Copernical Team
ESA Highlights: images and achievements from 2021

ESA Highlights: images and achievements from 2021
ESA Highlights 2021 is available online in this interactive format, which can be read on your desktop computer, laptop, tablet or phone.
Double drop test success for ExoMars parachutes
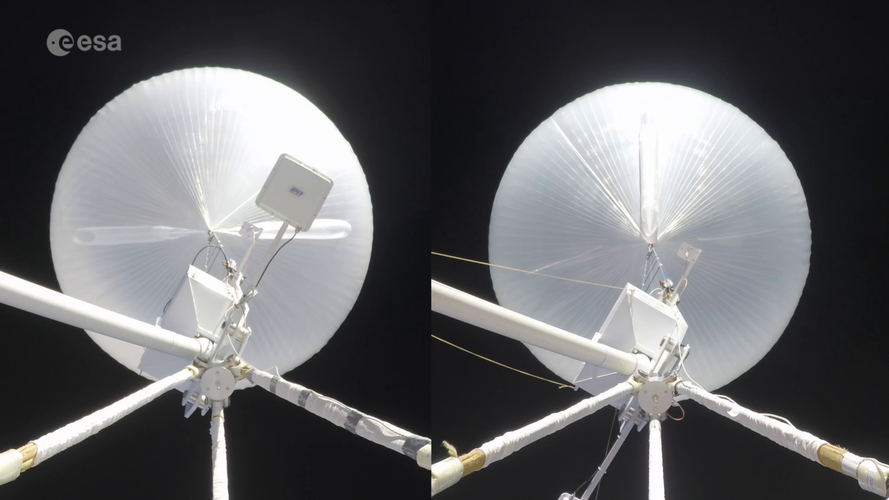

The largest parachute set to fly on Mars has completed its first successful high-altitude drop test, a critical milestone for ensuring the ExoMars mission is on track for launch in 2022. Both the first and second stage parachutes have now successfully flown this year.
Spelunking on the moon: New study explores lunar pits and caves
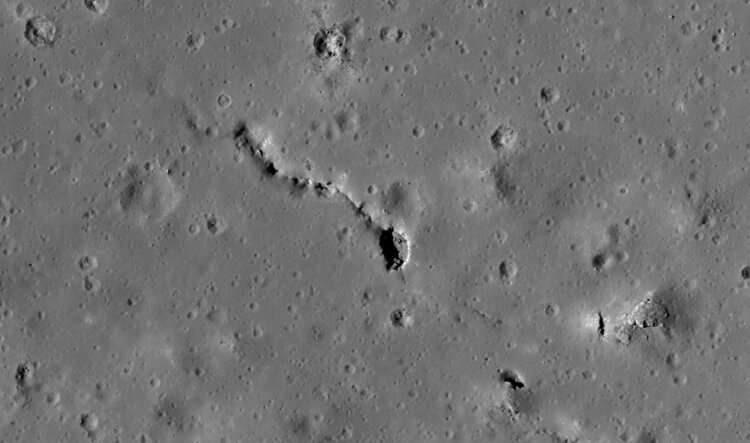

The moon may be a mostly uniform expanse of gray, but if you look closely, you can still find a few nooks and crannies in its surface, from deep trenches to pits and maybe even caves.
Now, researchers at CU Boulder have set out to explore what the environment might be like inside some of these shadowy features—many of which are too dark to see clearly from orbit.
The team's preliminary results suggest that pits and caves on the moon showcase remarkably stable conditions. They don't seem to experience the wild swings in temperature that are common at the moon's surface, said Andrew Wilcoski, a graduate student in the Department of Astrophysical and Planetary Sciences at CU Boulder. He will present the group's initial findings Friday at the American Geophysical Union fall meeting in New Orleans.
"If we're hoping to send people into these caves in the decades ahead, we want to know what they should expect down there," said Wilcoski, a co-author of the new research.
Bundle up for the 2021 Geminid meteors
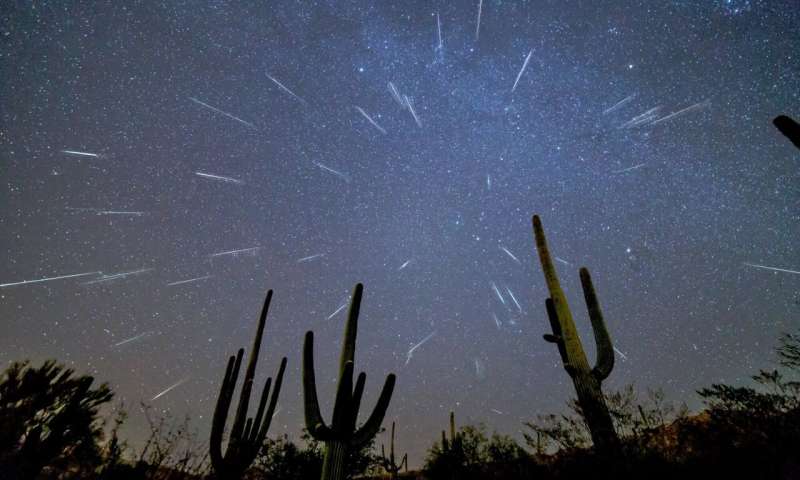

Ready to brave the cold? If you're like us, you haven't wasted an early clear sky morning to get out and see Comet C/2021 A1 Leonard before it heads southward. The coming days offer another early AM celestial sight: the Geminid meteors. To be sure, 2021 sees the Geminid meteors transpire under somewhat challenging conditions. But fear not: With a little planning and patience, you too can witness the "Tears of the Twins."
Circumstances for 2021: First, the bad news: the Geminids peak this year on Tuesday, December 14 at 7:00 Universal Time (UT) or ~2:00 AM EST, just over four days prior to full moon on the 19th. This puts the moon at 80 percent illumination waxing gibbous, meaning there's a narrow window of 'true darkness' between moonset and the beginning of dawn. For example, here in Norfolk, Virginia at latitude 37 degrees north, the moon sets at 2:53 AM EST on the 14th, and dawn begins at 5:37 AM EST just a few hours later.
Interview: Japanese tourist says space trip 'amazing'
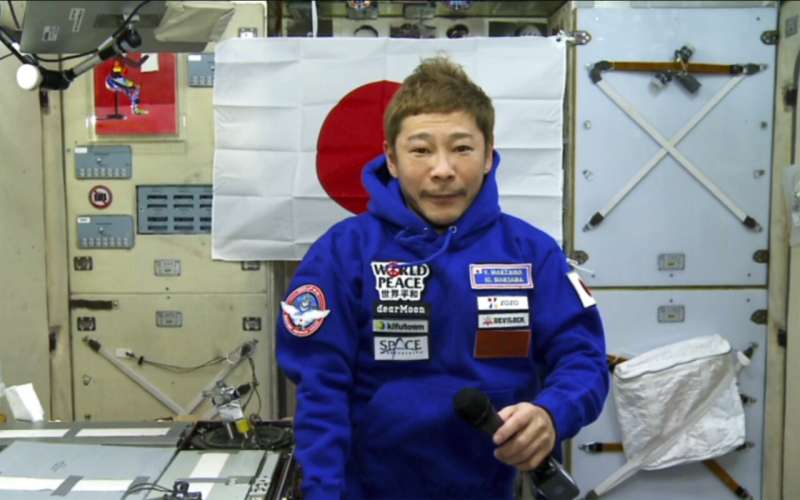

A Japanese space tourist on Monday rejected criticism from those who questioned his decision to pay a fortune for a trip to the International Space Station, saying the "amazing" experience was worth it.
First Vega-C rocket stages reach Europe’s Spaceport
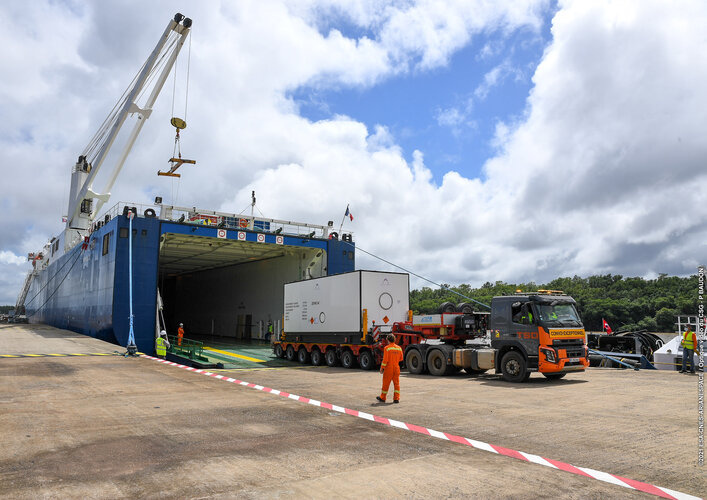 Image:
First Vega-C rocket stages reach Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana
Image:
First Vega-C rocket stages reach Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana Explore the Red Planet with ESA and PLAYMOBIL
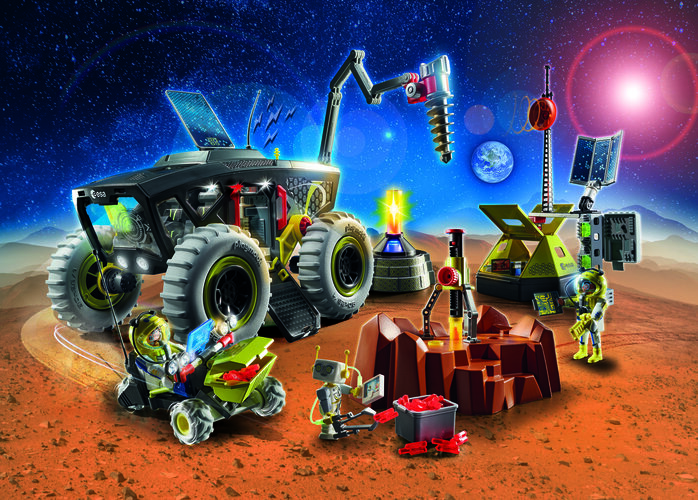

We’re already exploring Mars, with two spacecraft in orbit and an ambitious rover mission planned for launch next year – but now you can join in these martian adventures with your own PLAYMOBIL Mars Expedition!
NASA's 'Eyes on Asteroids' tool reveals near-Earth object neighborhood
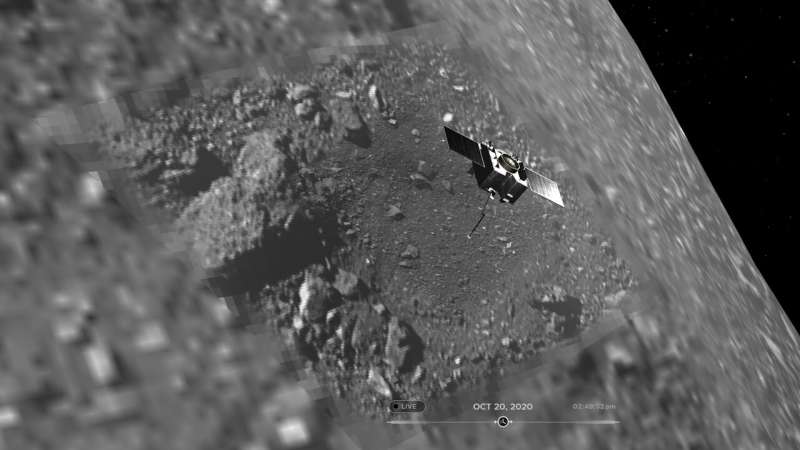

Through a new 3D real-time visualization tool, you can now explore the asteroids and comets that approach Earth's orbital neighborhood—and the spacecraft that visit these objects—with a click or a swipe. NASA's Eyes on Asteroids brings this data to any smartphone, tablet, or computer with an internet connection—no download required.
Thousands of asteroids and dozens of comets are discovered every single year, some of which—called near-Earth objects (NEOs)—follow orbits that pass through the inner solar system.
Five weird things that happen in outer space

It doesn't take a rocket scientist to know space is weird. But just how weird might surprise you. Space is dominated by invisible electromagnetic forces that we typically don't feel. It's also full of bizarre types of matter that we never experience on Earth. Here's five unearthly things that happen almost exclusively in outer space.
1. Plasma
On Earth, matter typically assumes one of three states: solid, liquid, or gas. But in space, 99.9% of normal matter is in an entirely different form—plasma. Made of loose ions and electrons, this substance is in a supercharged state beyond gas that's created when matter is heated to extreme temperatures or is plied with a strong electric current.
Although we rarely interact with plasma, we see it all the time. All the stars in the night sky, including the sun, are mostly made of plasma. It even appears occasionally on Earth in the form of bolts of lightning and in neon signs.
In comparison to gas, where individual particles chaotically zoom about, plasma can act collectively, like a team. It both conducts electricity and is influenced by electromagnetic fields—which operate under the very same force that keeps magnets on your fridge.
Out now: the December quarterly ESA Impact

ESA Impact 2021 Q4 edition
Great images and videos of climate change on view, BepiColombo flies by Mercury, Cheops gets a surprise, and more