
Copernical Team
AI helps discover new space anomalies
 The SNAD team, an international network of researchers including Matvey Kornilov, Associate Professor of the HSE University Faculty of Physics, has discovered 11 previously undetected space anomalies, seven of which are supernova candidates. The researchers analysed digital images of the Northern sky taken in 2018 using a k-D tree to detect anomalies through the 'nearest neighbour' method. Machi
The SNAD team, an international network of researchers including Matvey Kornilov, Associate Professor of the HSE University Faculty of Physics, has discovered 11 previously undetected space anomalies, seven of which are supernova candidates. The researchers analysed digital images of the Northern sky taken in 2018 using a k-D tree to detect anomalies through the 'nearest neighbour' method. Machi Wentian's small mechanical arm completes in-orbit tests
 The small mechanical arm mounted with Wentian, the first lab module of China's space station, has successfully completed in-orbit tests, according to the China Manned Space Agency (CMSA).
With the support of the ground team, the small mechanical arm has completed a series of in-orbit function and performance tests. All indexes performed well, achieving expected results, said the CMSA.
The small mechanical arm mounted with Wentian, the first lab module of China's space station, has successfully completed in-orbit tests, according to the China Manned Space Agency (CMSA).
With the support of the ground team, the small mechanical arm has completed a series of in-orbit function and performance tests. All indexes performed well, achieving expected results, said the CMSA. Wide view of early universe hints at galaxy among the earliest ever detected
 Two new images from NASA's James Webb Space Telescope show what may be among the earliest galaxies ever observed. Both images include objects from more than 13 billion years ago, and one offers a much wider field of view than Webb's First Deep Field image, which was released amid great fanfare July 12. The images represent some of the first out of a major collaboration of astronomers and other a
Two new images from NASA's James Webb Space Telescope show what may be among the earliest galaxies ever observed. Both images include objects from more than 13 billion years ago, and one offers a much wider field of view than Webb's First Deep Field image, which was released amid great fanfare July 12. The images represent some of the first out of a major collaboration of astronomers and other a NASA's ShadowCam launches aboard Korea Pathfinder Lunar Orbiter
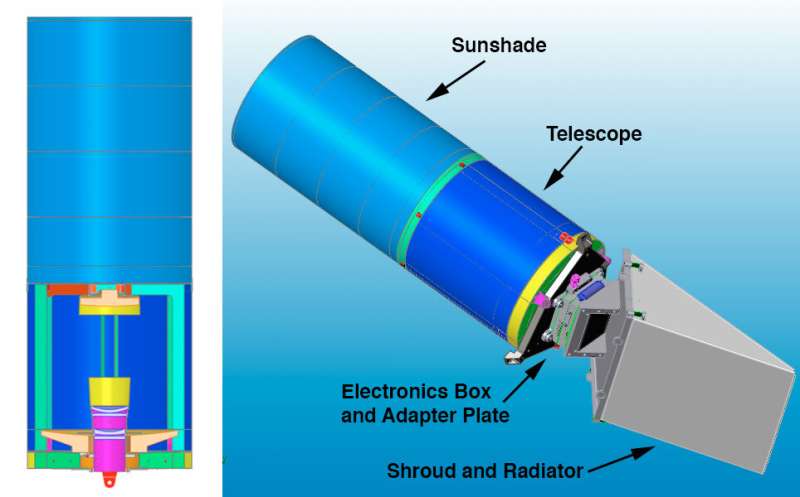
NASA's ShadowCam is heading to the Moon aboard Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI)'s Korea Pathfinder Lunar Orbiter (KPLO) mission. KPLO, also known as Danuri, launched at 7:08 p.m. EDT on a SpaceX Falcon 9 from Launch Complex 40 on the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on August 4.
Developed by Arizona State University and Malin Space Science Systems, ShadowCam is one of five instruments on board KARI's KPLO spacecraft.
A hypersensitive optical camera, ShadowCam, will collect images of permanently shadowed regions near the Moon's poles. This will allow ShadowCam to map the reflectance of these regions to search for evidence of ice deposits, observe seasonal changes, and measure the terrain inside the craters.
NASA Goddard's 'Web Around Asteroid Bennu' shows in SIGGRAPH film fest

Alongside cultural heavyweights such as Disney's "Encanto" and Warner Brothers' "The Batman," a short film created at Goddard shares the screen next week at a festival honoring standout works of computer animated storytelling.
"A Web Around Asteroid Bennu" highlights the tricky navigation it took for NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission to collect a sample from asteroid Bennu in 2020. Produced at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, the video will show in Vancouver, British Columbia, on Aug. 8 in the SIGGRAPH computer graphics conference's Electronic Theater, a qualifying venue for Academy Award consideration.
OSIRIS-REx completed a series of complicated maneuvers around Bennu over the course of two-and-a-half years before collecting its sample with a touch-and-go, or TAG, maneuver and exiting orbit. The various segments of this web-like flight path were highlighted in full by data visualizer Kel Elkins, of NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio at Goddard.
"I started working with the trajectory data in 2015," Elkins said. "And when you first see an image of all the different maneuvers it looks like a rat's nest. But it was really exciting to see these complicated maneuvers in 3D space.
10 years since landing, NASA's Curiosity Mars rover still has drive

Despite signs of wear, the intrepid spacecraft is about to start an exciting new chapter of its mission as it climbs a Martian mountain.
Ten years ago today, a jetpack lowered NASA's Curiosity rover onto the Red Planet, beginning the SUV-size explorer's pursuit of evidence that, billions of years ago, Mars had the conditions needed to support microscopic life.
100 days of Minerva
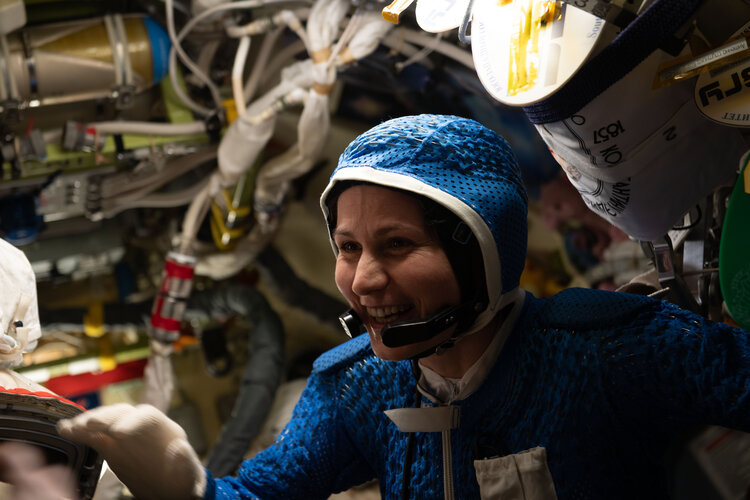

ESA astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti was launched to the International Space Station on 27 April as a part of Crew-4 for her second mission, Minerva. One hundred days in, mission Minerva is still going strong. From completing cutting-edge research in the world’s only orbiting laboratory to sharing daily life on the Space Station via TikTok, it’s all in a day’s work for an ESA astronaut.
Pure gold pin for space testing
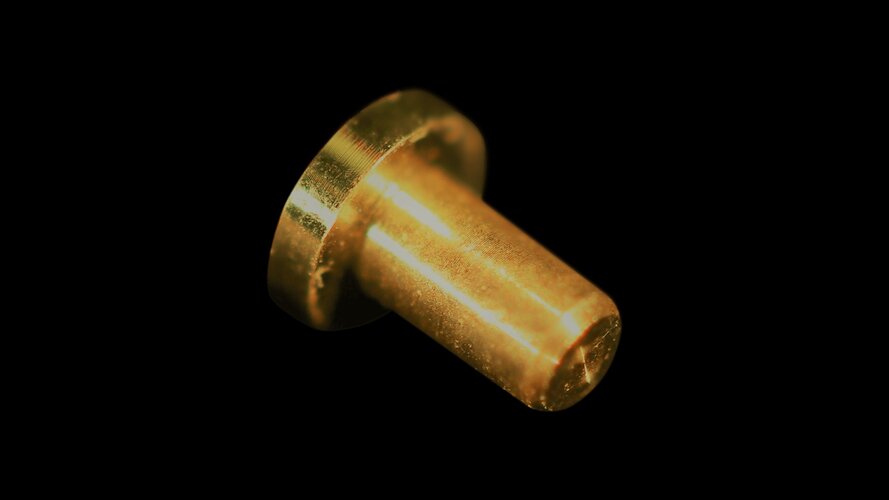 Image:
Pure gold pin for space testing
Image:
Pure gold pin for space testing Week in images: 01-05 August 2022
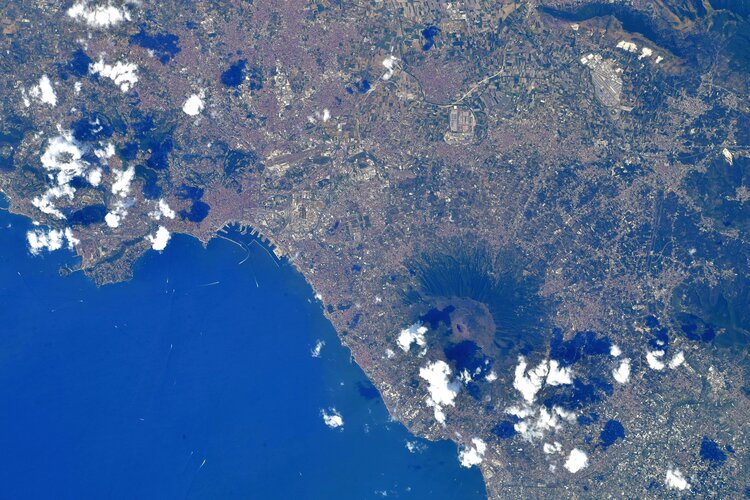

Week in images: 01-05 August 2022
Discover our week through the lens
South Korean spacecraft launched to the moon, country's 1st
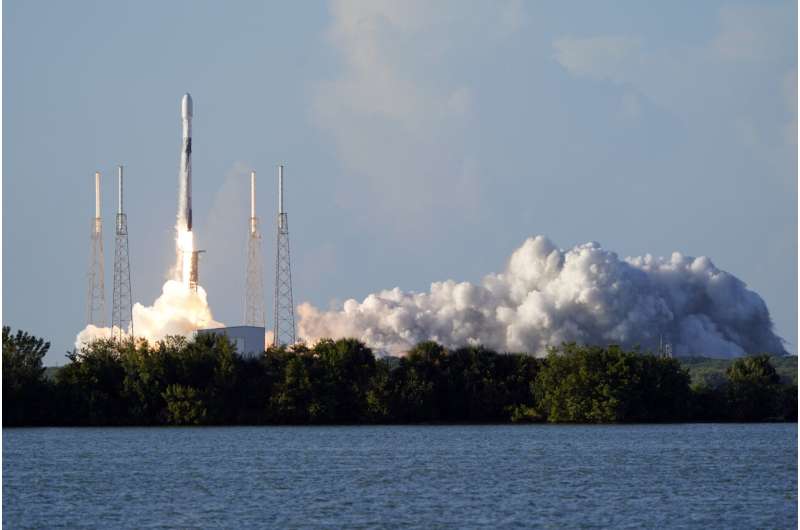

South Korea joined the stampede to the moon Thursday with the launch of a lunar orbiter that will scout out future landing spots.






























