
Copernical Team
Settle the TRAPPIST exoplanets: challenge for evolutionary computing
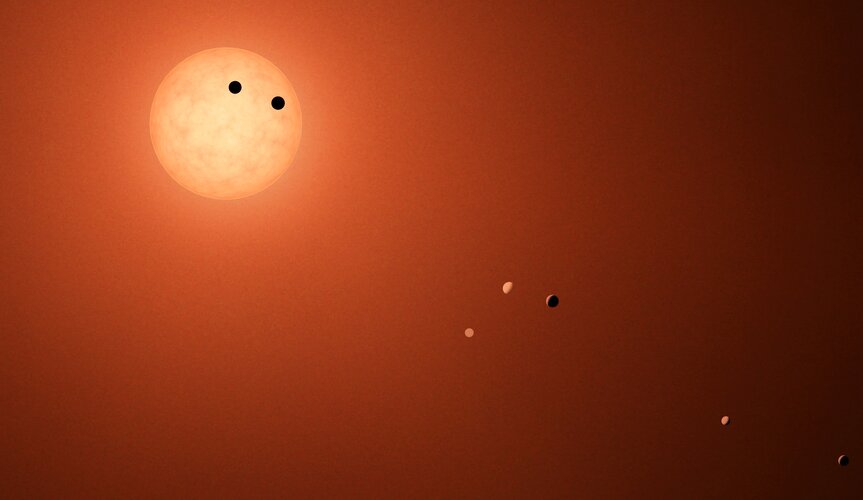

It reads like a work of science fiction: software that mates, reproduces and mutates being deployed to plan the exploration and settlement of the exotic TRAPPIST-1 solar system, around 40 light years away from Earth. In fact this is the latest competition conceived by ESA’s Advanced Concepts Team, this time seeking to challenge the worldwide evolutionary computing community.
Satellite navigation signals help map sea surface shape
 Video:
00:05:00
Video:
00:05:00
Monitoring the constantly changing shape of the sea surface is important for scientific and societal applications such as ocean current forecasting, climate research, ship routing, cable laying, and debris tracking.
A project supported by the Discovery element of ESA’s Basic Activities recently investigated a new technique to measure sea surface topography very precisely. The project was based on an idea submitted by the Institute for Space Studies of Catalonia (IEEC) through the Open Space Innovation Platform (OSIP) – ESA’s place for your space ideas.
The technique involves looking at satellite navigation (GNSS) signals that have been reflected off of
Turn your phone into a space monitoring tool
A newly released Android app will turn your smartphone into an instrument for crowdsourced science. Leave it by your window each night with your satnav positioning turned on and your phone will record small variations in satellite signals, gathering data for machine learning analysis of meteorology and space weather patterns.
Space-grown lettuce could help astronauts avoid bone loss
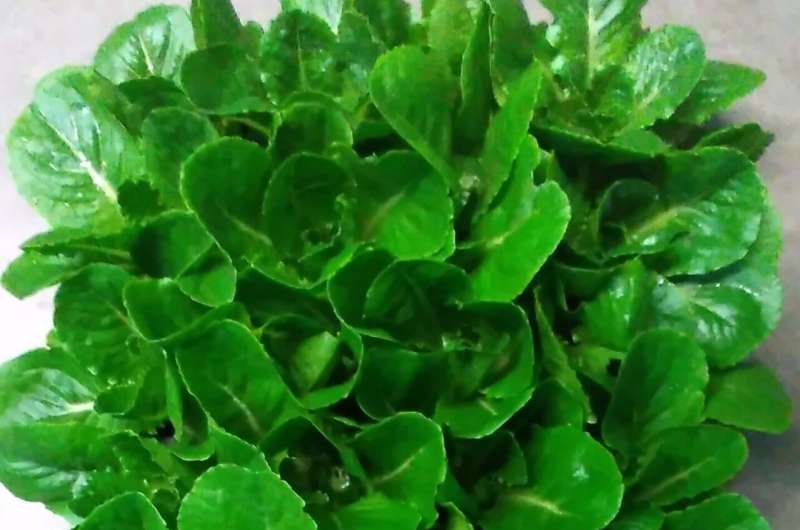

NASA is preparing to send humans to Mars sometime in the 2030s. The 3-year mission will expose astronauts to a long period of microgravity, which will cause them to lose bone mass. But now, scientists report transgenic lettuce that produces a bone-stimulating hormone. Someday, astronauts could grow the lettuce in space and help guard against bone loss—simply by eating a big bowl of salad. In addition, the lettuce might help stave off osteoporosis in resource-limited areas here on Earth, the researchers say.
The researchers will present their results today at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS).
Previous studies of astronauts on extended space missions have shown that they lose, on average, more than 1% of bone mass per month spent in space, a condition known as osteopenia.
Micro-geostationary satellite enters design phase

A small but powerful European telecommunications satellite – the first of a series – is to be developed under a contract signed between ESA and SWISSto12, an innovative company based in Renens, Switzerland.
Watch live: first space steps for Matthias

Tune in to ESA Web TV channel 2 from 12:30 CET (11:30 GMT) this Wednesday 23 March to watch ESA astronaut Matthias Maurer’s first spacewalk, known as US EVA 80, live from the International Space Station.
Cosmic milestone: NASA confirms 5,000 exoplanets

The count of confirmed exoplanets has just ticked past the 5,000 mark, representing a 30-year journey of discovery led by NASA space telescopes.
Not so long ago, we lived in a universe with only a small number of known planets, all of them orbiting our sun. But a new raft of discoveries marks a scientific high point: More than 5,000 planets are now confirmed to exist beyond our solar system.
Satellite operator OneWeb switches launches to SpaceX
 Global satellite communications company OneWeb said Monday that it will switch launches to Elon Musk's SpaceX, after suspending activities with Russia's Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan.
"OneWeb... announced today that the company and SpaceX entered into an agreement that will enable OneWeb to resume satellite launches," OneWeb said in a brief statement.
The terms of the agreement remai
Global satellite communications company OneWeb said Monday that it will switch launches to Elon Musk's SpaceX, after suspending activities with Russia's Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan.
"OneWeb... announced today that the company and SpaceX entered into an agreement that will enable OneWeb to resume satellite launches," OneWeb said in a brief statement.
The terms of the agreement remai Samantha’s second space mission: Minerva
 Video:
00:04:15
Video:
00:04:15
ESA astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti will return to the International Space Station in April 2022. Her second space mission is known as Minerva.
Inspired by Roman mythology, Samantha says the Minerva mission name and patch pay homage to the competence and sophisticated craftmanship of all those who make human spaceflight possible.
Samantha will travel to the Station alongside NASA astronauts Kjell Lindgren, Bob “Farmer” Hines and Jessica Watkins. Collectively known as Crew-4, the astronauts will be launched from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, USA, on a SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft.
When Samantha arrives at the Station, her Minerva mission officially
Methane detected over Poland’s coal mines
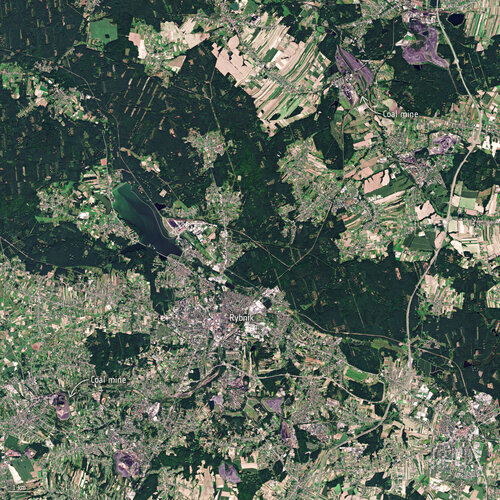

Data from the Tropomi instrument onboard the Copernicus Sentinel-5P satellite has been used to detect methane plumes over some of Europe’s largest methane-emitting coal mines.































