
Copernical Team
Purdue scientist among first to examine asteroid pieces from OSIRIS-REx mission
 To study the planets, someone has to go there: Either a human or a bot launches into space to physically explore other worlds. Scientists who study extraterrestrial materials can't usually bring their work home.
That's exactly what's happening this month, though, as NASA's OSIRIS-REx project brings home pieces of the asteroid Bennu.
The culmination of more than a decade of work by a
To study the planets, someone has to go there: Either a human or a bot launches into space to physically explore other worlds. Scientists who study extraterrestrial materials can't usually bring their work home.
That's exactly what's happening this month, though, as NASA's OSIRIS-REx project brings home pieces of the asteroid Bennu.
The culmination of more than a decade of work by a UFOs: What we will learn from the NASA panel investigating sightings
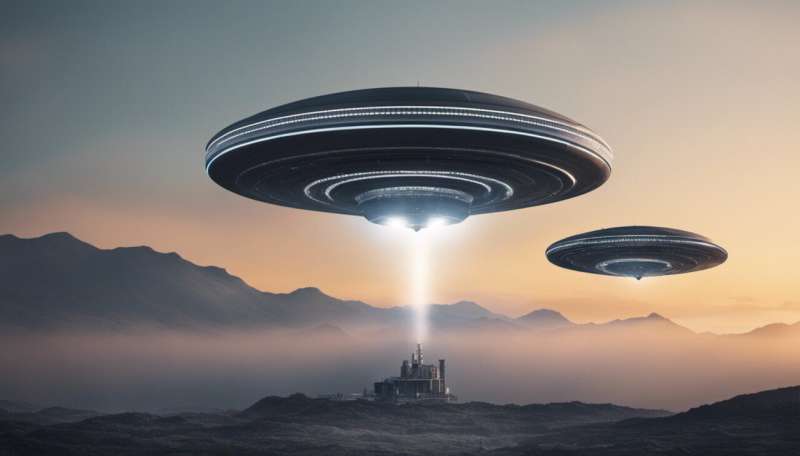

A committee set up by NASA has examined about 800 reports of unidentified anomalous phenomena (UAPs), or what most of us would call UFOs (unidentified flying objects). NASA defines these events as sightings "that cannot be identified as aircraft or known natural phenomena from a scientific perspective".
The creation of this committee shows that NASA is taking potential extraterrestrial events very seriously. On Wednesday, May 31 2023, the committee held its first public meeting to discuss what it is doing and what it has found so far, ahead of a full report later this year.
It revealed some reports are easy to explain as boats, planes or weather, some had comical, lunch-based origins, and only a few remain a mystery.
The committee is led by astrophysicist David Spergel and is made up of a team of experts ranging from university professors to a former astronaut. The study has been using declassified reports and images to try to explain some of the mysterious reports, which come from all sorts of sources including military personnel and commercial airline pilots.
Q&A: Decadal survey sets agenda for biological, physical sciences in space

The National Academies' latest decadal survey, "Thriving in Space," released Sept. 12, provides a roadmap for biological and physical sciences research, from the low orbit of Earth to the surface of Mars, through 2033.
Krystyn Van Vliet, vice president for research and innovation and a self-confessed "space geek," served as co-chair of the steering committee that produced the survey.
Van Vliet spoke with the Chronicle about her work on the project and its potential impact.
For the uninitiated, what is the decadal survey and why is it important?
Van Vliet: There are really two purposes. First, it's to give periodic input from the research community to the government as a signal for research priorities in the coming years. So it's a very science-driven effort where you gather input from people who have all kinds of interests and expertise and you say, "These are the big shots on goal that we should take as a country in the coming 10 years."
The second purpose is to develop a consensus report of a subset of that community, the steering committee that I co-chaired with Rob Ferl from the University of Florida, with input from hundreds of researchers who contributed input papers and dozens of people on the panels that worked on the report with us.
SpaceX test fires a Raptor engine, simulating a lunar landing
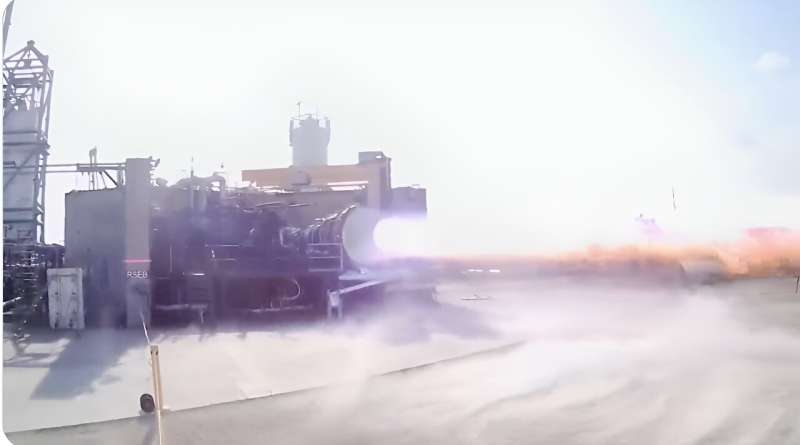

When NASA astronauts return to the surface of the moon in the Artemis III mission, the plan is to use a modified SpaceX Starship as their lunar lander. NASA announced last week that SpaceX has now demonstrated an important capability of the vacuum-optimized Raptor engine that will be used for the lander: an extreme cold start.
A test last month successfully confirmed the engine can be started in the frigid conditions of space, even when the vehicle has spent an extended time in space, where temperatures will drop lower than a shorter low-Earth orbit mission. The Raptor vacuum engine was chilled to mimic conditions after a long coast period in space, and then was successfully fired.
SpaceX has a video on X (formerly Twitter) showing the test firing.
NASA said that one challenge that differentiates Artemis missions from those in low Earth orbit is that the landers may sit in space without firing for an extended period of time, "causing the temperature of the hardware to drop to a level below what they would experience on a much shorter low Earth orbit mission.
Parker probe observes powerful coronal mass ejection 'vacuum up' interplanetary dust
On Sept. 5, 2022, NASA's Parker Solar Probe soared gracefully through one of the most powerful coronal mass ejections (CMEs) ever recorded—not only an impressive feat of engineering, but a huge boon for the scientific community.
Engineered compound shows promise in preventing bone loss in space

A study published in npj Microgravity, finds an engineered compound given to mice aboard the International Space Station (ISS) largely prevented the bone loss associated with time spent in space.
The study, led by a transdisciplinary team of professors at the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA) and the Forsyth Institute in Cambridge, Massachusetts, highlight a promising therapy to mitigate extreme bone loss from long-duration space travel as well as musculoskeletal degeneration on Earth.
Microgravity-induced bone loss has long been a critical concern for long-term space missions. Decreased mechanical loading due to microgravity induces bone loss at a rate 12-times greater than on Earth. Astronauts in low Earth orbit may experience bone loss up to 1% per month, endangering astronaut skeletal health and increasing risk for fractures during long-duration spaceflight and later in life.
The current mitigation strategy for bone loss relies on exercise-induced mechanical loading to promote bone formation but is far from perfect for crew members spending up to six months in microgravity.
Exercise does not always prevent bone loss, takes up valuable crew time, and may be contraindicated for certain types of injuries.
European space loses chief of Spaceport

With great sadness, we announce the passing of Daniel de Chambure on 16 September 2023 at the age of 61, after a short period of severe illness. His loss will be deeply felt by his many colleagues and friends at ESA and by the wider space community.
Sidus Space announces 180-Day extension on NASDAQ minimum pricing
 Sidus Space has been granted an additional 180 calendar days, or until March 11, 2024, (the "Second Compliance Period") to regain compliance with The Nasdaq Stock Market LLC ("NASDAQ").
On September 12, 2023, Sidus received a notification letter (the "Notification Letter") from the Listings Qualifications Department of NASDAQ. The Notification Letter states that, while Sidus has not regain
Sidus Space has been granted an additional 180 calendar days, or until March 11, 2024, (the "Second Compliance Period") to regain compliance with The Nasdaq Stock Market LLC ("NASDAQ").
On September 12, 2023, Sidus received a notification letter (the "Notification Letter") from the Listings Qualifications Department of NASDAQ. The Notification Letter states that, while Sidus has not regain Successful entry into service of Eutelsat Hotbird 13F and 13G satellites
 Eutelsat Communications (Euronext Paris: ETL) announces that its two high-power HOTBIRD 13F and HOTBIRD 13G satellites have entered into full commercial service. Located at Eutelsat's 13 degrees East flagship video neighbourhood, the satellites are reinforcing and enhancing the broadcast quality of around nine hundred television channels into more than 160 million homes across Europe, Northern A
Eutelsat Communications (Euronext Paris: ETL) announces that its two high-power HOTBIRD 13F and HOTBIRD 13G satellites have entered into full commercial service. Located at Eutelsat's 13 degrees East flagship video neighbourhood, the satellites are reinforcing and enhancing the broadcast quality of around nine hundred television channels into more than 160 million homes across Europe, Northern A Mapping the Sun's Interaction with Mercury's Surface
 A new study maps the infall of protons and electrons from the solar wind to geographical location on the surface of Mercury, giving scientists new insight into how interactions with the Sun alters the surface and produces Mercury's very thin atmosphere.
"Studies that have examined the infall of protons and electrons from the solar wind typically map the infall to the surface in terms of ti
A new study maps the infall of protons and electrons from the solar wind to geographical location on the surface of Mercury, giving scientists new insight into how interactions with the Sun alters the surface and produces Mercury's very thin atmosphere.
"Studies that have examined the infall of protons and electrons from the solar wind typically map the infall to the surface in terms of ti 






























