
Copernical Team
Terran Orbital PTD-3 enables 200Gbits space-to-ground optical link
 Terran Orbital Corporation (NYSE: LLAP) announced a significant achievement in space-to-ground communication, successfully enabling a 200 gigabits per second optical link through the Pathfinder Technology Demonstrator 3 (PTD-3) satellite. The NASA satellite hosts the TeraByte InfraRed Delivery (TBIRD) payload, funded by NASA's Space Communications and Navigation (SCaN) and developed by MIT Linco
Terran Orbital Corporation (NYSE: LLAP) announced a significant achievement in space-to-ground communication, successfully enabling a 200 gigabits per second optical link through the Pathfinder Technology Demonstrator 3 (PTD-3) satellite. The NASA satellite hosts the TeraByte InfraRed Delivery (TBIRD) payload, funded by NASA's Space Communications and Navigation (SCaN) and developed by MIT Linco Space Forge enables reusable satellites with new way of returning from space to Earth
 Space Forge reveals their patent protected design of a planet-friendly reusable re-entry system, which will enable the low cost and reliable return of satellites to Earth.
Although the cost of launching satellites into space has become lower through the use of reusability, all current commercial space return vehicles use ablative heat shields which require replacement after every flight. S
Space Forge reveals their patent protected design of a planet-friendly reusable re-entry system, which will enable the low cost and reliable return of satellites to Earth.
Although the cost of launching satellites into space has become lower through the use of reusability, all current commercial space return vehicles use ablative heat shields which require replacement after every flight. S Sales rocket for Zenno's fuel-free satellite pointing system
 Zenno Astronautics (Zenno) reports has surpassed $75M in product sales (USD 48M) for its world-first superconducting magnetorquer for spacecraft attitude control, the Z01.
Built on Zenno's proprietary superconducting magnet technology, Z01 is a fuel-free satellite pointing system designed to significantly increases the range of capabilities for attitude control in space, including fully au
Zenno Astronautics (Zenno) reports has surpassed $75M in product sales (USD 48M) for its world-first superconducting magnetorquer for spacecraft attitude control, the Z01.
Built on Zenno's proprietary superconducting magnet technology, Z01 is a fuel-free satellite pointing system designed to significantly increases the range of capabilities for attitude control in space, including fully au NASA calls end to Lunar Flashlight mission after some tech successes
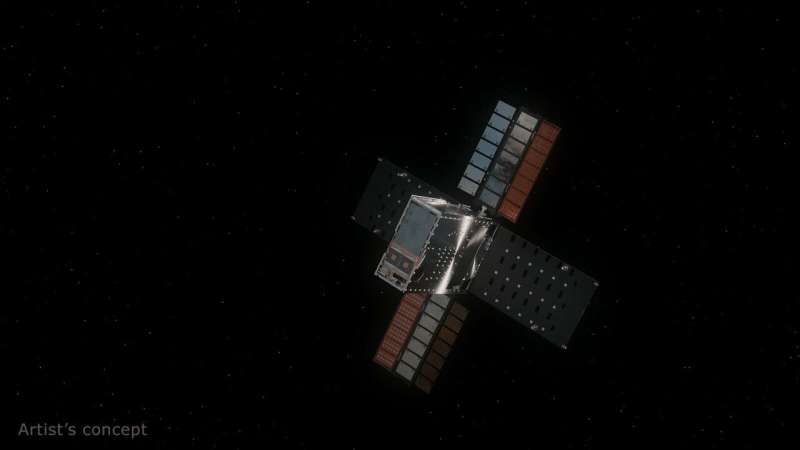

While the CubeSat couldn't reach the lunar South Pole to help seek ice, it fulfilled several technology goals that will empower future missions for the benefit of humanity.
NASA's Lunar Flashlight launched on Dec. 11, 2022, to demonstrate several new technologies, with an ultimate goal to seek out surface ice in the permanently shadowed craters of the moon's South Pole. Since then, the briefcase-size satellite's miniaturized propulsion system—the first of its kind ever flown—proved unable to generate enough thrust to get into lunar orbit, despite months of effort by the operations team.
Glass fibers in lunar regolith could help build structures on the moon
Through the Artemis Program, NASA plans to send the first astronauts to the moon in over 50 years. Before the decade is over, this program aims to establish the infrastructure that will allow for a "sustained program of lunar exploration and development." The European Space Agency (ESA) also has big plans, which include the creation of a moon Village that will serve as a spiritual successor to the International Space Station (ISS). China and Roscosmos also came together in June 2021 to announce that they would build the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS) around the lunar south pole.
In all cases, space agencies plan to harvest local resources to meet their construction and long-term needs—a process known as in-situ resource utilization (ISRU).
Webb finds water, and a new mystery, in rare main-belt comet
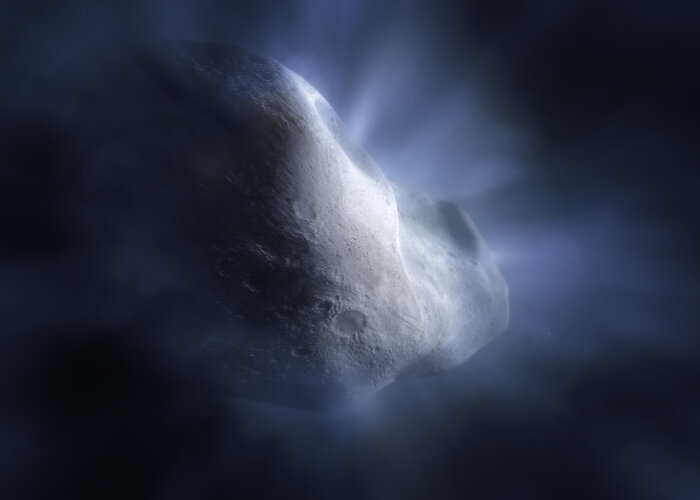

The NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope has enabled another long-sought scientific breakthrough, this time for Solar System scientists studying the origins of the water that has made life on Earth possible. Using Webb’s NIRSpec (Near-Infrared Spectrograph) instrument, astronomers have confirmed gas – specifically water vapour – around a comet in the main asteroid belt for the first time, proving that water from the primordial Solar System can be preserved as ice in that region. However, the successful detection of water comes with a new puzzle: unlike other comets, Comet 238P/Read had no detectable carbon dioxide.
Bacteria survive on radioactive elements
 Bacteria that feed on methanol are able to grow on certain rare earth elements as well as their radioactive relatives. These findings suggest a possible role for such bacteria in the decontamination of areas where actinides are spilled, or in the separation of lanthanides and actinides for analytical or preparative purposes, according to a study published in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
Bacteria that feed on methanol are able to grow on certain rare earth elements as well as their radioactive relatives. These findings suggest a possible role for such bacteria in the decontamination of areas where actinides are spilled, or in the separation of lanthanides and actinides for analytical or preparative purposes, according to a study published in the journal Angewandte Chemie. For 191st time, SpaceX booster successfully returns after launch
 SpaceX on Sunday morning successfully deployed another batch of Starlink satellites into space and successfully landed its first-stage booster.
The Falcon 9 rocket with the satellites lifted off from the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station just after midnight, illuminating the night skies over Florida's central east coast.
The first-stage booster then returned to Earth and landed
SpaceX on Sunday morning successfully deployed another batch of Starlink satellites into space and successfully landed its first-stage booster.
The Falcon 9 rocket with the satellites lifted off from the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station just after midnight, illuminating the night skies over Florida's central east coast.
The first-stage booster then returned to Earth and landed "Tianzhou Express" is online again, with five highlights
 On May 10, 2023, the Tianzhou-6 cargo spacecraft was successfully launched aboard the Long March 7 Yaoqi carrier rocket from the Wenchang Space Launch Site in China at 21:22 Beijing time. Roughly ten minutes after the launch, the spacecraft separated from the rocket and entered its predetermined orbit, with the solar panels operating smoothly, marking the launch as a complete success. The follow
On May 10, 2023, the Tianzhou-6 cargo spacecraft was successfully launched aboard the Long March 7 Yaoqi carrier rocket from the Wenchang Space Launch Site in China at 21:22 Beijing time. Roughly ten minutes after the launch, the spacecraft separated from the rocket and entered its predetermined orbit, with the solar panels operating smoothly, marking the launch as a complete success. The follow Tidal shocks can light up the remains of a star being pulled apart by a black hole
 The Universe is a violent place where even the life of a star can be cut short. This occurs when a star finds itself in a "bad" neighbourhood, specifically near a supermassive black hole.
These black holes weigh millions or even billions of times the mass of the Sun and typically reside in the centres of quiet galaxies. As a star moves closer to the black hole, it experiences the ever-incr
The Universe is a violent place where even the life of a star can be cut short. This occurs when a star finds itself in a "bad" neighbourhood, specifically near a supermassive black hole.
These black holes weigh millions or even billions of times the mass of the Sun and typically reside in the centres of quiet galaxies. As a star moves closer to the black hole, it experiences the ever-incr 































