Copernical Team
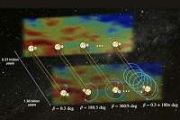
Spooky Earths seen by Hera’s HyperScout
 Image:
Spooky Earths seen by Hera’s HyperScout
Image:
Spooky Earths seen by Hera’s HyperScout Gateway HALO unit to support vital space science on lunar missions
 Stephanie Dudley, who leads mission integration and utilization for NASA's Gateway, is at the forefront of merging human space exploration and science aboard the upcoming lunar orbiting outpost. Set to serve as humanity's first space station orbiting the Moon, Gateway will offer a platform for astronauts to live, perform experiments, and prepare for extended missions, particularly targeting the
Stephanie Dudley, who leads mission integration and utilization for NASA's Gateway, is at the forefront of merging human space exploration and science aboard the upcoming lunar orbiting outpost. Set to serve as humanity's first space station orbiting the Moon, Gateway will offer a platform for astronauts to live, perform experiments, and prepare for extended missions, particularly targeting the China progresses in full-scale efforts for manned Moon landing by 2030
 China is accelerating its mission to place astronauts on the Moon by 2030, with substantial progress across development, testing, and infrastructure construction. In a recent press briefing, the China Manned Space Agency (CMSA) detailed the work underway to achieve this ambitious lunar objective, highlighting both technical advancements and testing milestones.
CMSA's strategy involves depl
China is accelerating its mission to place astronauts on the Moon by 2030, with substantial progress across development, testing, and infrastructure construction. In a recent press briefing, the China Manned Space Agency (CMSA) detailed the work underway to achieve this ambitious lunar objective, highlighting both technical advancements and testing milestones.
CMSA's strategy involves depl AXIS mission selected as NASA Astrophysics Probe competition finalist
 The MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research (MKI) is a project lead for one of two finalist missions recently selected for NASA's new Probe Explorers program. Working with collaborators at the University of Maryland and Goddard Space Flight Research Center, the team will produce a one-year concept study to launch the Advanced X-ray Imaging Satellite (AXIS) in 2032.
Erin Kar
The MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research (MKI) is a project lead for one of two finalist missions recently selected for NASA's new Probe Explorers program. Working with collaborators at the University of Maryland and Goddard Space Flight Research Center, the team will produce a one-year concept study to launch the Advanced X-ray Imaging Satellite (AXIS) in 2032.
Erin Kar Axient secures contract for Resilient GPS Constellation under USSF Initiative
 Axient, now operating under Astrion following its recent acquisition, has received a Performer Agreement through an Other Transaction Agreement (OTA) established between the Space Enterprise Consortium (SpEC) and Space Systems Command. This contract supports the U.S. Space Force's mission by advancing a next-generation Resilient GPS (R-GPS) satellite constellation, designed to enhance space infr
Axient, now operating under Astrion following its recent acquisition, has received a Performer Agreement through an Other Transaction Agreement (OTA) established between the Space Enterprise Consortium (SpEC) and Space Systems Command. This contract supports the U.S. Space Force's mission by advancing a next-generation Resilient GPS (R-GPS) satellite constellation, designed to enhance space infr Aerodata earns EASA certification for GPS anti-jamming and anti-spoofing tech
 Aerodata AG has secured a Supplemental Type Certificate (STC) from the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) for its GPS Anti-Jamming and Anti-Spoofing system. This newly certified technology is compatible with Garmin 5000 avionics and is installed in Cessna Citation Latitude aircraft.
In response to the rising risk of GPS jamming and spoofing affecting civil and military aviation,
Aerodata AG has secured a Supplemental Type Certificate (STC) from the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) for its GPS Anti-Jamming and Anti-Spoofing system. This newly certified technology is compatible with Garmin 5000 avionics and is installed in Cessna Citation Latitude aircraft.
In response to the rising risk of GPS jamming and spoofing affecting civil and military aviation, SwRI unveils new facility for advanced EMC EMI testing for spacecraft
 Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) has expanded its Space System Spacecraft and Payload Processing Facility with a newly installed semi-anechoic shielded chamber dedicated to spacecraft electromagnetic compatibility and interference (EMC/EMI) testing. This addition marks an essential advancement in SwRI's strategy to offer a fully integrated spacecraft test and processing center within its 74,0
Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) has expanded its Space System Spacecraft and Payload Processing Facility with a newly installed semi-anechoic shielded chamber dedicated to spacecraft electromagnetic compatibility and interference (EMC/EMI) testing. This addition marks an essential advancement in SwRI's strategy to offer a fully integrated spacecraft test and processing center within its 74,0 New 3D printed metal alloy enhances durability for space exploration
 The research team at Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS), led by Dr. Jeong Min Park of the Nano Materials Research Division, has developed a highly durable metal 3D-printed alloy designed to meet the demands of space exploration. Collaborating with Professor Jung Gi Kim of Gyeongsang National University and Professor Hyoung Seop Kim of POSTECH, the team created an alloy optimized for the
The research team at Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS), led by Dr. Jeong Min Park of the Nano Materials Research Division, has developed a highly durable metal 3D-printed alloy designed to meet the demands of space exploration. Collaborating with Professor Jung Gi Kim of Gyeongsang National University and Professor Hyoung Seop Kim of POSTECH, the team created an alloy optimized for the GomSpace selected by Proteus Space to support AI-designed satellite mission
 GomSpace North America has been awarded a $250,000 (2.6 MSEK) contract to provide critical components and technical expertise for an ambitious new satellite mission led by Proteus Space. The mission aims to establish a world record in satellite design, assembly, and testing speed, enabled by Proteus Space's innovative AI-driven design platform, MERCURY.
Proteus Space, recognized for its ad
GomSpace North America has been awarded a $250,000 (2.6 MSEK) contract to provide critical components and technical expertise for an ambitious new satellite mission led by Proteus Space. The mission aims to establish a world record in satellite design, assembly, and testing speed, enabled by Proteus Space's innovative AI-driven design platform, MERCURY.
Proteus Space, recognized for its ad Illuminating ancient origins of 4BN year-old Asteroid Ryugu
 Researchers at the Advanced Photon Source (APS) recently participated in an international study of fragments from asteroid 162173 Ryugu, collected by a Japanese space mission. The APS, a light source facility operated by the Department of Energy, employed Mossbauer spectroscopy - a technique uniquely suited to studying small samples - on specks of dust from Ryugu. The results revealed that the a
Researchers at the Advanced Photon Source (APS) recently participated in an international study of fragments from asteroid 162173 Ryugu, collected by a Japanese space mission. The APS, a light source facility operated by the Department of Energy, employed Mossbauer spectroscopy - a technique uniquely suited to studying small samples - on specks of dust from Ryugu. The results revealed that the a