Copernical Team
FAA: Georgia spaceport decision near, but more study needed

A federal agency expects to announce its decision Monday on whether to allow a launchpad that would send commercial rockets into space from coastal Georgia.
However, the Federal Aviation Administration is emphasizing that a license authorizing Camden County to operate a spaceport would not yet permit the launch of any rockets.
In a letter released Friday by the FAA, the agency said a more comprehensive review would be needed before any rockets can be launched from Georgia.
Even if the license for Spaceport Camden is approved, "it would not authorize a single launch," an FAA executive wrote to the U.S. Department of the Interior.
"Simply put: to obtain a Vehicle Operator License, many more reviews remain, and no outcome is guaranteed," the letter stated.
Any company seeking to launch from the site would need to obtain a Vehicle Operator License and undergo a separate environmental and safety evaluation, according to the FAA.
Camden County, in the southeastern corner of the state, has spent nearly 10 years and $10 million pursuing the goal of having what would be the nation's newest commercial spaceport.
NASA confirms next Friday for Webb Space Telescope launch

Investing recovery and resilience funds in space projects
Green and digital transition in Europe will benefit from ESA expertise that supports national plans for investing recovery and resilience funds in space projects.
At the 303rd ESA Council meeting in Paris on 15 December 2021, ESA Member States took the decision to further the role of ESA as provider of expertise in support of national space plans, in particular in order to accompany the investment of Italian recovery and resilience funds in space programmes.
Paving the way to thriving in space
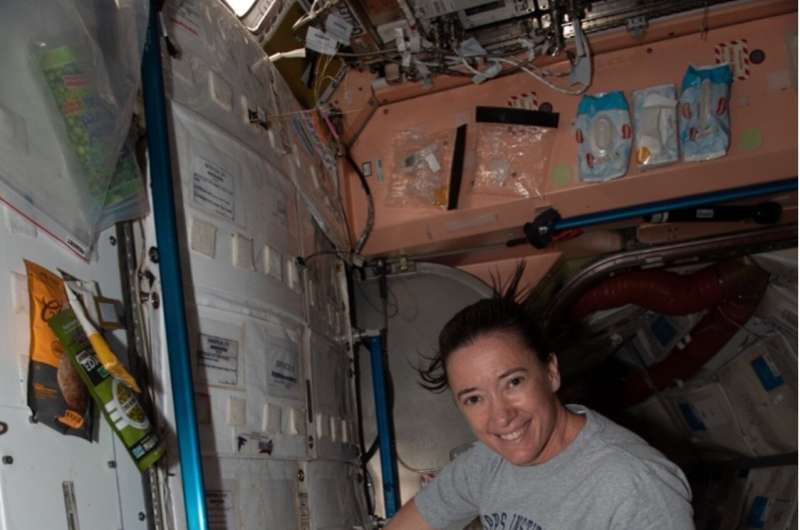

In late December, SpaceX-24 will deliver a payload to the International Space Station. Three new experiments that will help scientists better understand specific biological and physical phenomena will be on board.
"It's really exciting when we get to conduct new investigations aboard the Space Station," said Dr. Craig Kundrot, Director of NASA's Biological and Physical Sciences Division. "What these three experiments have in common is each will contribute fundamental scientific insights that will both enable our astronauts to thrive on their future long-range missions and provide tangible benefits to people on Earth."
Growing plants in harsh conditions:
The Plant RNA Regulation Redux in Multi Variable Platform (MVP-Plant-01) experiment will profile and monitor a plant's shoot and root development under microgravity conditions. The results of this experiment will help scientists better understand the molecular mechanisms and regulatory networks behind how plants sense and adapt to environmental changes. Ultimately, the findings could help scientists design plants that will be able to withstand adverse environmental conditions, both during long spaceflights and here on Earth.
Opening a 50-year-old Christmas present from the Moon
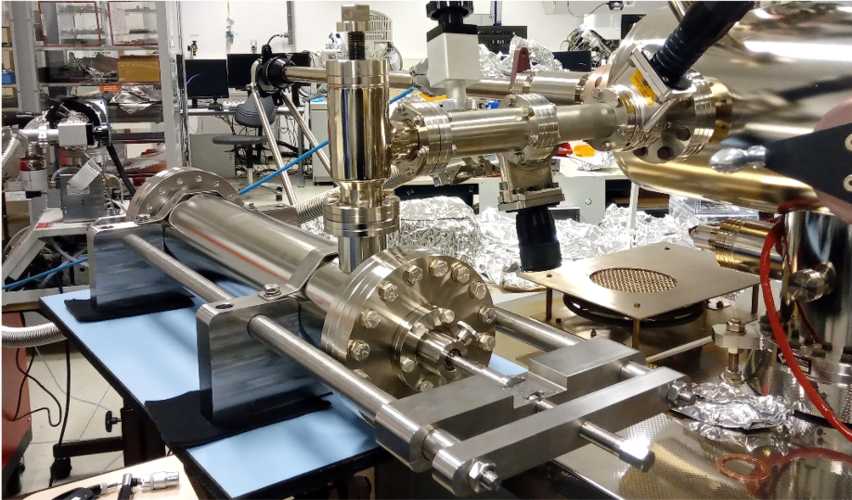
A pretty special gift unwrapping will soon take place – a piercing tool built by ESA will open a Moon soil container from Apollo 17 that has gone untouched for nearly 50 years. The opening will allow the extraction of precious lunar gases which may have been preserved in the sample.
Earth from Space: Kourou, French Guiana
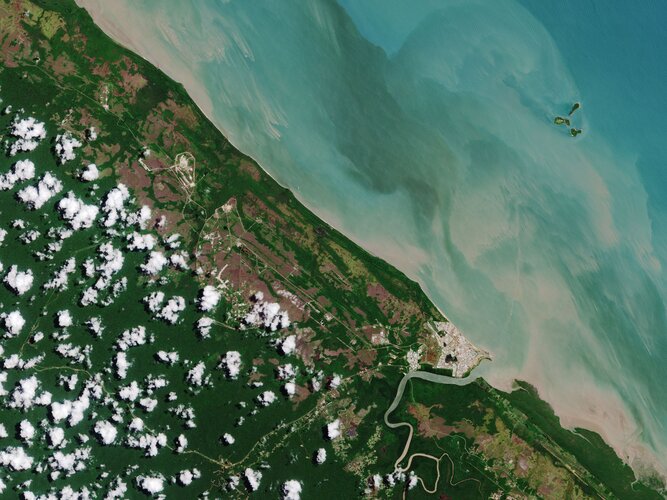

Ahead of the upcoming Ariane 5 launch of the James Webb Space Telescope, the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission takes us over Kourou – home to Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana, an overseas department of France.
Press briefing Webb Telescope
 Video:
00:45:03
Video:
00:45:03
Replay of the 16 December 2021 online press briefing about the James Webb Space Telescope.
Speakers:
- Günther Hasinger, ESA Director of Science
- Daniel Neuenschwander, ESA Director of Space Transportations
- Thomas Zurbuchen, NASA’s Associate Administrator for science
- Antonella Nota, ESA Webb Project Scientist
- Gillian Wright, European Principal Investigator for the MIRI instrument
Developed and constructed over more than 30 years, Webb is a remarkable feat of engineering and technology – with the largest astronomical mirror ever flown in space, sophisticated new scientific instruments, and a sunshield the size of a tennis court.
Webb is designed to answer outstanding questions about the
Year in images 2021

Year in images 2021
Our year through the lens: a selection of our favourite images for 2021
DiCaprio and Lawrence big up science in doomsday comedy
 For Hollywood A-listers Leonardo DiCaprio and Jennifer Lawrence, their new end-of-the-world comedy was a chance to send a little respect back to scientists.
In "Don't Look Up", released on December 24 on Netflix, they play two astronomers who discover a comet will wipe out life on Earth within six months, but then try in vain to get politicians and the media to take the threat seriously.
For Hollywood A-listers Leonardo DiCaprio and Jennifer Lawrence, their new end-of-the-world comedy was a chance to send a little respect back to scientists.
In "Don't Look Up", released on December 24 on Netflix, they play two astronomers who discover a comet will wipe out life on Earth within six months, but then try in vain to get politicians and the media to take the threat seriously.