
Copernical Team
STEM student experiments win Flight Opportunity in NASA Tech Contest
 NASA selected 57 winning teams in an inaugural nationwide challenge designed to attract, engage, and prepare future science, technology, engineering, and mathematics professionals. The winning teams of the NASA TechRise Student Challenge will gain real world STEM experience by building experiments that autonomously operate and collect data from the edge of space aboard a suborbital rocket or a h
NASA selected 57 winning teams in an inaugural nationwide challenge designed to attract, engage, and prepare future science, technology, engineering, and mathematics professionals. The winning teams of the NASA TechRise Student Challenge will gain real world STEM experience by building experiments that autonomously operate and collect data from the edge of space aboard a suborbital rocket or a h China's new generation carrier rocket Long March-8 ready for launch
 China plans to launch its new generation carrier rocket Long March-8 Y2 between late February and early March from the southern island of Hainan, sources with the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, the country's leading rocket maker, said on Friday.
The rocket arrived at the Wenchang Space Launch Center Friday after a week of ocean transport. It will undergo final assembly and tes
China plans to launch its new generation carrier rocket Long March-8 Y2 between late February and early March from the southern island of Hainan, sources with the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, the country's leading rocket maker, said on Friday.
The rocket arrived at the Wenchang Space Launch Center Friday after a week of ocean transport. It will undergo final assembly and tes NASA emergency beacons save 330 lives in 2021

In 2021, NASA technology saved 330 lives in the U.S. network region of the international satellite-aided search and rescue effort, Cospas-Sarsat. NASA has lent technical expertise to the Cospas-Sarsat program since its founding, aiding in the rescue of over 48,000 individuals globally.
Users purchasing commercially available 406 MHz frequency Cospas-Sarsat beacons have free access to the network, which provides accurate and reliable emergency location services. When users activate these beacons, they send signals through satellite instruments to ground stations that can calculate their position. The network then alerts first responders to the location and nature of the emergency.
Beacons are available in three types: Personal Locator Beacons (PLBs), for use by hikers and other explorers; Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacons (EPIRBs), designed for maritime use; and Emergency Locator Transmitters (ELTs) for aviation. In 2021, 106 rescues were PLBs, 195 were EPIRBS, and 29 were ELTs.
In recent years, NASA's Search and Rescue (SAR) office has helped Cospas-Sarsat to enhance its network with aviation studies, next-generation beacon technology, and new capabilities for Artemis astronauts. The office is also working on a lunar search and rescue concept, or LunaSAR, as part of NASA's lunar network development effort, LunaNet.
Mid-level flare erupts from sun
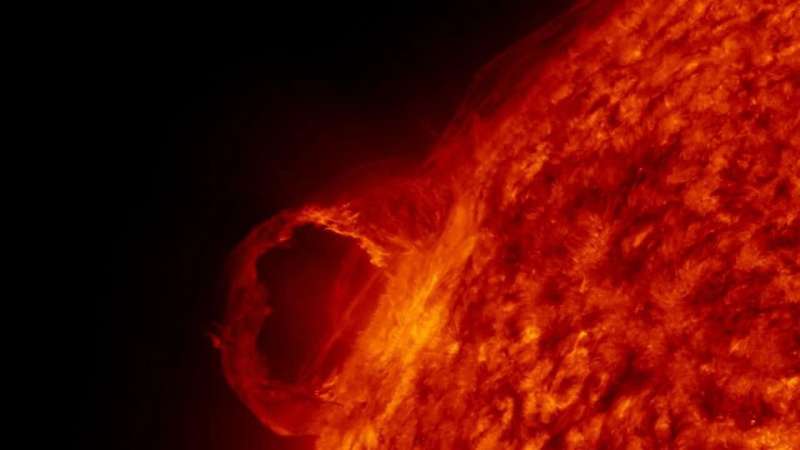

The sun emitted a mid-level solar flare on Jan. 20, 2022, peaking at 1:01 a.m. EST. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, which watches the sun constantly, captured an image of the event.
Solar flares are powerful bursts of energy. Flares and solar eruptions can impact radio communications, electric power grids, navigation signals, and pose risks to spacecraft and astronauts.
This flare is classified as a M5.5 class flare.
Explore further
NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center: spaceweather.gov/
NASA's TESS hits milestone of 5,000 exoplanet candidates
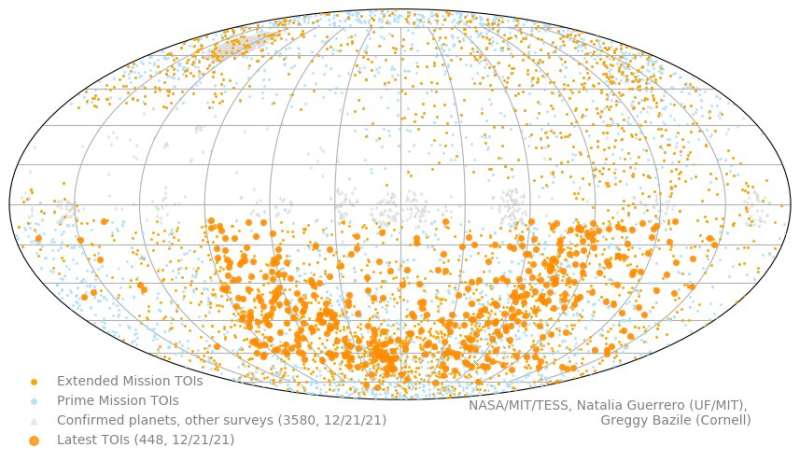
The catalog of planet candidates found with NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) recently passed 5,000 TOIs, or TESS Objects of Interest.
New location, same ASIM
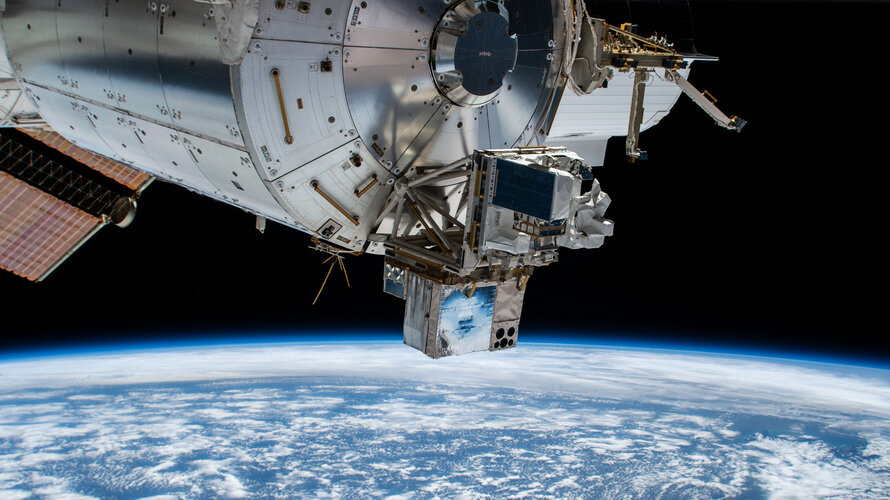 Image:
Image:
The first-of-its-kind complement of instruments dubbed the ‘space storm hunter’ hangs out in its new location outside the International Space Station in this image taken by on of the Station’s external cameras.
The Atmosphere–Space Interactions Monitor, or ASIM for short, measures electric events in Earth’s upper atmosphere with cameras, photometers and X- and gamma-ray detectors.
Last week ASIM was switched off and moved by robotic arm to another spot outside the Columbus module to make room for an American payload. Now in its new location, the instrument is being activated and so far things are going well.
From its new
Week in images: 17 - 21 January 2022

Week in images: 17 - 21 January 2022
Discover our week through the lens
Earth from Space: Mecklenburg–West Pomerania, Germany

Part of Mecklenburg–West Pomerania, also known as Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, a state in northeast Germany is featured in this image captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission. A portion of the northwest coast of Poland can be seen in the right of the image.
ESA/WEF panel discussion and call with Matthias Maurer
 Video:
01:00:30
Video:
01:00:30
Watch the replay of ‘Live from Space: The Next Frontier for Knowledge and Action’. ESA astronaut Matthias Maurer, live from the from the International Space Station discussed with a panel of prominent experts and industry leaders, including ESA’s Director General Josef Aschbacher, about how space research can improve life on our planet.
Ariane 6 upper stage readies for tests at Europe's Spaceport
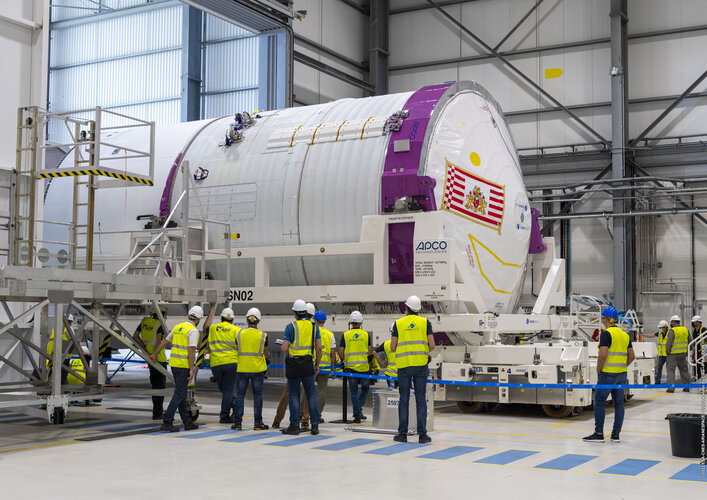

The central core of ESA’s new generation Ariane 6 launch vehicle arrived at Europe’s Spaceport on 18 January and is now inside the launch vehicle assembly building.
































