Copernical Team
Iron integral to the development of life on Earth - and the possibility of life on other planets
 Iron is an essential nutrient that almost all life requires to grow and thrive. Iron's importance goes all the way back to the formation of the planet Earth, where the amount of iron in the Earth's rocky mantle was 'set' by the conditions under which the planet formed and went on to have major ramifications for how life developed.
Now, scientists at the University of Oxford have uncovered
Iron is an essential nutrient that almost all life requires to grow and thrive. Iron's importance goes all the way back to the formation of the planet Earth, where the amount of iron in the Earth's rocky mantle was 'set' by the conditions under which the planet formed and went on to have major ramifications for how life developed.
Now, scientists at the University of Oxford have uncovered Gas bubbles in rock pores - a nursery for life on Early Earth
 Where and how did life begin on Early Earth more than 3.5 billion years ago from non-living chemicals? Discovering the answer to this question has long been debated and is a challenge for scientists. One thing that scientists can look for is potential environments that allowed life to spark. A key necessity for the first cells on Earth is the ability to make compartments and evolve to facilitate
Where and how did life begin on Early Earth more than 3.5 billion years ago from non-living chemicals? Discovering the answer to this question has long been debated and is a challenge for scientists. One thing that scientists can look for is potential environments that allowed life to spark. A key necessity for the first cells on Earth is the ability to make compartments and evolve to facilitate The uneven universe
 It is almost always assumed in cosmological calculations that there is a even distribution of matter in the universe. This is because the calculations would be much too complicated if the position of every single star were to be included. In reality, the universe is not uniform: in some places there are stars and planets, in others there is just a void.
Physicists Michael te Vrugt and Prof
It is almost always assumed in cosmological calculations that there is a even distribution of matter in the universe. This is because the calculations would be much too complicated if the position of every single star were to be included. In reality, the universe is not uniform: in some places there are stars and planets, in others there is just a void.
Physicists Michael te Vrugt and Prof Airbus and DLR intensify cooperation
 Airbus and the German Aerospace Center are expanding their cooperation in research on climate protection in aviation. Under an agreement signed by Nicole Dreyer-Langlet, Airbus' VP Research and Technology Representative, Germany, and Markus Fischer, DLR Divisional Board Member Aeronautics, future joint projects will focus, in particular, on emission measurements for new types of aviation fuels,
Airbus and the German Aerospace Center are expanding their cooperation in research on climate protection in aviation. Under an agreement signed by Nicole Dreyer-Langlet, Airbus' VP Research and Technology Representative, Germany, and Markus Fischer, DLR Divisional Board Member Aeronautics, future joint projects will focus, in particular, on emission measurements for new types of aviation fuels, High-tech sleeping bag could solve vision issues in space
 A subtle smile emerged on Dr. James Leidner's face as he envisioned telling people of the unusual contribution he made to mankind's mission to Mars.
For 72 straight hours, the study volunteer lay in a bed at UT Southwestern, the monotony broken only at night when researchers placed his lower body in a sealed, vacuum-equipped sleeping bag to pull down body fluids that naturally flowed int
A subtle smile emerged on Dr. James Leidner's face as he envisioned telling people of the unusual contribution he made to mankind's mission to Mars.
For 72 straight hours, the study volunteer lay in a bed at UT Southwestern, the monotony broken only at night when researchers placed his lower body in a sealed, vacuum-equipped sleeping bag to pull down body fluids that naturally flowed int Bezos' Blue Origin completes third crewed space flight
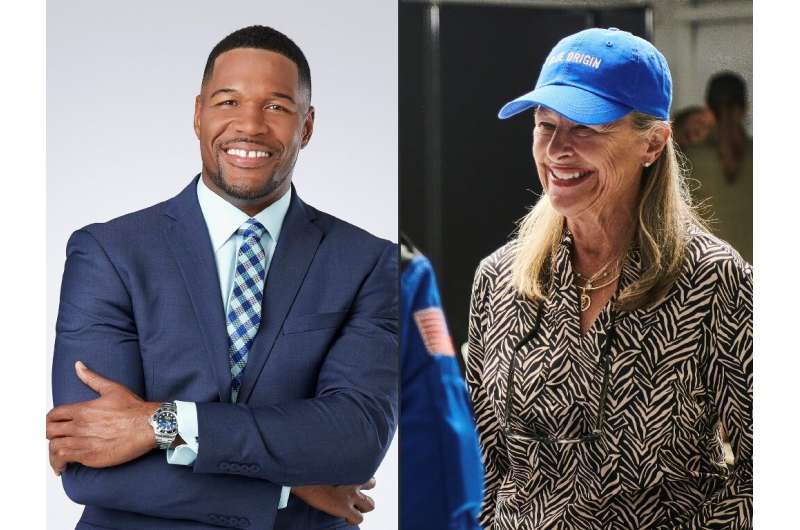

Jeff Bezos' Blue Origin company blasted its third private crew into space on Saturday and brought it back safely, this time including the daughter of the first American astronaut.
The stubby white spacecraft with a round tip blasted off into clear blue skies over West Texas for a roughly 11-minute trip to just beyond the internationally recognized boundary of space, 62 miles (100 kilometers) high.
The six-member crew hooted with glee as they unbuckled to enjoy a few minutes of weightlessness, looking out at space through tall windows in the capsule.
"I've never seen anything like that," one unidentified crew member said as Blue Origin livestreamed the flight.
Daughter of first American astronaut launches on Blue Origin flight
 Jeff Bezos' Blue Origin company blasted its third private crew to space on Saturday, this time including the daughter of the first American astronaut.
The stubby white spacecraft with a round tip blasted off into clear blue skies over West Texas for a roughly 11 minute trip to just beyond the internationally-recognized boundary of space, 62 miles (100 kilometers) high.
The six-member cre
Jeff Bezos' Blue Origin company blasted its third private crew to space on Saturday, this time including the daughter of the first American astronaut.
The stubby white spacecraft with a round tip blasted off into clear blue skies over West Texas for a roughly 11 minute trip to just beyond the internationally-recognized boundary of space, 62 miles (100 kilometers) high.
The six-member cre Blue Origin poised to send NFL, TV's Strahan into space
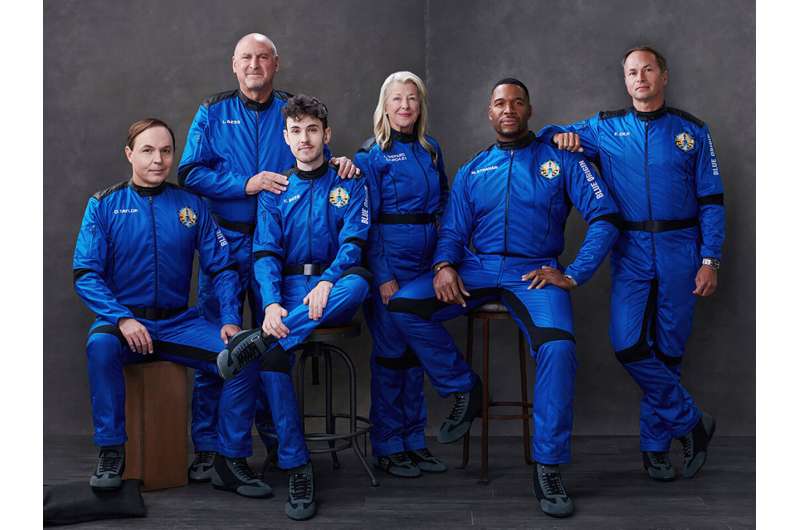

Jeff Bezos' rocket company, Blue Origin, is about to send former NFL great Michael Strahan into space—with a football.
The co-host of ABC's "Good Morning America" and former New York Giant prepped Saturday for a morning blastoff from West Texas. Five others will join him on the 10-minute flight, including the eldest daughter of the first American in space, Alan Shepard. Blue Origin's New Shepard rocket is named for him.
New space economy ready to lift off thanks to Finnish innovation
 The new space economy is taking a giant leap as space technology turns towards improving the future of life here on earth. As the sector grows, innovative Finnish companies are leading the way using their digital and tech-savvy expertise as well as stellar engineering skills to bring space back down to earth.
According to Morgan Stanley's Space Team the global space industry will surge to
The new space economy is taking a giant leap as space technology turns towards improving the future of life here on earth. As the sector grows, innovative Finnish companies are leading the way using their digital and tech-savvy expertise as well as stellar engineering skills to bring space back down to earth.
According to Morgan Stanley's Space Team the global space industry will surge to A young, sun-like star may hold warnings for life on Earth
 Astronomers spying on a stellar system located dozens of lightyears from Earth have, for the first time, observed a troubling fireworks show: A star named EK Draconis ejected a massive burst of energy and charged particles in an event that was much more powerful than anything scientists have seen in our own solar system.
The researchers, including astrophysicist Yuta Notsu of the Universit
Astronomers spying on a stellar system located dozens of lightyears from Earth have, for the first time, observed a troubling fireworks show: A star named EK Draconis ejected a massive burst of energy and charged particles in an event that was much more powerful than anything scientists have seen in our own solar system.
The researchers, including astrophysicist Yuta Notsu of the Universit