Copernical Team
Organic materials essential for life on Earth are found for the first time on the surface of an asteroid
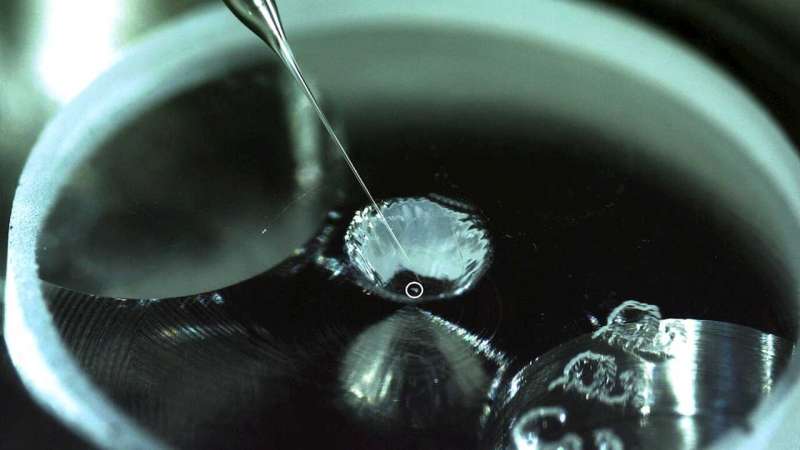
New research from Royal Holloway, has found water and organic matter on the surface of an asteroid sample returned from the inner Solar System. This is the first time that organic materials, which could have provided chemical precursors for the origin of life on Earth, have been found on an asteroid.
The single grain sample was returned to Earth from asteroid Itokawa by JAXA's first Hayabusa mission in 2010. The sample shows that water and organic matter that originate from the asteroid itself have evolved chemically through time.
The research paper suggests that Itokawa has been constantly evolving over billions of years by incorporating water and organic materials from foreign extra-terrestrial material, just like the Earth. In the past, the asteroid will have gone through extreme heating, dehydration and shattering due to catastrophic impact. However, despite this, the asteroid came back together from the shattered fragments and rehydrated itself with water that was delivered via the in fall of dust or carbon-rich meteorites.
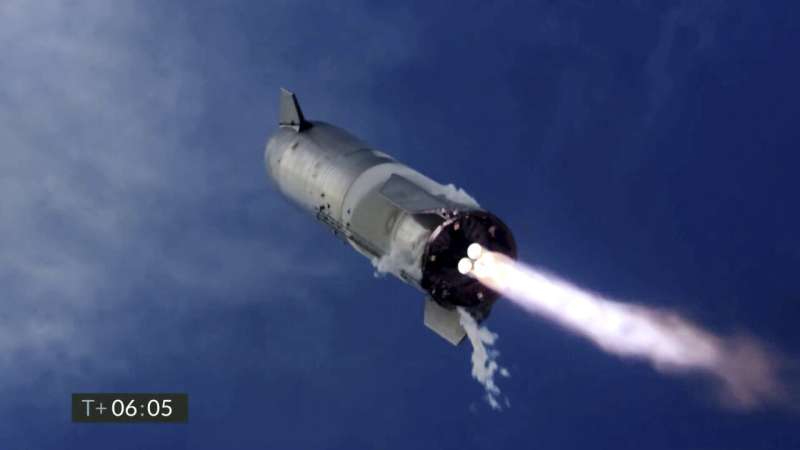
SpaceX Starship lands upright, then explodes in latest test

Chinese astronauts training for space station crewed flights
Monitoring methane emissions from gas pipelines
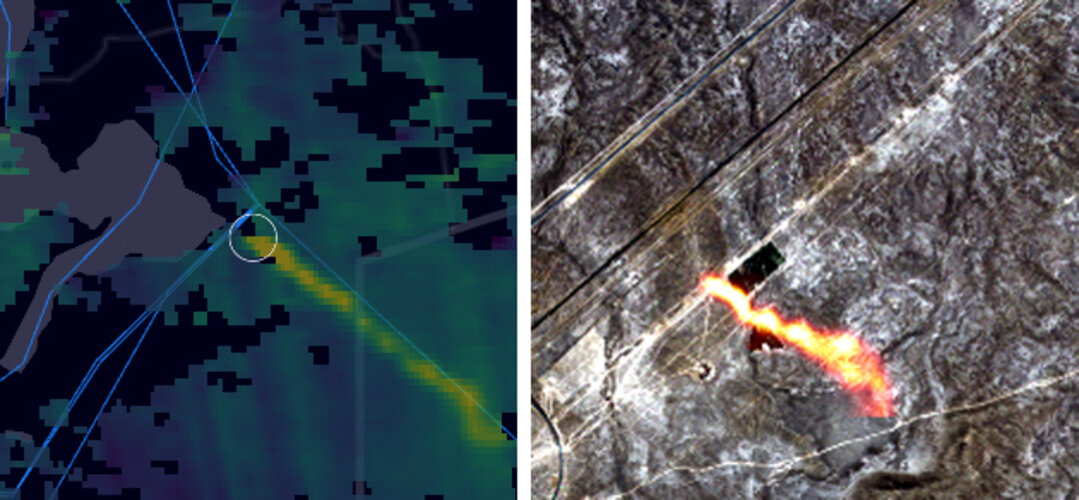
For the first time, scientists, using satellite data from the Copernicus Sentinel missions, are now able to detect individual methane plumes leaking from natural gas pipelines around the globe.
Webb Telescope completes final functional tests to prepare for launch
 February marked significant progress for NASA's James Webb Space Telescope, which completed its final functional performance tests at Northrop Grumman in Redondo Beach, California. Testing teams successfully completed two important milestones that confirmed the observatory's internal electronics are all functioning as intended, and that the spacecraft and its four scientific instruments can send
February marked significant progress for NASA's James Webb Space Telescope, which completed its final functional performance tests at Northrop Grumman in Redondo Beach, California. Testing teams successfully completed two important milestones that confirmed the observatory's internal electronics are all functioning as intended, and that the spacecraft and its four scientific instruments can send China tests high-thrust rocket engine for upcoming space station missions
 A Chinese high-thrust oxyhydrogen engine designed for the Long March-5 carrier rocket has completed a 520-second test in Beijing in preparation for space station missions, the engine's maker said on Wednesday.
Developed by an institute under the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), the engine is the most advanced cryogenic liquid rocket engine that has been put into u
A Chinese high-thrust oxyhydrogen engine designed for the Long March-5 carrier rocket has completed a 520-second test in Beijing in preparation for space station missions, the engine's maker said on Wednesday.
Developed by an institute under the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), the engine is the most advanced cryogenic liquid rocket engine that has been put into u ISS Leaks May Be Caused by Metal Fatigue, Micrometeorite Impact, Source Says
 A commission of Russian State Space Corporation Roscosmos believes that cracks in Russia's Zvezda module at the International Space Station (ISS) were most likely formed due to metal fatigue or micrometeorite impact, a source in the rocket and space sphere said on Wednesday.
The commission unites experts from Roscosmos, the Rocket and Space Corporation Energia, the Central Research Institu
A commission of Russian State Space Corporation Roscosmos believes that cracks in Russia's Zvezda module at the International Space Station (ISS) were most likely formed due to metal fatigue or micrometeorite impact, a source in the rocket and space sphere said on Wednesday.
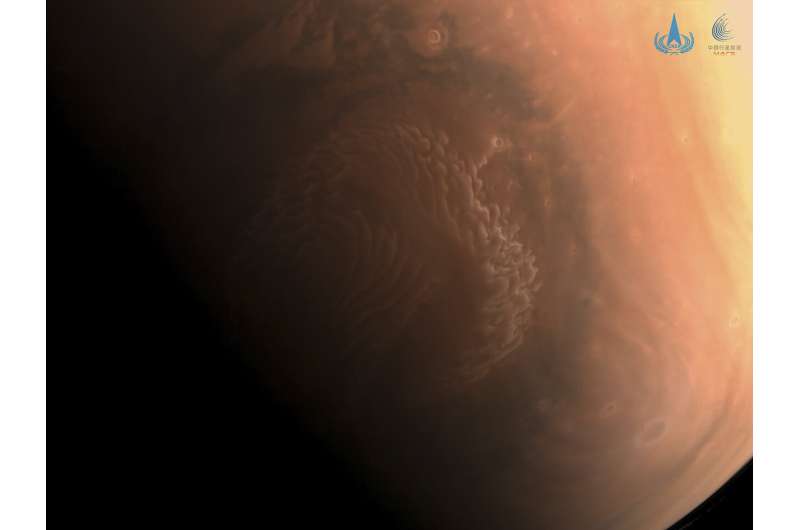
The commission unites experts from Roscosmos, the Rocket and Space Corporation Energia, the Central Research Institu China shows first high-def pictures of Mars taken by Tianwen 1
 The China National Space Administration made public on Thursday morning the first high-definition pictures of Mars taken by the nation's spacecraft.
The pictures - two black-and-white and one color - were shot recently by China's Tianwen 1 robotic probe when the spacecraft was travelling in Mars orbit, according to the administration.
The two black-and-white 7-meter-resolution images
The China National Space Administration made public on Thursday morning the first high-definition pictures of Mars taken by the nation's spacecraft.
The pictures - two black-and-white and one color - were shot recently by China's Tianwen 1 robotic probe when the spacecraft was travelling in Mars orbit, according to the administration.
The two black-and-white 7-meter-resolution images Planetary science intern leads study of Martian crust
 The planet Mars has no global magnetic field, although scientists believe it did have one at some point in the past. Previous studies suggest that when Mars' global magnetic field was present, it was approximately the same strength as Earth's current field.
Surprisingly, instruments from past Mars missions, both orbiters and landers, have spotted patches on the planet's surface that are st
The planet Mars has no global magnetic field, although scientists believe it did have one at some point in the past. Previous studies suggest that when Mars' global magnetic field was present, it was approximately the same strength as Earth's current field.
Surprisingly, instruments from past Mars missions, both orbiters and landers, have spotted patches on the planet's surface that are st China's commercial rocket SD-3 to make maiden flight in 2022
 Smart Dragon-3 (SD-3), the third member of China's Dragon series commercial carrier rockets family, will make its maiden flight in 2022, its developer said Wednesday.
A four-stage solid-propellant rocket, the SD-3 will be the largest and have the highest carrying capacity among the Dragon series, according to the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology.
With a maximum diameter of
Smart Dragon-3 (SD-3), the third member of China's Dragon series commercial carrier rockets family, will make its maiden flight in 2022, its developer said Wednesday.
A four-stage solid-propellant rocket, the SD-3 will be the largest and have the highest carrying capacity among the Dragon series, according to the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology.
With a maximum diameter of