Copernical Team
Week in images: 15 - 19 November 2021
Week in images: 15 - 19 November 2021
Discover our week through the lens
Rocky roads through Lanzarote
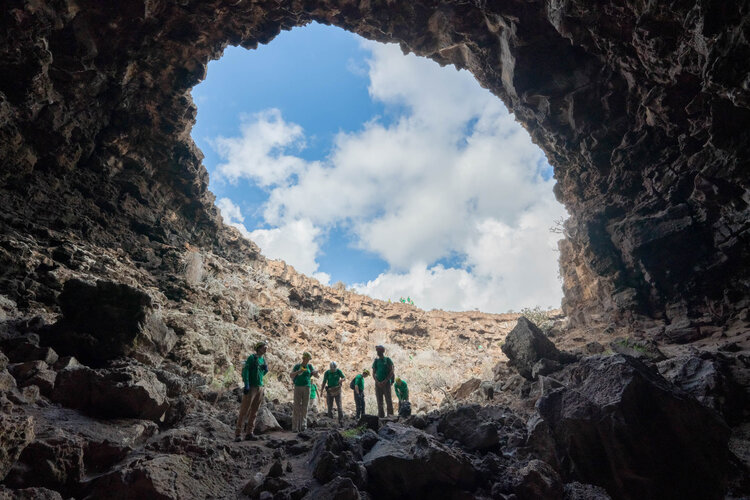 Image:
Image:
Take away the clouds, bulk up the humans with suits and add an orange-red filter and this could be an image from a future mission to Mars.
The actual site, the Corona lava tube in Lanzarote, Spain, is closer than one might think to the Red Planet.
That’s why participants of ESA’s Pangaea course came here this week for the third session of their planetary geology training.
ESA astronaut Andreas Mogensen, ESA engineer Robin Eccleston and NASA astronaut Kathleen Rubins are this year’s students learning from geologists how to best explore the Moon and Mars right here on Earth.
Before ending up in
Space dust presents opportunities, challenges as Parker Solar Probe speeds towards Sun
 Propelled by a recent swing past Venus, NASA's Parker Solar Probe is healthy and performing normally as it heads toward its next closest approach to the Sun on Nov. 21.
Parker Solar Probe will break its own distance and speed records on that approach - the 10th of 24 planned, progressively closer trips around the Sun - when it comes about 5.3 million miles (8.5 million kilometers) from the
Propelled by a recent swing past Venus, NASA's Parker Solar Probe is healthy and performing normally as it heads toward its next closest approach to the Sun on Nov. 21.
Parker Solar Probe will break its own distance and speed records on that approach - the 10th of 24 planned, progressively closer trips around the Sun - when it comes about 5.3 million miles (8.5 million kilometers) from the "Alien" invasions and the need for planetary biosecurity
 The era of space exploration brings with it a new risk: invasion. The peril comes not from little green men arriving on flying saucers but, rather, from microbiological contamination of Earth from extraterrestrial environments and vice versa. Writing in BioScience, Anthony Ricciardi, of McGill University, and colleagues describe the dangers posed by such organisms and outline an approach to addr
The era of space exploration brings with it a new risk: invasion. The peril comes not from little green men arriving on flying saucers but, rather, from microbiological contamination of Earth from extraterrestrial environments and vice versa. Writing in BioScience, Anthony Ricciardi, of McGill University, and colleagues describe the dangers posed by such organisms and outline an approach to addr Alien organisms - hitchhikers of the galaxy
 Scientists warn, without good biosecurity measures 'alien organisms' on Earth may become a reality stranger than fiction.
Published in international journal BioSciences, a team of scientists, including Dr Phill Cassey, Head of the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at the University of Adelaide, are calling for greater recognition of the biosecurity risks ahead of the space ind
Scientists warn, without good biosecurity measures 'alien organisms' on Earth may become a reality stranger than fiction.
Published in international journal BioSciences, a team of scientists, including Dr Phill Cassey, Head of the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at the University of Adelaide, are calling for greater recognition of the biosecurity risks ahead of the space ind The worlds next door: Looking for habitable planets around Alpha Centauri
 A mission to discover new planets potentially capable of sustaining life around Earth's nearest neighbor, Alpha Centauri, was announced this week by Sydney University.
The proposed telescope project will look for planets in the 'Goldilocks' zone around the star system just four light years away, where temperatures could allow for liquid surface water on rocky planets.
Work on the pro
A mission to discover new planets potentially capable of sustaining life around Earth's nearest neighbor, Alpha Centauri, was announced this week by Sydney University.
The proposed telescope project will look for planets in the 'Goldilocks' zone around the star system just four light years away, where temperatures could allow for liquid surface water on rocky planets.
Work on the pro Curiosity continues to dine on Zechstein drill fines
 The SAM and CheMin instrument teams decided that they did not require further analyses of the "Zechstein" drill sample. It is the turn of the arm-mounted MAHLI and APXS instruments to have their taste of the drilled fines. The Zechstein sample held within the drill bit assembly will be dumped out onto the ground, imaged by MAHLI and then analyzed by APXS to determine the composition.
The c
The SAM and CheMin instrument teams decided that they did not require further analyses of the "Zechstein" drill sample. It is the turn of the arm-mounted MAHLI and APXS instruments to have their taste of the drilled fines. The Zechstein sample held within the drill bit assembly will be dumped out onto the ground, imaged by MAHLI and then analyzed by APXS to determine the composition.
The c Ingenuity makes short hop to the north for Flight 16
 With Flight 15, Ingenuity began the journey back towards "Wright Brothers Field" at "Octavia E. Butler Landing," the site where Perseverance touched down with Ingenuity in February. This flight was performed with the recently-increased rotor speed of 2,700 rpm. After reviewing the data from Flight 15, the Ingenuity team is prepared to attempt our Flight 16 no earlier than Thursday, Nov. 18.
With Flight 15, Ingenuity began the journey back towards "Wright Brothers Field" at "Octavia E. Butler Landing," the site where Perseverance touched down with Ingenuity in February. This flight was performed with the recently-increased rotor speed of 2,700 rpm. After reviewing the data from Flight 15, the Ingenuity team is prepared to attempt our Flight 16 no earlier than Thursday, Nov. 18. Highly specialized team to design vehicle for sustainable lunar surface mobility operations
 Northrop Grumman, is teaming up with AVL, Intuitive Machines, Lunar Outpost, and Michelin to design a Lunar Terrain Vehicle (LTV) to transport NASA's Artemis astronauts around the lunar surface. This team provides multi-disciplinary expertise that is ready to deliver an innovative solution to NASA for lunar surface mobility.
"Together with our teammates, we will provide NASA with an agile
Northrop Grumman, is teaming up with AVL, Intuitive Machines, Lunar Outpost, and Michelin to design a Lunar Terrain Vehicle (LTV) to transport NASA's Artemis astronauts around the lunar surface. This team provides multi-disciplinary expertise that is ready to deliver an innovative solution to NASA for lunar surface mobility.
"Together with our teammates, we will provide NASA with an agile Twin of NASA's Perseverance Mars rover begins terrain tests
 OPTIMISM, the full-scale engineering model of Perseverance, begins a series of rigorous tests to assess the risk of potential driving hazards on the surface of the Red Planet.
On a recent day in November, the car-size rover rolled slowly forward, then stopped, perched on the threshold of a Martian landscape. But this rover, named OPTIMISM, wasn't on the Red Planet. And the landscape was a
OPTIMISM, the full-scale engineering model of Perseverance, begins a series of rigorous tests to assess the risk of potential driving hazards on the surface of the Red Planet.
On a recent day in November, the car-size rover rolled slowly forward, then stopped, perched on the threshold of a Martian landscape. But this rover, named OPTIMISM, wasn't on the Red Planet. And the landscape was a