
Copernical Team
Space storms could cause chaos without forecast developments
 The world is unprepared for the next big storm from outer space, an overwhelming majority of scientists agree.
Nine in ten space weather experts said that without accurate forecasting of space weather, Earth would suffer serious damage to its infrastructure. Of the 144 scientists surveyed on the dangers of geomagnetic storms, just over half said current forecasting capabilities were not go
The world is unprepared for the next big storm from outer space, an overwhelming majority of scientists agree.
Nine in ten space weather experts said that without accurate forecasting of space weather, Earth would suffer serious damage to its infrastructure. Of the 144 scientists surveyed on the dangers of geomagnetic storms, just over half said current forecasting capabilities were not go Voyager 2 goes silent with a temporary communication interruption with Earth
 Amidst its epic journey into the cosmos, NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft has temporarily lost contact with the blue planet. An accidental deviation of the antenna's alignment on July 21 has caused an unexpected silence in the spacecraft's interstellar communications.
Voyager 2, nestled over 12.3 billion miles (19.9 billion kilometers) away from Earth, slightly misaligned its antenna by 2 degre
Amidst its epic journey into the cosmos, NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft has temporarily lost contact with the blue planet. An accidental deviation of the antenna's alignment on July 21 has caused an unexpected silence in the spacecraft's interstellar communications.
Voyager 2, nestled over 12.3 billion miles (19.9 billion kilometers) away from Earth, slightly misaligned its antenna by 2 degre Momentus completes payload deployment from vigoride-6 mission
 Momentus Inc. (NASDAQ: MNTS), the space technology firm, announced that it has successfully launched and deployed all payloads from its Vigoride-6 mission. The mission was carried out via the SpaceX Transporter-7 mission in April 2023.
Since last year, Momentus has had three successful missions, deploying a total of 15 customer satellites, along with placing three of its Vigoride Orbital S
Momentus Inc. (NASDAQ: MNTS), the space technology firm, announced that it has successfully launched and deployed all payloads from its Vigoride-6 mission. The mission was carried out via the SpaceX Transporter-7 mission in April 2023.
Since last year, Momentus has had three successful missions, deploying a total of 15 customer satellites, along with placing three of its Vigoride Orbital S Oxford researchers pioneer outer space machine learning model
 In an unprecedented move, a research team at the University of Oxford has successfully trained a machine learning model aboard a satellite in outer space. This groundbreaking achievement has the potential to significantly enhance the functionalities of remote-sensing satellites, making real-time monitoring and on-the-spot decision making possible for a host of applications.
Remote-sensing
In an unprecedented move, a research team at the University of Oxford has successfully trained a machine learning model aboard a satellite in outer space. This groundbreaking achievement has the potential to significantly enhance the functionalities of remote-sensing satellites, making real-time monitoring and on-the-spot decision making possible for a host of applications.
Remote-sensing JUPITER 3 set to revolutionize satellite connectivity across the Americas
 The successful deployment of Hughes Network Systems' JUPITER 3 ultra-high-density satellite, also known as EchoStar XXIV, has marked a significant leap forward in the field of satellite internet connectivity. The mission was carried out with the assistance of a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket, launching from the iconic Kennedy Space Center Launch Pad 39A in Florida.
The EchoStar subsidiary comm
The successful deployment of Hughes Network Systems' JUPITER 3 ultra-high-density satellite, also known as EchoStar XXIV, has marked a significant leap forward in the field of satellite internet connectivity. The mission was carried out with the assistance of a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket, launching from the iconic Kennedy Space Center Launch Pad 39A in Florida.
The EchoStar subsidiary comm Two supermoons in August mean double the stargazing fun

European wind-mapping satellite returned safely to Earth
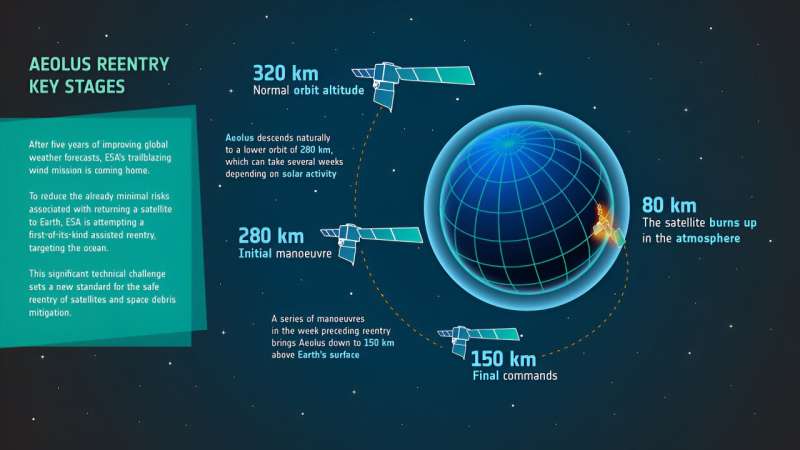
A European wind-mapping satellite has returned successfully to Earth following a delicate assisted return designed to minimize damage from flying debris, the European Space Agency said on Saturday.
It is the first time ESA's mission control had attempted an assisted re-entry through the planet's atmosphere.
The Aeolus satellite—named after the guardian of wind in Greek mythology—was launched in 2018 to measure Earth's global wind patterns, and thus improve both short-term weather forecasting and our understanding of man-made climate change.
"Surpassing scientific expectations and exceeding its planned life in orbit, the Aeolus wind mission has been hailed as one of ESA's most successful Earth observation missions," the agency said on its website.
"And now, its end will go down in history too, thanks to the ingenuity of the agency's mission control team, who guided this remarkable satellite down to Earth's atmosphere for a safe reentry."
The one-ton satellite re-entered the atmosphere above Antarctica at around 02:00 GMT on Saturday, after several days of complex maneuvers, it added.
These lowered its orbit from its operating altitude of 320 kilometers (200 miles) to 120 kilometers so it could re-enter the atmosphere and burn up safely.
The world's largest ComSat ever built launches on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket
 SpaceX's Falcon Heavy rocket, launched for the seventh time, was scheduled to lift off on July 26th at 11:04 p.m. EDT, a violation of abort criteria has forced the mission to be scrubbed with 1 minute and 5 seconds left on the clock.
The company had to delay the mission from July 27th "To complete vehicle checkouts".
Hughes Network Systems's Jupiter 3/EchoStar XXIV satellite launched
SpaceX's Falcon Heavy rocket, launched for the seventh time, was scheduled to lift off on July 26th at 11:04 p.m. EDT, a violation of abort criteria has forced the mission to be scrubbed with 1 minute and 5 seconds left on the clock.
The company had to delay the mission from July 27th "To complete vehicle checkouts".
Hughes Network Systems's Jupiter 3/EchoStar XXIV satellite launched Historic Aeolus reentry – how it happened
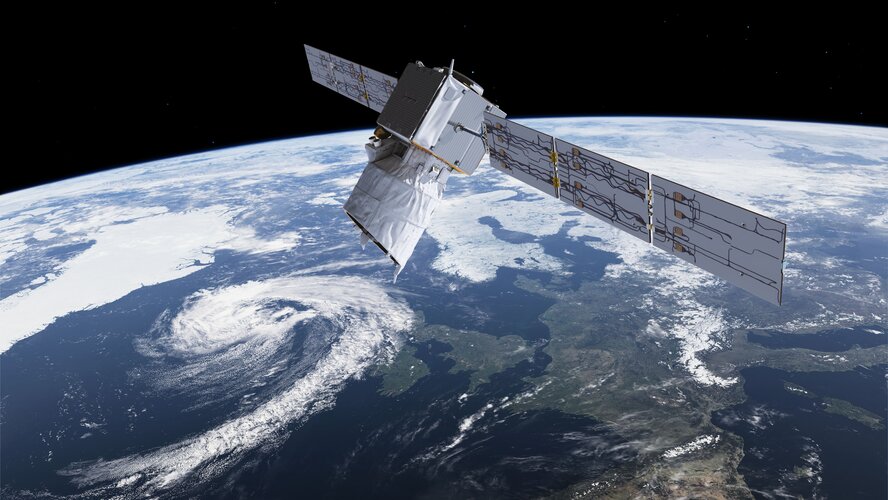

Historic Aeolus reentry – how it happened
Get rolling updates on the Aeolus reentry, on the Rocket Science blog
Aeolus: a historic end to a trailblazing mission
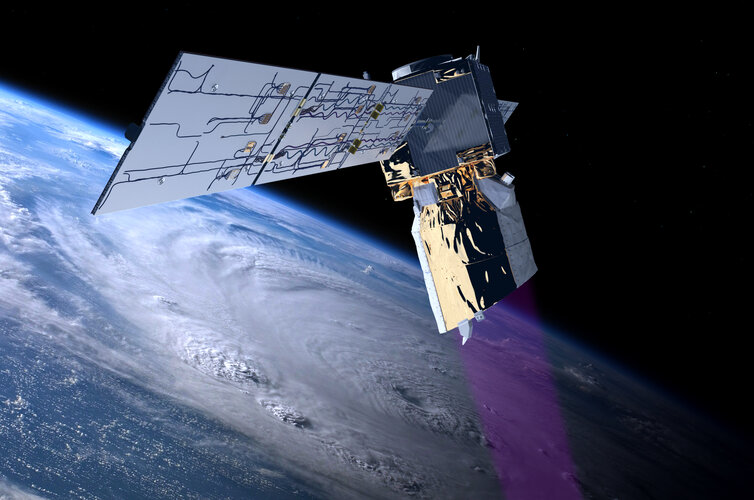

Surpassing scientific expectations and exceeding its planned life in orbit, the Aeolus wind mission has been hailed as one of ESA’s most successful Earth observation missions. And now, its end will go down in history too, thanks to the ingenuity of the Agency’s mission control team who guided this remarkable satellite down to Earth’s atmosphere for a safe reentry.
































