Copernical Team
Discovery Telescope plays key role in DART planetary defense test mission
 Within two weeks, the DART spacecraft will impact the asteroid moon Dimorphos as it completes the world's first planetary defense test mission. The success of the effort relies heavily on the Lowell Discovery Telescope, which scientists are using for both before- and after-impact observations.
The DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test) mission is an outgrowth of ongoing interest in planet
Within two weeks, the DART spacecraft will impact the asteroid moon Dimorphos as it completes the world's first planetary defense test mission. The success of the effort relies heavily on the Lowell Discovery Telescope, which scientists are using for both before- and after-impact observations.
The DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test) mission is an outgrowth of ongoing interest in planet Wind drives geology on Mars these days
 A new paper based on exploration by the NASA's Curiosity Mars rover-and reviewed by an astronaut while she was on the International Space Station (ISS), in what may be a first for peer-reviewed science literature-describes how dramatically different geology on Mars works from that on Earth.
The paper is part of an ongoing attempt to understand the rock cycle on the Red Planet-that is, how
A new paper based on exploration by the NASA's Curiosity Mars rover-and reviewed by an astronaut while she was on the International Space Station (ISS), in what may be a first for peer-reviewed science literature-describes how dramatically different geology on Mars works from that on Earth.
The paper is part of an ongoing attempt to understand the rock cycle on the Red Planet-that is, how Flying to (hypothetical) Planet 9: Why visit it, how could we get there and would it surprise us like Pluto?
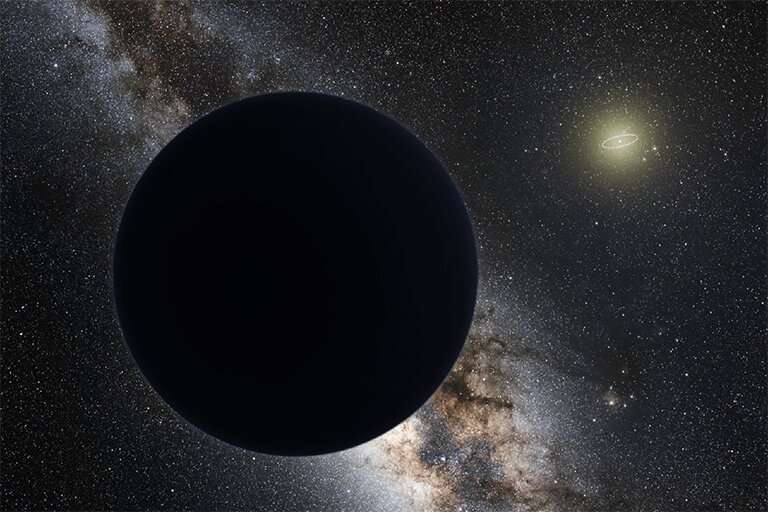

In a recent study submitted to Earth and Planetary Astrophysics, an international team of researchers discuss the various mission design options for reaching a hypothetical Planet 9, also known as "Planet X," which state-of-the-art models currently estimate to possess a semi-major axis of approximately 400 astronomical units (AU). The researchers postulate that sending a spacecraft to Planet 9 could pose scientific benefits much like when NASA's New Horizons spacecraft visited Pluto in 2015. But does Planet 9 actually exist?
"It is hard to put a specific number on the confidence level because so many uncertainties remain," said Dr. Manavsi Lingam, who is an Assistant Professor at the Florida Institute of Technology, and a co-author on the study.
DART spacecraft prepares to collide with asteroid target later this month
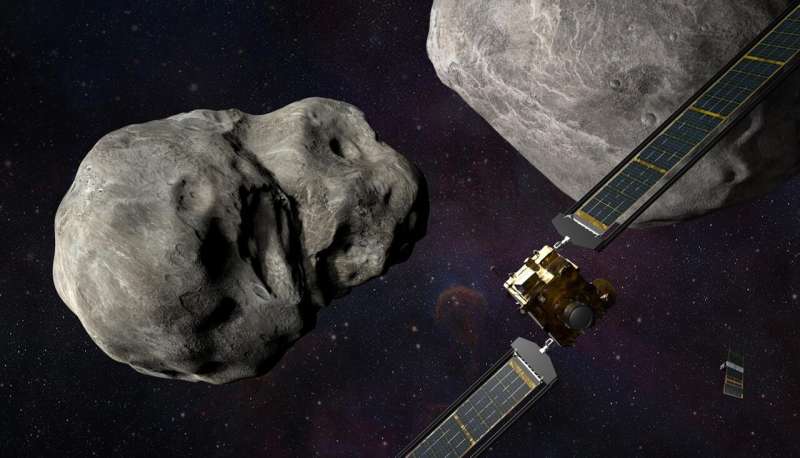

As NASA prepares to usher in a new form of planetary defense, one Johns Hopkins engineer will be eagerly awaiting the big collision that she is helping orchestrate.
Elena Adams, the mission systems engineer at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, and her team will spend the next two weeks carefully observing Didymos, a double-asteroid system that poses no threat to Earth and yet will be the target of NASA's Double Asteroid Redirection Test—a first-of-its-kind, proof-of-concept mission that will intentionally crash a spacecraft into an asteroid's moonlet to deflect it away from its course.
"During the day of impact, I'll be more of a conductor, making sure that all of the orchestra is following the beat and playing their parts," said Adams, who will discuss the mission during talk in Hodson Hall on the university's Homewood campus on Thursday at 5 p.m.
ESA astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti becomes first European female ISS commander

ESA astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti will soon fulfil the role of commander of the International Space Station, taking over from fellow Expedition 67 crew member Oleg Artemyev.
Artemis I moon mission: Researchers collaborate to send manikins to measure radiation
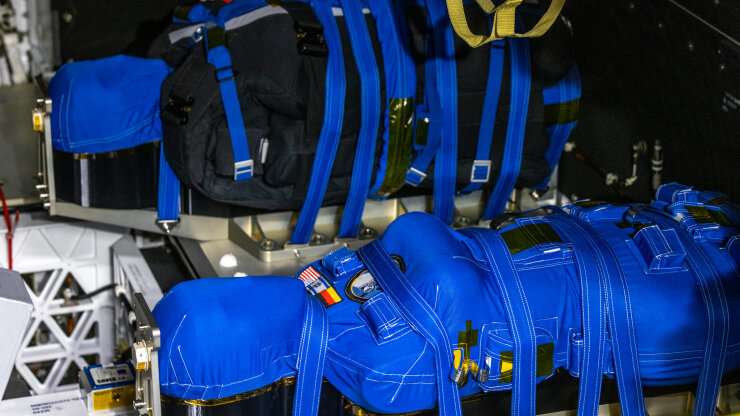

When NASA's Artemis I mission launches later this year, its crew will include Helga and Zohar, two manikin models designed in collaboration with Duke University.
These models, called "phantoms," are made of materials that mimic human bones, soft tissue and organs, and they'll be fitted with sensors that will measure radiation exposure as they travel to the moon and back. Paul Segars and Ehsan Samei, both researchers at the Carl E. Ravin Advanced Imaging Laboratories at the Duke University School of Medicine, helped develop these phantoms using methods originally created to study how different medical procedures, tools and techniques precisely affect organs throughout the human body.
"Usually these 'phantoms' are virtual, and we use them to create avatars of patients. The goal of our work is that instead of conducting a clinical trial on human patients, you can use these avatars and run a simulated clinical trial through a computer," explains Samei, the Reed and Martha Rice Distinguished Professor of Radiology.
Taking the dazzle out of CryoSat yields a first
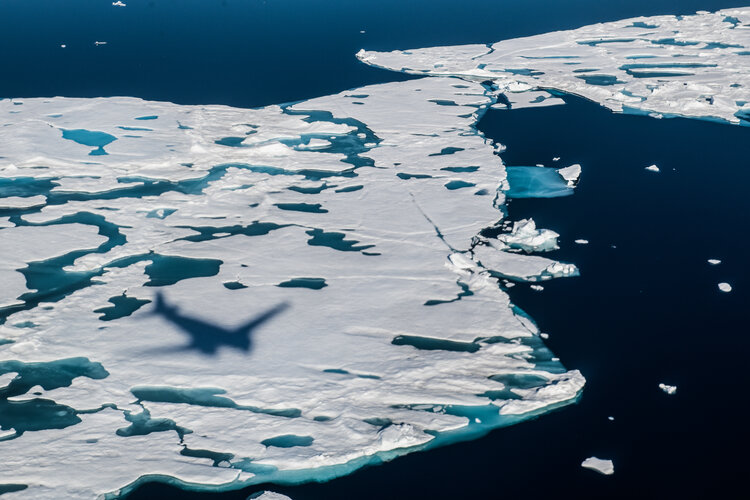

Since it was launched more than 12 years ago, ESA’s CryoSat ice mission has dazzled by way of its sheer technological and scientific excellence. This superb Earth Explorer satellite has returned a wealth of information that has transformed our understanding of Earth’s ice and how it is responding to climate change. In some circumstances, however, being dazzled isn’t a good thing, particularly when it comes to measuring the height of sea ice from space during the summer.
A paper published in Nature describes how scientists have now found an ingenious way of removing
Galileo Second Generation technology tested in ESA labs
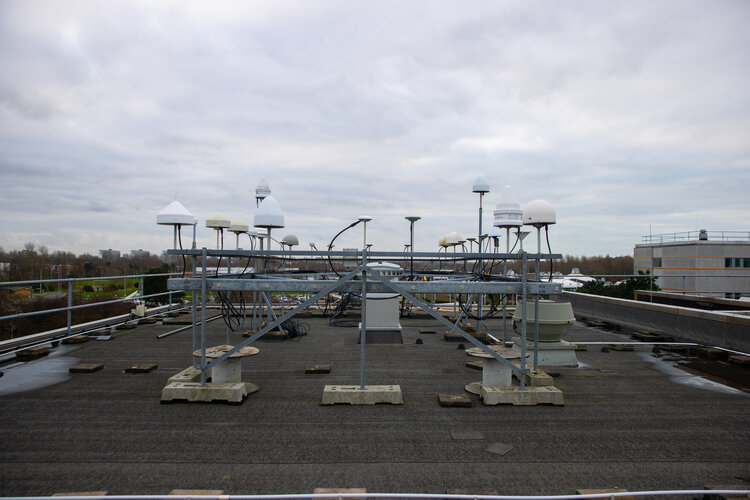

Europe’s first generation Galileo constellation is already the world’s most precise satellite navigation system – delivering metre-scale positioning to more than 3.5 billion users worldwide – but Galileo Second Generation will enable still better performance and an expanded range of services. Essential elements of the G2 system are currently being evaluated in ESA laboratories, including key algorithms to synchronise satellite timings and determine orbits as well as test versions of a satnav receiver and emergency beacon.
Northrop Grumman's rocket development reaches new heights
 When you think of a rocket launch, you probably imagine a glistening white cylinder emerging from a cloud of smoke and fire making its way into outer space. But while the sight of a launch may only last a few minutes, not many see the dedication, long hours and incredible team effort that made it all possible.
"It's not the hardware or the software-it's the people on the launch vehicle tea
When you think of a rocket launch, you probably imagine a glistening white cylinder emerging from a cloud of smoke and fire making its way into outer space. But while the sight of a launch may only last a few minutes, not many see the dedication, long hours and incredible team effort that made it all possible.
"It's not the hardware or the software-it's the people on the launch vehicle tea MDA Selected by Airbus OneWeb Satellites for US Government Program
 MDA Ltd. (TSX: MDA), a leading provider of advanced technology and services to the rapidly expanding global space industry, has been selected by Airbus OneWeb Satellites, LLC (AOS) to design and build Ka-Band steerable antennas. The MDA antennas will be integrated into the portfolio of Arrow commercial small satellites manufactured by AOS.
"We are pleased to be selected by Airbus OneWeb Sa
MDA Ltd. (TSX: MDA), a leading provider of advanced technology and services to the rapidly expanding global space industry, has been selected by Airbus OneWeb Satellites, LLC (AOS) to design and build Ka-Band steerable antennas. The MDA antennas will be integrated into the portfolio of Arrow commercial small satellites manufactured by AOS.
"We are pleased to be selected by Airbus OneWeb Sa