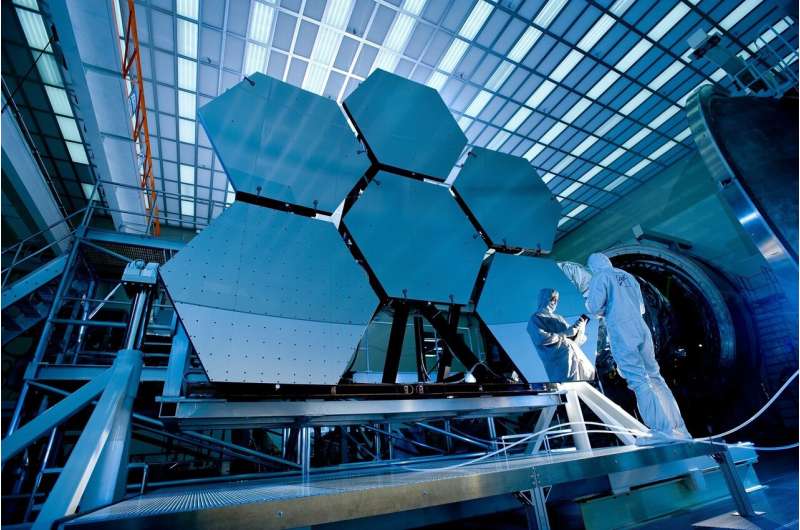

Engineering teams have completed additional testing confirming NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is ready for flight, and launch preparations are resuming toward Webb's target launch date of Wednesday, Dec. 22, at 7:20 a.m. EST.
Additional testing was conducted this week to ensure the observatory's health following an incident that occurred when the release of a clamp band caused a vibration throughout the observatory.
On Wednesday, Nov. 24, engineering teams completed these tests, and a NASA-led anomaly review board concluded no observatory components were damaged in the incident. A "consent to fuel" review was held, and NASA gave approval to begin fueling the observatory. Fueling operations will begin Thursday, Nov. 25, and will take about 10 days.
The Webb Space Telescope is an international partnership with the European and Canadian space agencies. It will explore every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe, and everything in between. Webb will reveal new and unexpected discoveries, and help humanity understand the origins of the universe and our place in it.
Parker Solar Probe completes a record-setting swing by the sun
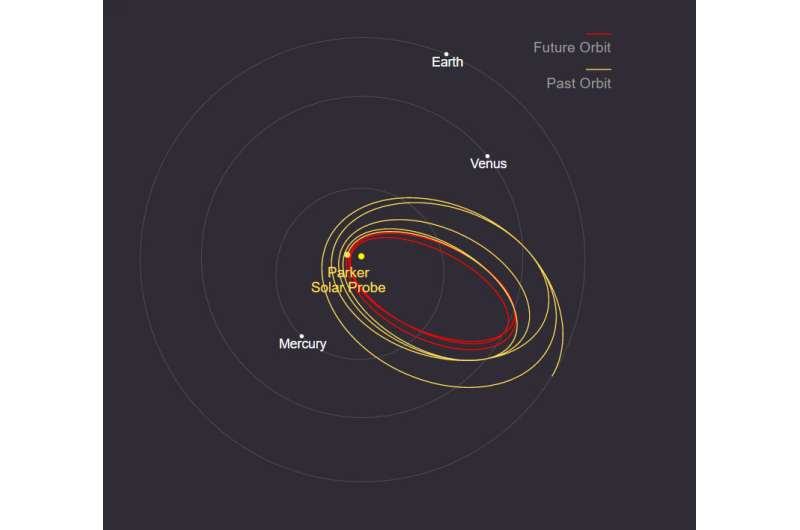
Blazing along at space-record speeds that would get it from Earth to the Moon in under an hour, NASA's Parker Solar Probe completed its 10th close approach to the sun on Nov. 21, coming within 5.3 million miles (8.5 million kilometers) of the solar surface.
The close approach (known as perihelion), also at a record distance, occurred at 4:25 a.m. EST (8:25 UTC), with Parker Solar Probe moving 364,660 miles per hour (586,864 kilometers per hour).































