
Copernical Team
'Many will follow': SpaceX sends all-civilian crew into orbit
 A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying four space tourists blasted off Wednesday night from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the first mission to orbit the globe with an all-civilian crew.
A huge fireball illuminated the sky as the rocket's nine engines began to pull away from Earth at 8:02 pm (0002 GMT Thursday).
Around 12 minutes later, the Dragon capsule separated from the rocket's
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying four space tourists blasted off Wednesday night from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the first mission to orbit the globe with an all-civilian crew.
A huge fireball illuminated the sky as the rocket's nine engines began to pull away from Earth at 8:02 pm (0002 GMT Thursday).
Around 12 minutes later, the Dragon capsule separated from the rocket's Affordable housing in outer space: Scientists develop cosmic concrete from space dust and astronaut blood
 Transporting a single brick to Mars can cost more than a million British pounds - making the future construction of a Martian colony seem prohibitively expensive. Scientists at The University of Manchester have now developed a way to potentially overcome this problem, by creating a concrete-like material made of extra-terrestrial dust along with the blood, sweat and tears of astronauts.
In
Transporting a single brick to Mars can cost more than a million British pounds - making the future construction of a Martian colony seem prohibitively expensive. Scientists at The University of Manchester have now developed a way to potentially overcome this problem, by creating a concrete-like material made of extra-terrestrial dust along with the blood, sweat and tears of astronauts.
In A gem of a lab will bring the world of quantum physics into the light
 The novel design for a next-generation diamond sensor with capabilities that range from producing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of single molecules to detecting slight anomalies in the Earth's magnetic field to guide aircraft that lack access to global positioning systems (GPS) will be developed by a collaboration of scientists led by the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Princeton Plasma Phy
The novel design for a next-generation diamond sensor with capabilities that range from producing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of single molecules to detecting slight anomalies in the Earth's magnetic field to guide aircraft that lack access to global positioning systems (GPS) will be developed by a collaboration of scientists led by the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Princeton Plasma Phy NASA Lab studies sleepiness and use of automated systems
 Drowsy driving accounts for a large proportion of car crashes, according to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. So, you might think self-driving cars would fix that. After all, computers just don't get sleepy.
But today's vehicles are only partially automated, requiring the human driver to stay alert, monitor the road, and take over at a moment's notice. A new study conduct
Drowsy driving accounts for a large proportion of car crashes, according to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. So, you might think self-driving cars would fix that. After all, computers just don't get sleepy.
But today's vehicles are only partially automated, requiring the human driver to stay alert, monitor the road, and take over at a moment's notice. A new study conduct Chinese astronauts complete three-month space mission
 Three Chinese astronauts have completed the country's longest crewed mission and started their journey home on Thursday after 90 days at the Tiangong space station conducting spacewalks and scientific experiments.
"The Shenzhou-12 manned spacecraft has successfully separated from the space station's core module," state broadcaster CCTV said Thursday.
The mission was part of China's heavi
Three Chinese astronauts have completed the country's longest crewed mission and started their journey home on Thursday after 90 days at the Tiangong space station conducting spacewalks and scientific experiments.
"The Shenzhou-12 manned spacecraft has successfully separated from the space station's core module," state broadcaster CCTV said Thursday.
The mission was part of China's heavi SpaceX Inspiration4 lifts off on first all-civilian orbital mission
 The SpaceX mission Inspiration4 - the first all-private orbital spaceflight - lifted off from Florida on Wednesday night, carrying four civilians led by philanthropist and pilot Jared Isaacman.
The Falcon 9 rocket carried the Crew Dragon capsule into a mostly clear night sky as planned at 8:02 p.m. EDT from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center.
"The Inspiration 4 have lif
The SpaceX mission Inspiration4 - the first all-private orbital spaceflight - lifted off from Florida on Wednesday night, carrying four civilians led by philanthropist and pilot Jared Isaacman.
The Falcon 9 rocket carried the Crew Dragon capsule into a mostly clear night sky as planned at 8:02 p.m. EDT from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center.
"The Inspiration 4 have lif Quest airlock | Space Station 360 (in French with English subtitles available)
 Video:
00:01:34
Video:
00:01:34
ESA astronaut Thomas Pesquet takes you on a tour of the International Space Station like no other. Filmed with a 360 camera, the Space Station 360 series lets you explore for yourself alongside Thomas’s explanation – episode four is NASA’s Quest airlock.
The Quest airlock is the Station’s smallest module, but it is vital for going on spacewalks. This is where the astronauts suit up into their spacesuits, prepare for the spacewalk and enter the airlock to go outside for maintenance, installing new equipment or science experiments.
Follow Thomas: https://blogs.esa.int/exploration/it/category/astronauts/thomas-pesquet/
The video is in French, to activate the English
3 crew leave China's space station for Earth after 90 days

Three astronauts who lived for 90 days on China's space station departed Thursday in preparation for returning to Earth.
The national space agency said Nie Haisheng, Liu Boming and Tang Hongbo boarded the Shenzhou-12 spacecraft and undocked from the space station at 8:56 a.m. Thursday (0056 GMT).
State broadcaster CCTV aired footage of the astronauts securing packages inside their spacecraft, which is due to parachute to a location in the Gobi Desert near the Jiuquan launch center on Friday.
What’s going on with the ozone?
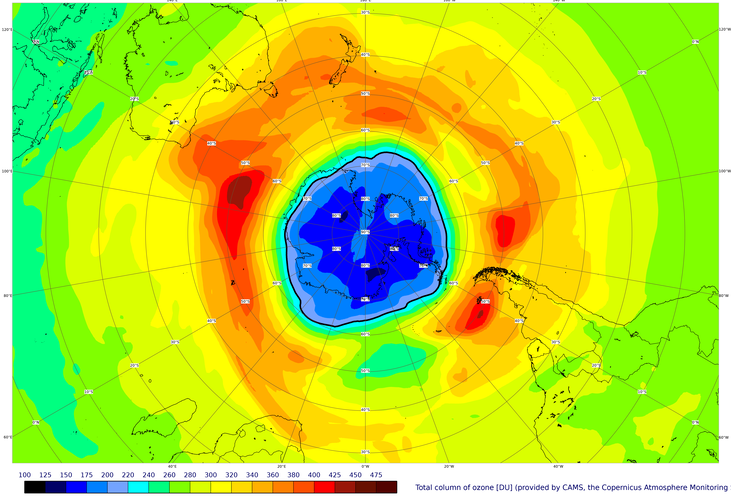
World governments agreed in the late 1980s to protect Earth’s ozone layer by phasing out ozone-depleting substances emitted by human activities, under the Montreal Protocol. The phase out of these substances has not only helped protect the ozone layer for future generations but has also protected human health and ecosystems by limiting the harmful ultraviolet radiation from reaching Earth. On 16 September, the International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone Layer, we take a closer look at this year’s ozone hole.
 Image:
To the Moon!
Image:
To the Moon! 






























