
Copernical Team
Japanese company successfully operates its water-based propulsion system in orbit
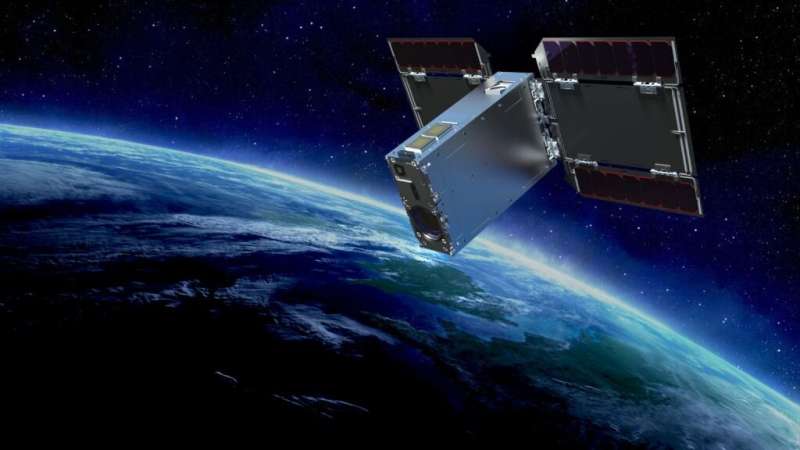

New in-space propulsion techniques seem to be popping out of the woodwork. The level of innovation behind moving things around in space is astounding, and now a company from Japan has just hit a significant milestone. Pale Blue, which I assumed was named as a nod to a beloved Carl Sagan book, recently successfully tested their in-orbit water-based propulsion system, adding yet another safe, affordable propulsion system to satellite designers' repertoires.
Using water to jet around space might seem relatively simplistic. However, despite its simplicity and relatively low cost, water jets for satellitepropulsion systems have not yet been widely adopted. This first Pale Blue system, which launched with Sony's EYE satellite as part of its STAR SPHERE program to take pictures of the Earth, was the first time the company successfully tested its system in space.
They did so by operating it for approximately two minutes in early March and adjusting the EYE satellite's orbit in LEO.
NASA plans 2 super pressure balloon test flights from New Zealand
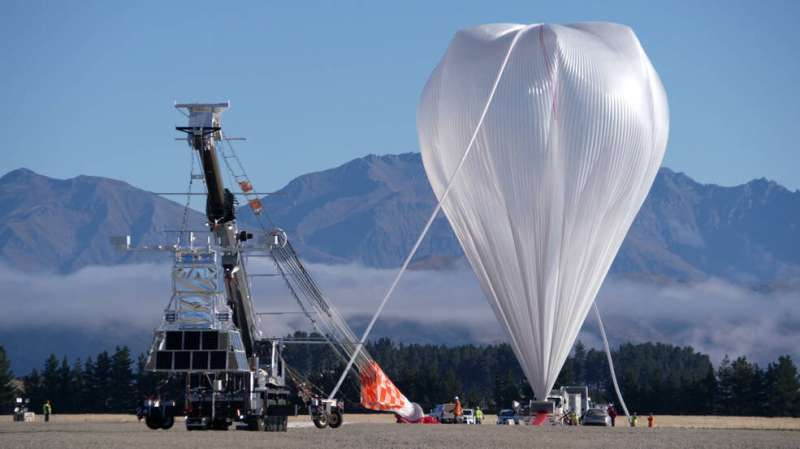

NASA's Scientific Balloon Program is scheduled to conduct two super pressure balloon (SPB) launches from Wānaka, New Zealand, to further test and qualify the technology, which can offer cost savings compared to space missions.
While the two launches are primarily to test the SPB technology, NASA is also flying science payloads as missions of opportunity on each balloon. The balloons may also be visible from the ground during their flights, which are planned for up to 100 days or more.
"The super pressure balloon technology is a real game-changer for conducting cutting-edge science at the edge of space at a fraction of the cost of flying into space," said Debbie Fairbrother, NASA's Balloon Program Office chief based at the agency's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia.
First woman, Black astronaut, Canadian to make 2024 flight around Moon
 NASA unveiled the crew on Monday for its first human mission to the Moon in more than 50 years - including the first woman and Black man to participate in a lunar flight.
Three Americans and one Canadian will fly around the Moon next year, becoming the first astronauts to venture that deep into space since the historic Apollo missions ended in 1972.
The flight, dubbed Artemis II, is sch
NASA unveiled the crew on Monday for its first human mission to the Moon in more than 50 years - including the first woman and Black man to participate in a lunar flight.
Three Americans and one Canadian will fly around the Moon next year, becoming the first astronauts to venture that deep into space since the historic Apollo missions ended in 1972.
The flight, dubbed Artemis II, is sch Kenya to launch first operational satellite next week
Kenya will launch its first operational satellite next week in a landmark achievement for the country's space program, the government said on Monday.
Taifa-1, or Nation-1 in Swahili, is scheduled to be launched on April 10 aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from the Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
"The mission is an important milestone," the defense ministry and Kenya Space Agency said in a joint statement, adding that it would contribute significantly to the country's "budding space economy".
The observation satellite is "fully designed and developed" by Kenyan engineers and will be used to provide data on agriculture and food security, among other areas, the statement said.
Testing and manufacturing of the parts were done in collaboration with a Bulgarian aerospace manufacturer, it added.
An East African economic powerhouse, Kenya is suffering its worst drought in decades after five failed rain seasons.
The satellite launch will add to a push by African nations for scientific innovation and the development of space programs.
Egypt was the first African country to send a satellite into space in 1998.
In 2018, Kenya launched its first experimental nano-satellite from the International Space Station.
As of 2022, at least 13 African countries had manufactured 48 satellites, according to Space in Africa, a Nigeria-based firm that tracks African space programs.
New ESA astronaut candidates start basic training
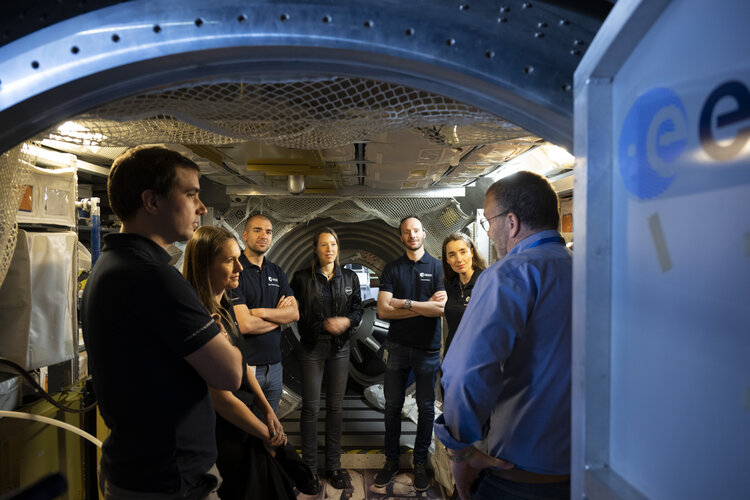 Image:
Image:
ESA's newly selected astronaut candidates of the class of 2022 arrived at the European Astronaut Centre in Cologne, Germany, on 3 April 2023 to begin their 12-month basic training.
The group of five candidates, Sophie Adenot, Pablo Álvarez Fernández, Rosemary Coogan, Raphaël Liégeois, and Marco Sieber, are part of the 17-member astronaut class of 2022, selected from 22 500 applicants from across ESA Member States in November 2022.
The astronaut candidates will be trained to the highest level of standards in preparation for future space missions. During basic training, this includes learning all about space exploration, technical and scientific disciplines, space
Runoff: not as you might think

Runoff and river discharge are important components in Earth’s water cycle, but as climate change tightens its grip, heatwaves and instances of drought are increasingly hitting the headlines. One would assume that this hotter weather leads to reduced water runoff, but an innovative way of using information from satellites suggests that this isn’t always the case.
Integral team at ESOC during safe mode commissioning
 Image:
Integral team at ESOC during safe mode commissioning
Image:
Integral team at ESOC during safe mode commissioning Integral's 'new safe mode' activates for the first time
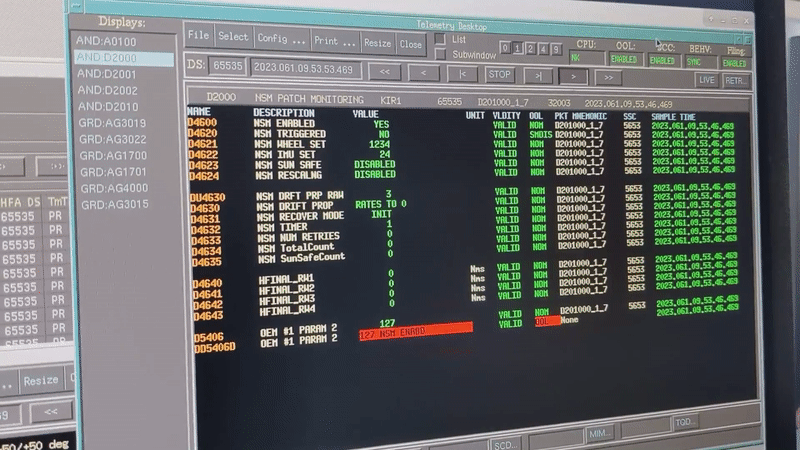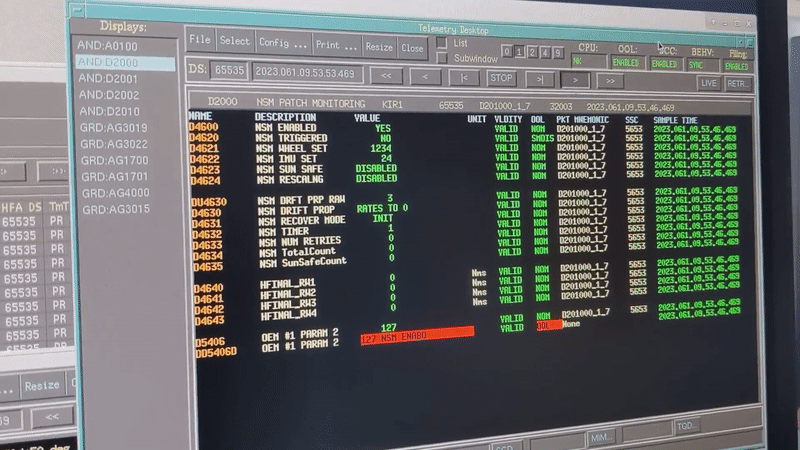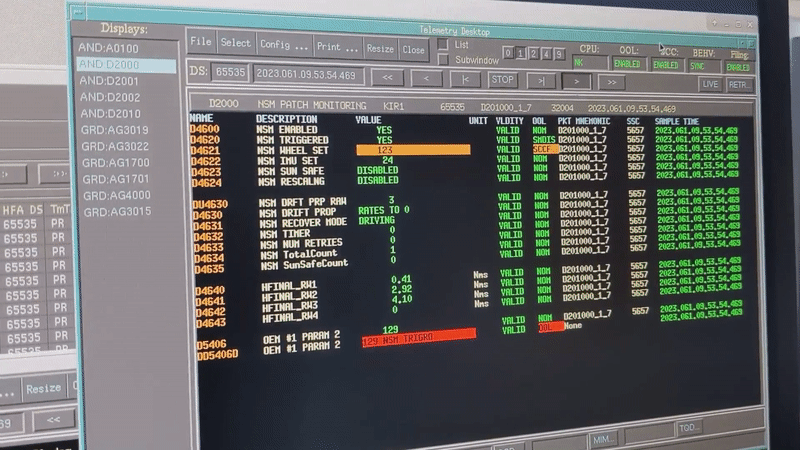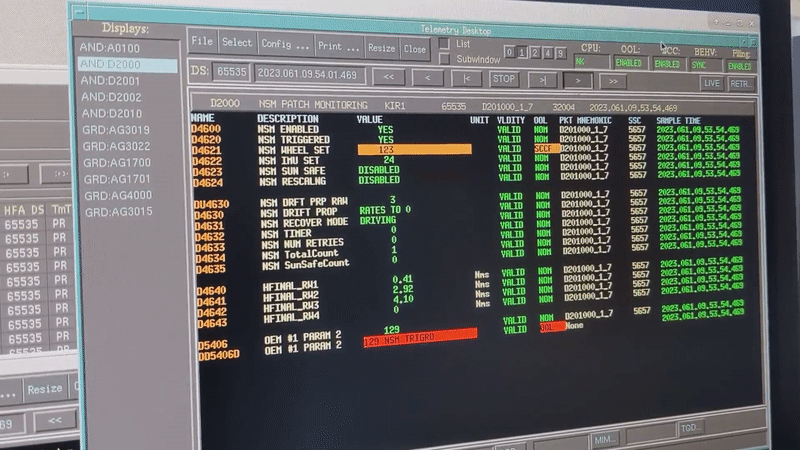 Image:
Integral's 'new safe mode' activates for the first time
Image:
Integral's 'new safe mode' activates for the first time Hack-A-Sat competition highlights on-orbit hacking
 The Department of the Air Force, or DAF, in collaboration with the Air Force Research Laboratory, or AFRL, and Space Systems Command, opened registration Feb. 22, 2023, for the qualification round of the fourth annual "Hack-A-Sat" competition, the world's first satellite hacking contest hosted for an on-orbit satellite.
Hack-A-Sat is an opportunity for hackers, researchers and everyday ent
The Department of the Air Force, or DAF, in collaboration with the Air Force Research Laboratory, or AFRL, and Space Systems Command, opened registration Feb. 22, 2023, for the qualification round of the fourth annual "Hack-A-Sat" competition, the world's first satellite hacking contest hosted for an on-orbit satellite.
Hack-A-Sat is an opportunity for hackers, researchers and everyday ent 
































