Copernical Team
Direct-to-device satellite connectivity trial successfully conducted in India by Viasat and BSNL
 Viasat, Inc. (NASDAQ: VSAT), a leader in satellite communications, has announced the first successful demonstration of direct-to-device satellite connectivity in India, in partnership with BSNL, the country's telecom provider.
The trial took place at the India Mobile Congress, one of Asia's largest technology events, where Viasat showcased satellite-powered two-way messaging services. The
Viasat, Inc. (NASDAQ: VSAT), a leader in satellite communications, has announced the first successful demonstration of direct-to-device satellite connectivity in India, in partnership with BSNL, the country's telecom provider.
The trial took place at the India Mobile Congress, one of Asia's largest technology events, where Viasat showcased satellite-powered two-way messaging services. The Gilat wins $15 Million in satellite communications orders
 Gilat Satellite Networks Ltd. (Nasdaq: GILT, TASE: GILT), a global leader in satellite networking solutions, has secured around $15 million in orders from major satellite operators. The orders cover the company's advanced communication systems designed for GEO, MEO, and LEO satellite constellations, with delivery planned over the next 18 months.
The new contracts emphasize Gilat's strong p
Gilat Satellite Networks Ltd. (Nasdaq: GILT, TASE: GILT), a global leader in satellite networking solutions, has secured around $15 million in orders from major satellite operators. The orders cover the company's advanced communication systems designed for GEO, MEO, and LEO satellite constellations, with delivery planned over the next 18 months.
The new contracts emphasize Gilat's strong p China sets ambitious space science development goals through 2050
 China has launched its first medium- and long-term space science development plan, outlining a comprehensive roadmap through 2050 aimed at establishing the country as a leading space science power.
The development plan was introduced on Tuesday at a press conference held by the State Council Information Office and jointly released by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, China National Space Ad
China has launched its first medium- and long-term space science development plan, outlining a comprehensive roadmap through 2050 aimed at establishing the country as a leading space science power.
The development plan was introduced on Tuesday at a press conference held by the State Council Information Office and jointly released by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, China National Space Ad Contract secures build for ESA's Harmony mission
 ESA has awarded a contract valued at over euro 280 million to OHB in Germany to construct two Harmony Earth Explorer satellites. The mission aims to deliver important new data about Earth's dynamic systems, including land surface changes from seismic and volcanic activities, as well as glacier movements. Additionally, it will provide insights into the interactions between the ocean and atmosphe
ESA has awarded a contract valued at over euro 280 million to OHB in Germany to construct two Harmony Earth Explorer satellites. The mission aims to deliver important new data about Earth's dynamic systems, including land surface changes from seismic and volcanic activities, as well as glacier movements. Additionally, it will provide insights into the interactions between the ocean and atmosphe Ciseres AI satellites aim to revolutionize disaster response
 This week, the European Space Agency (ESA) launched the Ciseres project at the International Aeronautics Congress in Milan. Ciseres is a small satellite mission designed to speed up emergency response times by employing artificial intelligence (AI). As part of ESA's Civil Security from Space (CSS) initiative, the project aims to deliver critical updates to first responders and government officia
This week, the European Space Agency (ESA) launched the Ciseres project at the International Aeronautics Congress in Milan. Ciseres is a small satellite mission designed to speed up emergency response times by employing artificial intelligence (AI). As part of ESA's Civil Security from Space (CSS) initiative, the project aims to deliver critical updates to first responders and government officia Sidus Space receives FCC approval to expand satellite constellation in Low Earth Orbit
 Sidus Space, Inc. (NASDAQ: SIDU) announced that it has secured approval from the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to operate a micro constellation of remote sensing satellites in Low Earth Orbit (LEO). This regulatory clearance marks a significant step forward in the company's plan to broaden its orbital presence and provide versatile, cost-efficient data acquisition services through
Sidus Space, Inc. (NASDAQ: SIDU) announced that it has secured approval from the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to operate a micro constellation of remote sensing satellites in Low Earth Orbit (LEO). This regulatory clearance marks a significant step forward in the company's plan to broaden its orbital presence and provide versatile, cost-efficient data acquisition services through HydRON: Optical (laser-based) satellites for faster data sharing in space
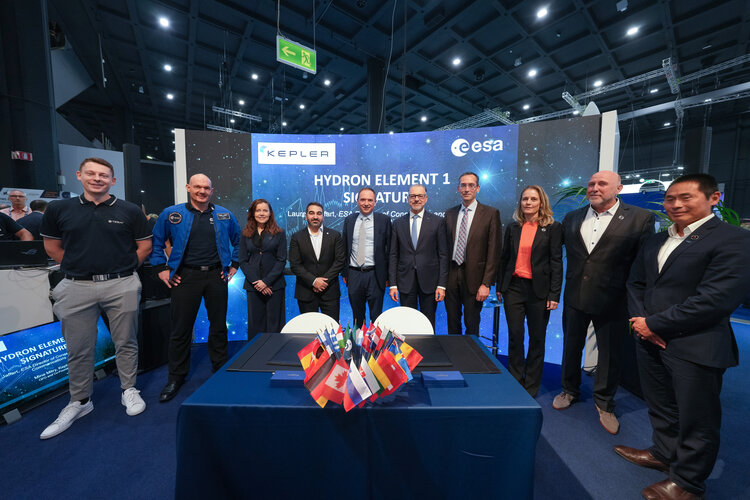

At the International Astronautical Congress (IAC) in Milan this week, ESA signed a contract for Element #1, the first phase of the HydRON Demonstration System. HydRON, which stands for High thRoughput Optical Network, is set to transform the way data-collecting satellites communicate, using laser technology that will allow satellites to connect with each other and ground networks much faster.
Zoom into the first page of ESA Euclid's great cosmic atlas
 On 15 October 2024, ESA's Euclid space mission unveiled the first segment of its vast cosmic map, showcasing millions of stars and galaxies.
Presented at the International Astronautical Congress in Milan, Italy, by ESA's Director General Josef Aschbacher and Director of Science Carole Mundell, this initial section is an impressive 208-gigapixel mosaic. Compiled from 260 observations conduc
On 15 October 2024, ESA's Euclid space mission unveiled the first segment of its vast cosmic map, showcasing millions of stars and galaxies.
Presented at the International Astronautical Congress in Milan, Italy, by ESA's Director General Josef Aschbacher and Director of Science Carole Mundell, this initial section is an impressive 208-gigapixel mosaic. Compiled from 260 observations conduc Sun reaches maximum phase in 11-Year Solar Cycle
 In a teleconference with reporters on Tuesday, representatives from NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and the international Solar Cycle Prediction Panel announced that the Sun has reached its solar maximum period, which could continue for the next year.
The solar cycle is a natural cycle the Sun goes through as it transitions between low and high magnetic ac
In a teleconference with reporters on Tuesday, representatives from NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and the international Solar Cycle Prediction Panel announced that the Sun has reached its solar maximum period, which could continue for the next year.
The solar cycle is a natural cycle the Sun goes through as it transitions between low and high magnetic ac NASA launches coding competition to organize solar eclipse images
 NASA is launching a coding competition to get some much-needed help with organizing images from April's solar eclipse for the 2024 Eclipse Megamovie project.
"Thanks to the efforts of over 145 citizen scientists, more than 1 terabyte of photographs were collected and are now being analyzed," NASA said. "These images will help scientists track disappearing jets and plumes, shedding light
NASA is launching a coding competition to get some much-needed help with organizing images from April's solar eclipse for the 2024 Eclipse Megamovie project.
"Thanks to the efforts of over 145 citizen scientists, more than 1 terabyte of photographs were collected and are now being analyzed," NASA said. "These images will help scientists track disappearing jets and plumes, shedding light