
Copernical Team
Mysterious 'blue blobs' reveal a new kind of star system
 University of Arizona astronomers have identified five examples of a new class of stellar system. They're not quite galaxies and only exist in isolation.
The new stellar systems contain only young, blue stars, which are distributed in an irregular pattern and seem to exist in surprising isolation from any potential parent galaxy.
The stellar systems - which astronomers say appear thr
University of Arizona astronomers have identified five examples of a new class of stellar system. They're not quite galaxies and only exist in isolation.
The new stellar systems contain only young, blue stars, which are distributed in an irregular pattern and seem to exist in surprising isolation from any potential parent galaxy.
The stellar systems - which astronomers say appear thr 4 buildings at observatory in Arizona lost in wildfire
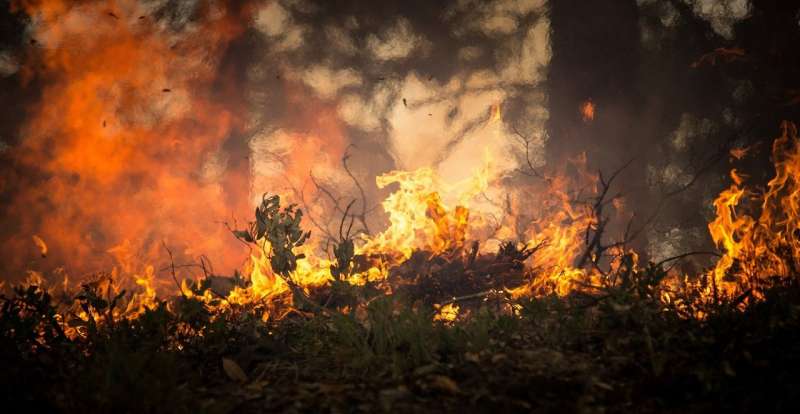

Four non-scientific buildings at the Kitt Peak National Observatory southwest of Tucson were lost in a wildfire, but early indications show other buildings on the property didn't appear to be damaged, authorities said Saturday.
Buell T. Jannuzi, who leads the Department of Astronomy at the University of Arizona, said the fire didn't appear to have damaged the telescope and science buildings at the observatory, though a closer examination of the site hadn't yet been made due to safety concerns.
"This is the most threatening fire I can remember at Kitt Peak in the last 25 years," Jannuzi said.
The fire reached the observatory early Friday. Crews were planning to assess the damage at the observatory later Saturday if conditions allowed for safe entry into the area.
Kitt Peak National Observatory is operated by NOIRLab, the National Science Foundation's center for ground-based optical-infrared astronomy. The University of Arizona, which has had a telescope at the site since 1962, is a tenant of the observatory.
The lightning-caused fire, which led to an evacuation of the observatory earlier this week, had grown to 27 square miles (71 kilometers) by Saturday.
SpaceX Falcon 9 launches for its 13th time, a record for the company
 A SpaceX Falcon 9 lifted off on its record 13th launch on Friday afternoon as it sent 53 Starlink satellites into orbit.
The rocket took off from pad 39A at Kennedy Space Center, with the first stage sticking a successful return and landing at the Shortfall of Gravitas drone ship shortly after lift off.
SpaceX said the same first stage booster support was used in the GPS III-3, T
A SpaceX Falcon 9 lifted off on its record 13th launch on Friday afternoon as it sent 53 Starlink satellites into orbit.
The rocket took off from pad 39A at Kennedy Space Center, with the first stage sticking a successful return and landing at the Shortfall of Gravitas drone ship shortly after lift off.
SpaceX said the same first stage booster support was used in the GPS III-3, T Did a giant radio telescope in China just discover aliens? Not so FAST
 This phrase is the standard that astronomers will be applying to a curious signal captured with China's "Sky Eye" telescope that might be a transmission from alien technology.
An article reporting the signal was posted on the website of China's state-backed Science and Technology Daily newspaper, but was later removed. So have astronomers finally found evidence of intelligent found life be
This phrase is the standard that astronomers will be applying to a curious signal captured with China's "Sky Eye" telescope that might be a transmission from alien technology.
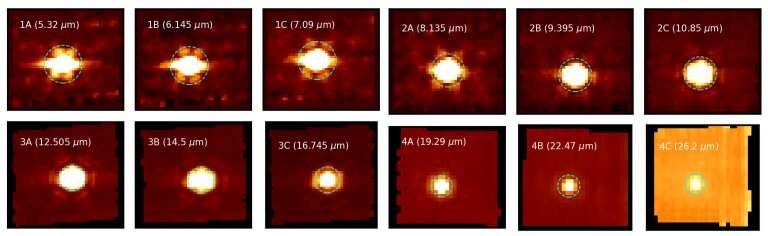
An article reporting the signal was posted on the website of China's state-backed Science and Technology Daily newspaper, but was later removed. So have astronomers finally found evidence of intelligent found life be Webb's mid-infrared spectroscopy will reveal molecules, elements
Evan Leppink: Seeking a way to better stabilize the fusion environment
 "Fusion energy was always one of those kind-of sci-fi technologies that you read about," says nuclear science and engineering PhD candidate Evan Leppink. He's recalling the time before fusion became a part of his daily hands-on experience at MIT's Plasma Science and Fusion Center, where he is studying a unique way to drive current in a tokamak plasma using radiofrequency (RF) waves.
Now, a
"Fusion energy was always one of those kind-of sci-fi technologies that you read about," says nuclear science and engineering PhD candidate Evan Leppink. He's recalling the time before fusion became a part of his daily hands-on experience at MIT's Plasma Science and Fusion Center, where he is studying a unique way to drive current in a tokamak plasma using radiofrequency (RF) waves.
Now, a NASA, ESA finalize agreements on climate, 1 cooperation
 NASA Administrator Bill Nelson and ESA Director General Josef Aschbacher signed two agreements Wednesday at the ESA Council meeting in Noordwijk, Netherlands, further advancing the space agencies' cooperation on Earth science and Artemis missions.
"With these two agreements, NASA and ESA are strengthening the relationship on two of our agencies' primary mission areas: Artemis and Earth sci
NASA Administrator Bill Nelson and ESA Director General Josef Aschbacher signed two agreements Wednesday at the ESA Council meeting in Noordwijk, Netherlands, further advancing the space agencies' cooperation on Earth science and Artemis missions.
"With these two agreements, NASA and ESA are strengthening the relationship on two of our agencies' primary mission areas: Artemis and Earth sci German radar satellite TerraSAR-X - 15 years in space and still in perfect shape
 Fifteen years - who would have thought it? The German radar satellite TerraSAR-X, which was launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan at 08:14 local time on 15 June 2007, was originally designed to last five and a half years - until the end of 2012. It has been delivering data of outstanding quality ever since, regardless of weather conditions, cloud cover and daylight levels. The scie
Fifteen years - who would have thought it? The German radar satellite TerraSAR-X, which was launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan at 08:14 local time on 15 June 2007, was originally designed to last five and a half years - until the end of 2012. It has been delivering data of outstanding quality ever since, regardless of weather conditions, cloud cover and daylight levels. The scie China's deep space exploration laboratory starts operation
 China's deep space exploration laboratory has started operations, the China National Space Administration (CNSA) said Tuesday.
Co-established by the CNSA, Anhui Province and the University of Science and Technology of China, the laboratory is headquartered in Hefei, capital city of Anhui.
It has completed various preparatory work and entered a new stage of substantial operation and c
China's deep space exploration laboratory has started operations, the China National Space Administration (CNSA) said Tuesday.
Co-established by the CNSA, Anhui Province and the University of Science and Technology of China, the laboratory is headquartered in Hefei, capital city of Anhui.
It has completed various preparatory work and entered a new stage of substantial operation and c Northrop Grumman runs Laser Communication Demonstration for Tranche 1 constellation
 Northrop Grumman Corporation has announced the successful ground demonstration of a secure networked laser communications system for proliferated-LEO constellations supporting the U.S. military.
Performed for SDA leadership, the demonstration validated compatibility between commercially developed laser communication and secure U.S. government encryption hardware, providing a baseline for N
Northrop Grumman Corporation has announced the successful ground demonstration of a secure networked laser communications system for proliferated-LEO constellations supporting the U.S. military.
Performed for SDA leadership, the demonstration validated compatibility between commercially developed laser communication and secure U.S. government encryption hardware, providing a baseline for N 































