Copernical Team
European Space Agency stops cooperation with Russian lunar missions
 The European Space Agency on Wednesday ended cooperation with Russia on three missions to the Moon due to Moscow's invasion of Ukraine, following a previous decision to do the same for a Mars mission.
The ESA said it would "discontinue cooperative activities" on Luna-25, 26 and 27, a series of Russian lunar missions on which the European agency had aimed to test new equipment and technology.
The European Space Agency on Wednesday ended cooperation with Russia on three missions to the Moon due to Moscow's invasion of Ukraine, following a previous decision to do the same for a Mars mission.
The ESA said it would "discontinue cooperative activities" on Luna-25, 26 and 27, a series of Russian lunar missions on which the European agency had aimed to test new equipment and technology. Mars astronauts will create fuel by having a shower

When astronauts begin exploring Mars, they will face numerous challenges. Aside from the time and energy it takes to get there and all the health risks that come with long-duration missions in space, there are also the hazards of the Martian environment itself. These include Mars' incredibly thin and toxic and toxic atmosphere, the high levels of radiation the planet is exposed to, and the fact that the surface is extremely cold and drier than the driest deserts on Earth.
As a result, missions to Mars will need to leverage local resources to provide all the basic necessities, a process known as In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU).
James Webb telescope's coldest instrument reaches operating temperature

NASA's James Webb Space Telescope will see the first galaxies to form after the Big Bang, but to do that, its instruments first need to get cold—really cold. On April 7, Webb's Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI)—a joint development by NASA and ESA (European Space Agency)—reached its final operating temperature below 7 kelvins (minus 447 degrees Fahrenheit, or minus 266 degrees Celsius).
COMET upgrade for ESA’s mission design centre
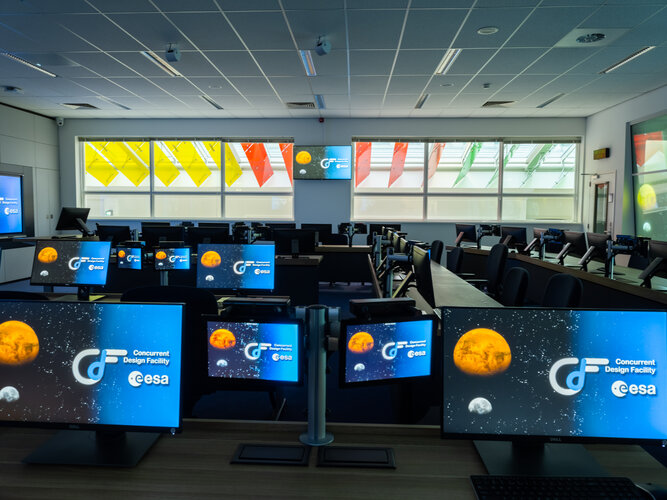

ESA has a new tool for designing space missions. The Agency’s Concurrent Design Facility – bringing together different experts for the rapid creation and evaluation of virtual spacecraft designs – has adopted an advanced software tool, COMET, which will help extend the use of digital models into further mission development phases. Its open source nature means it is freely available beyond ESA Member States, facilitating international cooperation with wider space agencies, research institutions or companies.
Media session - ESA Council extraordinary meeting
 Video:
01:15:00
Video:
01:15:00
ESA Director General Josef Aschbacher shares the outcome of the ESA Council extraordinary meeting in this virtual Q&A with journalists. Additional updates are provided on ESA’s main programmes, the overall rollout of Agenda 2025 on the way to the ESA Ministerial Meeting in November 2022 as well as further implications of the current geopolitical situation on ESA’s activities.
Tiny but precise: Team creates compact device to help spaceships land safely on planets
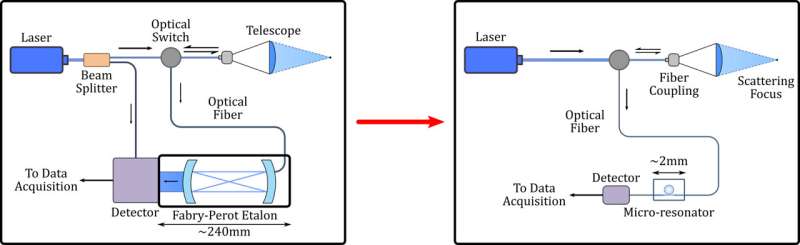
A NASA-funded team led by SMU researchers think that their small, lightweight device developed to measure spaceship velocity will improve the odds of successful landings on Mars and other planets.
Smaller, they say, is better in space.
The optical microresonator built by the team is only 2 millimeters in length, compared to the velocity-monitoring tool most commonly used on spacecraft—the Fabry-Perot interferometer—which can be as long as 500 millimeters. NASA and other space agencies may be able to use the microresonator to get an accurate, quick measurement of how fast a spaceship is moving in a specific direction.
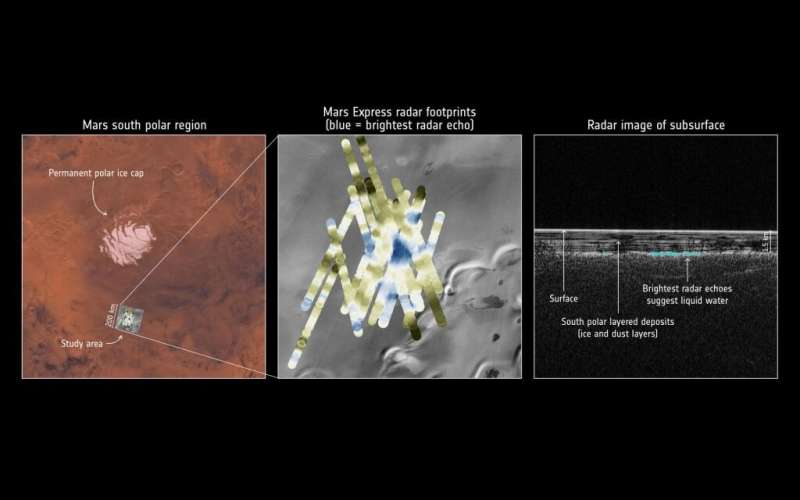
Image: The largest antenna ever tested in ESA's Hertz radio frequency test chamber
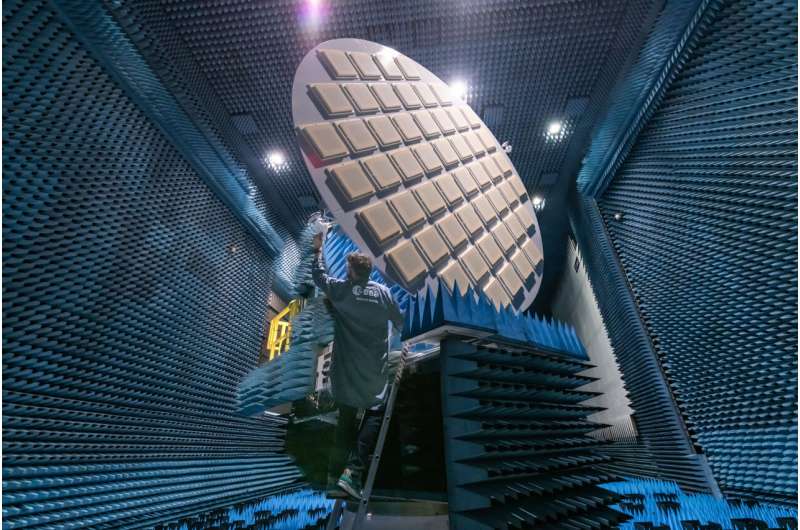

The largest antenna ever tested in ESA's Hertz radio frequency test chamber is this 5-m diameter transponder antenna, which will operate down on the ground to help calibrate the Biomass mission, which will chart all the forests on Earth.
"This is a particularly challenging test campaign both in terms of the size of the antenna and the very low P-band frequency that Biomass will be using, which allows it to pierce through forest canopies to acquire individual trees," explains ESA antenna engineer Luis Rolo, overseeing the test campaign.
"Usually when we test a large satellite here, its antenna is significantly smaller, typically between 0.5 and 2 meters across. But this entire structure is a radiating antenna in its own right, its sides coming near to the chamber walls.
"What this means is that the testing process highlight some aspects of the chamber we've never seen before, even after many years of testing. But we've come up with a measurement method involving multiple acquisitions from different spots within the chamber, combined carefully to subtract such environmental effects, yielding very accurate results.
Image: Axiom Mission 1 at Pad 39A and Artemis I at Pad 39B
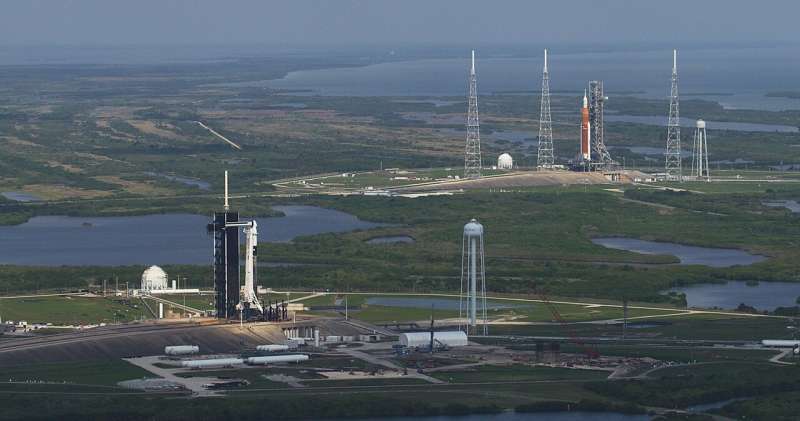

Axiom Mission 1 (Ax-1) is in the foreground on Launch Pad 39A with NASA's Artemis I in the background on Launch Pad 39B on April 6, 2022.
This is the first time two totally different types of rockets and spacecraft designed to carry humans are on the sister pads at the same time—but it won't be the last as NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida continues to grow as a multi-user spaceport to launch both government and commercial rockets.
Ax-1 liftoff is scheduled at 11:17 a.m. EDT Friday, April 8, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
Explore further
Register for Living Planet Symposium 2022
Register for Living Planet Symposium 2022
Redirecting ESA programmes in response to geopolitical crisis
Press Release N° 16–2022
Following the Russian aggression against Ukraine, ESA’s Director General has initiated a comprehensive review of all activities currently undertaken in cooperation with Russia and Ukraine. The objective is to determine the possible consequences of this new geopolitical context for ESA programmes and activities and to create a more resilient and robust space infrastructure for Europe.