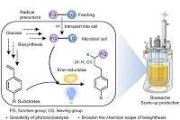
Copernical Team
US Army tests multi-orbit solutions leveraging MEO capabilities amid SES's upcoming O3b mPOWER launch
 SES Government Solutions (SES GS), a wholly-owned subsidiary of SES, supports the U.S. Army in conducting a series of cutting-edge trials and testing of commercial satellite constellations in multiple orbits, as well as services and ground terminals, in the U.S. Government's effort to establish Multi-Domain Operations (MDO) by 2028.
Most recently, the U.S. Army announced its integrated gro
SES Government Solutions (SES GS), a wholly-owned subsidiary of SES, supports the U.S. Army in conducting a series of cutting-edge trials and testing of commercial satellite constellations in multiple orbits, as well as services and ground terminals, in the U.S. Government's effort to establish Multi-Domain Operations (MDO) by 2028.
Most recently, the U.S. Army announced its integrated gro Space Force mission blasts off from Florida after multiple delays
 A mission overseen by the U.S. Space Force to send equipment into space aboard an Atlas V rocket lifted off from Florida early Tuesday after a delay of several days.
United Launch Alliance sent the Space Test Program-3 (STP-3) mission into space from Launch Complex 41 at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at about 5:19 a.m. EST Tuesday.
The mission lifted off carry
A mission overseen by the U.S. Space Force to send equipment into space aboard an Atlas V rocket lifted off from Florida early Tuesday after a delay of several days.
United Launch Alliance sent the Space Test Program-3 (STP-3) mission into space from Launch Complex 41 at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at about 5:19 a.m. EST Tuesday.
The mission lifted off carry Oculus Observatory set to disrupt space situational awareness globally
 The 'Oculus Observatory' is a new kind of space observatory, designed, built, and managed by Silentium Defence, which delivers the widest field of view, and the most cost-effective monitoring of objects in orbit, anywhere in the world.
Opened today, by Head of the Australian Space Agency, Enrico Palermo, 'Oculus' is located on the fringe of South Australia's dark sky reserve in the Mid-Mur
The 'Oculus Observatory' is a new kind of space observatory, designed, built, and managed by Silentium Defence, which delivers the widest field of view, and the most cost-effective monitoring of objects in orbit, anywhere in the world.
Opened today, by Head of the Australian Space Agency, Enrico Palermo, 'Oculus' is located on the fringe of South Australia's dark sky reserve in the Mid-Mur Europe opens up a new space to commercial services

ESA is calling on industry to come forward with ideas for crew and cargo transportation, operations, payloads, research, living quarters and even astronaut training. All of this could develop into new services in an effort to enlarge the space ecosystem to the commercial sphere.
NASA Launches New Mission to Explore Universe’s Most Dramatic Objects
 NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) mission launched at 1 a.m. EST Thursday on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) mission launched at 1 a.m. EST Thursday on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A Saarland space feast sprinkled with science
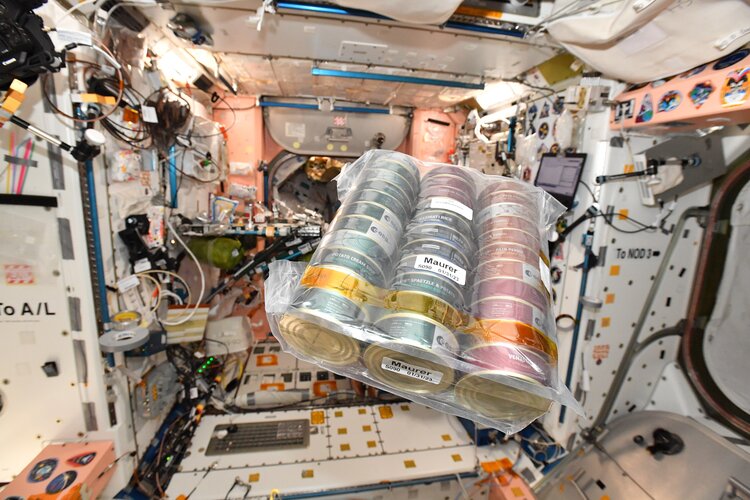

European food has always been out of this world, but this week ESA astronaut Matthias Maurer shared a taste of his home region, Saarland – with a serving of science – during a space-based Saint Nicholas feast.
Blood disc for astronaut diagnosis
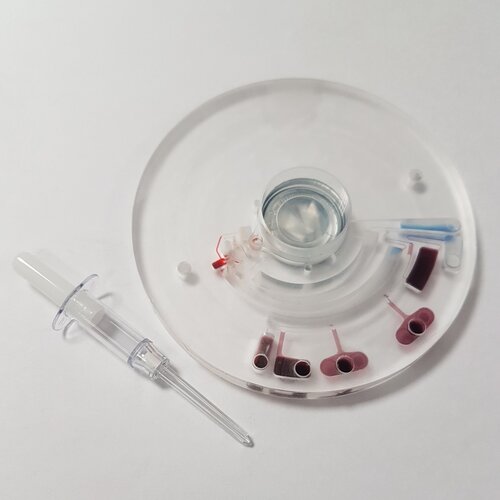 Image:
Blood disc for astronaut diagnosis
Image:
Blood disc for astronaut diagnosis Astronomers find final missing piece of galaxy cluster collision puzzle
 Astronomers have a model of how galaxy cluster collisions go through different stages, taking on various shapes. A blunt body shape turns into a sharp cone, which turns into a tongue-like shape. The first and last have been observed many times, but the sharp cone was always missing. Until now. Publication in Astronomy and Astrophysics.
Most galaxies live in clusters: groups of hundreds or
Astronomers have a model of how galaxy cluster collisions go through different stages, taking on various shapes. A blunt body shape turns into a sharp cone, which turns into a tongue-like shape. The first and last have been observed many times, but the sharp cone was always missing. Until now. Publication in Astronomy and Astrophysics.
Most galaxies live in clusters: groups of hundreds or New technique reveals the age of massive Southern Cross star
 An international team of astronomers from Australia, the United States and Europe has for the first-time unlocked the interior structure of Beta Crucis - a bright blue giant star that features on the flags of Australia, Brazil, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea and Samoa.
With an entirely new approach, the team led by Dr Daniel Cotton, found the star to be 14.5 times as massive as the Sun and
An international team of astronomers from Australia, the United States and Europe has for the first-time unlocked the interior structure of Beta Crucis - a bright blue giant star that features on the flags of Australia, Brazil, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea and Samoa.
With an entirely new approach, the team led by Dr Daniel Cotton, found the star to be 14.5 times as massive as the Sun and Simulated Webb Images of Quasar and Galaxy Surrounding Quasar
 Very distant, active supermassive black holes are the brightest beacons in the universe. Known as quasars, these behemoths are surrounded by equally distant galaxies. In recent decades, researchers have gone on a cosmic treasure hunt and identified the three most distant quasars known over the last three years - each more than 13 billion light-years from Earth. Astronomers theorize that it can t
Very distant, active supermassive black holes are the brightest beacons in the universe. Known as quasars, these behemoths are surrounded by equally distant galaxies. In recent decades, researchers have gone on a cosmic treasure hunt and identified the three most distant quasars known over the last three years - each more than 13 billion light-years from Earth. Astronomers theorize that it can t