
Copernical Team
China plans robotic spacecraft to collect samples from asteroid
 The Chinese government has approved a plan to send a robotic spacecraft to collect samples from an asteroid, according to the China National Space Administration's Lunar Exploration and Space Program Center.
The mission, called Tianwen 2, is designed to launch a probe to obtain samples from the 2016 HO3, the smallest and closest "quasi-satellite" to Earth, and bring them back. After accomp
The Chinese government has approved a plan to send a robotic spacecraft to collect samples from an asteroid, according to the China National Space Administration's Lunar Exploration and Space Program Center.
The mission, called Tianwen 2, is designed to launch a probe to obtain samples from the 2016 HO3, the smallest and closest "quasi-satellite" to Earth, and bring them back. After accomp Major collaboration reveals new insights on binary star systems
 Scientists have long been intrigued by X-ray binary star systems, where two stars orbit around each other with one of the two stars being either a black hole or a neutron star. Both black holes and neutron stars are created in supernova explosions and are very dense - giving them a massive gravitational pull. This makes them capable of capturing the outer layers of the normal star that orbits ar
Scientists have long been intrigued by X-ray binary star systems, where two stars orbit around each other with one of the two stars being either a black hole or a neutron star. Both black holes and neutron stars are created in supernova explosions and are very dense - giving them a massive gravitational pull. This makes them capable of capturing the outer layers of the normal star that orbits ar Dark matter halos: the key to understanding galaxies
 We have come a long way in understanding the universe around us, thanks to current technological advances, such as the construction of huge telescopes or satellites with increasingly powerful instruments. However, it is disturbing that most of the universe components (matter and energy) are still unknown to us. In the "recipe" to "build" a universe like ours, we have to put two ingredients that
We have come a long way in understanding the universe around us, thanks to current technological advances, such as the construction of huge telescopes or satellites with increasingly powerful instruments. However, it is disturbing that most of the universe components (matter and energy) are still unknown to us. In the "recipe" to "build" a universe like ours, we have to put two ingredients that The outburst of a neutron star reveals the nature of phenomena only observed in black holes
 X-ray binaries are systems formed by a compact object, a neutron star or a black hole, and a star of a similar size to the Sun. The compact object swallows matter from the companion star through a disk that emits large amounts of light, especially in X-rays. This process in which the compact object attracts matter, known as accretion, usually occurs in violent eruptions during which the system b
X-ray binaries are systems formed by a compact object, a neutron star or a black hole, and a star of a similar size to the Sun. The compact object swallows matter from the companion star through a disk that emits large amounts of light, especially in X-rays. This process in which the compact object attracts matter, known as accretion, usually occurs in violent eruptions during which the system b Humanity's quest to discover the origins of life in the universe
 "We are living in an extraordinary moment in history," says Didier Queloz, who directs ETH Zurich's Centre for Origin and Prevalence of Life and the Leverhulme Centre for Life in the Universe at Cambridge. While still a doctoral student Queloz was the first to discover an exoplanet - a planet orbiting a solar-type star outside of Earth's solar system. A discovery for which he would later receive
"We are living in an extraordinary moment in history," says Didier Queloz, who directs ETH Zurich's Centre for Origin and Prevalence of Life and the Leverhulme Centre for Life in the Universe at Cambridge. While still a doctoral student Queloz was the first to discover an exoplanet - a planet orbiting a solar-type star outside of Earth's solar system. A discovery for which he would later receive Ozone-measuring Instrument on NOAA-21 Satellite Captures its First Images
 On February 9, 2023, an ozone-measuring instrument on the recently launched NOAA-21 satellite opened its doors and, over the course of a week, gathered data for its first global image. The Ozone Mapping and Profiler Suite (OMPS) consists of three sensors that monitor Earth's ozone layer and track its recovery.
The map above, created using OMPS data, shows total ozone concentrations in the
On February 9, 2023, an ozone-measuring instrument on the recently launched NOAA-21 satellite opened its doors and, over the course of a week, gathered data for its first global image. The Ozone Mapping and Profiler Suite (OMPS) consists of three sensors that monitor Earth's ozone layer and track its recovery.
The map above, created using OMPS data, shows total ozone concentrations in the What we learned from the asteroid-smashing DART mission
 On Sept. 26, 2022, at precisely 6:14 p.m. ET, a box-shaped spacecraft no bigger than a loveseat smashed directly into an asteroid wider than a football field. The planned impact knocked the space rock off its orbit, showing for the first time that an asteroid can potentially be deflected away from Earth.
The spacecraft was the key part of DART, NASA's Double Asteroid Redirection Test, whic
On Sept. 26, 2022, at precisely 6:14 p.m. ET, a box-shaped spacecraft no bigger than a loveseat smashed directly into an asteroid wider than a football field. The planned impact knocked the space rock off its orbit, showing for the first time that an asteroid can potentially be deflected away from Earth.
The spacecraft was the key part of DART, NASA's Double Asteroid Redirection Test, whic Hansel and Gretel's breadcrumb trick inspires robotic exploration of caves on Mars and beyond
 House hunting on Mars could soon become a thing, and researchers at the University of Arizona are already in the business of scouting real estate that future astronauts could use as habitats. Researchers in the UArizona College of Engineering have developed technology that would allow a flock of robots to explore subsurface environments on other worlds.
"Lava tubes and caves would make per
House hunting on Mars could soon become a thing, and researchers at the University of Arizona are already in the business of scouting real estate that future astronauts could use as habitats. Researchers in the UArizona College of Engineering have developed technology that would allow a flock of robots to explore subsurface environments on other worlds.
"Lava tubes and caves would make per NASA delivers hardware for commercial lunar payload mission
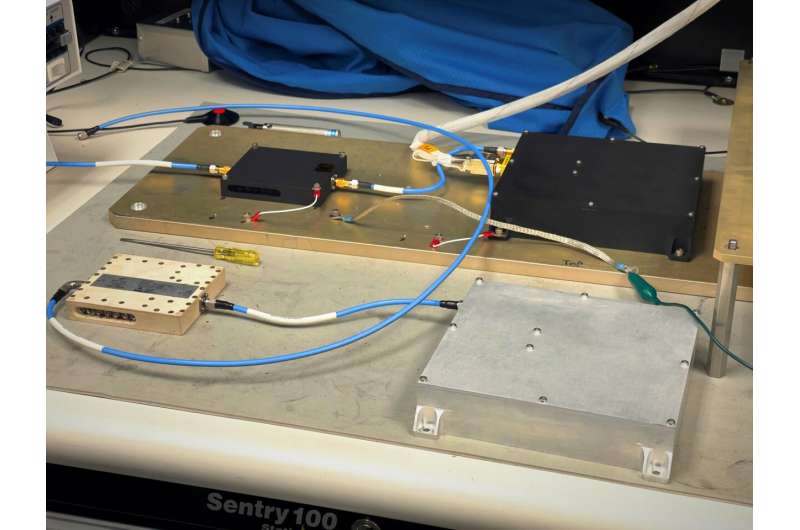
Ever wondered how your phone knows exactly where you are? Or how it can provide directions from one place to another?
In the United States, we rely on the Global Positioning System (GPS)—a satellite constellation orbiting Earth that provides precise location and timing information. What a lot of people don't know is that GPS is just one constellation of location and timing satellites. There are currently six GPS-like systems, known as global navigation satellite systems, or GNSS, that provide navigation services to Earthlings traveling the globe.
But what if we could use these Earth-based systems beyond our planet?
In 2024, as part of the NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative, Firefly Aerospace will land the "Blue Ghost" lander on the lunar surface.
First ever Canadian lunar rover will hunt for water ice on the moon
 The first ever Canadian rover to set wheels on the moon is currently under construction for a mission set to launch as early as 2026. The rover will explore the south polar region of the moon in a search for water ice in the lunar soil.
Rovers are simply "mobile robotic vehicles that allow us to explore the surfaces of other planets," explains Chris Herd, a professor in the Department of E
The first ever Canadian rover to set wheels on the moon is currently under construction for a mission set to launch as early as 2026. The rover will explore the south polar region of the moon in a search for water ice in the lunar soil.
Rovers are simply "mobile robotic vehicles that allow us to explore the surfaces of other planets," explains Chris Herd, a professor in the Department of E 































