Copernical Team
SpaceX to launch SpaceLogistics Mission Extension Pod for Optus satellite
 Northrop Grumman Corporation's SpaceLogistics has announced a launch agreement for its Mission Robotic Vehicle (MRV) spacecraft, and the sale of its first Mission Extension Pod (MEP).
Under the launch agreement, SpaceX will provide launch services for a planned spring 2024 launch of the MRV and several MEPs. Optus, Australia's largest satellite owner and operator, recently completed a purchase
Northrop Grumman Corporation's SpaceLogistics has announced a launch agreement for its Mission Robotic Vehicle (MRV) spacecraft, and the sale of its first Mission Extension Pod (MEP).
Under the launch agreement, SpaceX will provide launch services for a planned spring 2024 launch of the MRV and several MEPs. Optus, Australia's largest satellite owner and operator, recently completed a purchase NASA rocket team to chase pulsating aurora
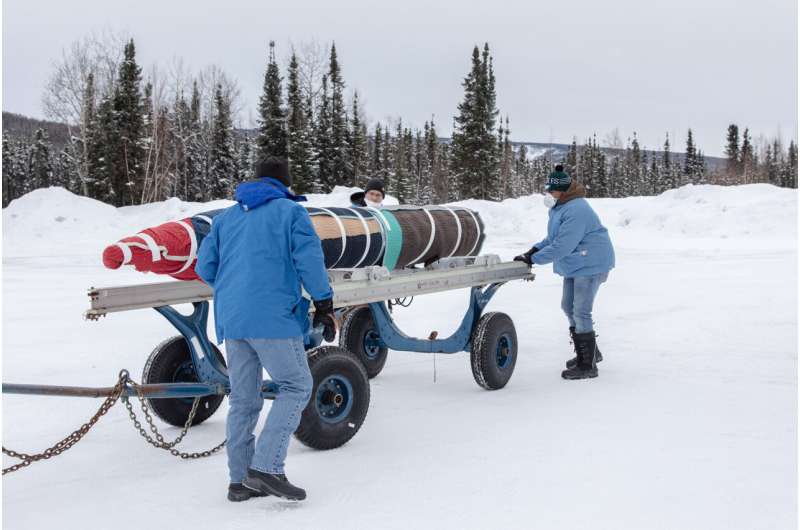

A new NASA sounding rocket mission will soon take to the Alaskan skies. The LAMP mission, short for Loss through Auroral Microburst Pulsations, will fly above an often-overlooked kind of northern lights to test a theory on what causes them. The launch window at Poker Flat Research Range in Fairbanks, Alaska, opens on Feb. 24, 2022.
The aurora borealis, or northern lights, is a familiar treat to those who call northern latitudes home. Auroras come in different shapes and colors, waving their ribbons of vibrant green, red and purple across the sky. But one variety of aurora displays a peculiar behavior: it pulsates.
High-flying NASA 'NACHOS' instrument may help predict volcanic eruptions
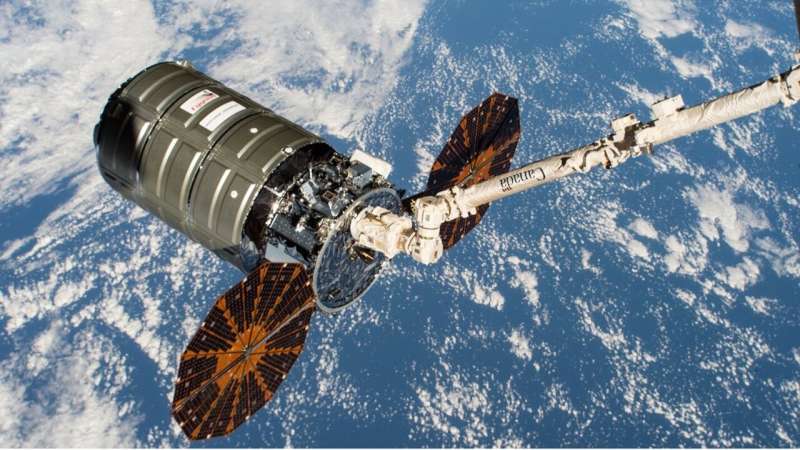

NASA is launching a prototype instrument that could make it easier to monitor volcanic activity and air quality. Perched aboard a CubeSat about 300 miles (480 kilometers) above Earth's surface, the "Nanosat Atmospheric Chemistry Hyperspectral Observation System," or NACHOS, will use a compact hyperspectral imager to locate sources of trace gasses in areas as small as 0.15 square miles (0.4 square kilometers)—about the size of the Mall of America in Minnesota. NACHOS is part of Northrop Grumman's 17th resupply mission to the International Space Station from NASA's Wallops Flight Facility on Wallops Island, Virginia.
If successful, NACHOS will be the smallest, highest resolution space-based instrument dedicated to monitoring atmospheric trace gasses like sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen dioxide, paving the way for future Earth-observing systems that will not only help predict volcanic eruptions, but also monitor air quality around specific cities, neighborhoods, and even individual power plants.
One week left to apply for the 2022 YGT Programme!

The ESA YGT call for applications closes 28 February 2022. Don’t hesitate to apply and kick-start your career in space today! Positions are available in engineering, science, IT and business services. Find out more and apply now.
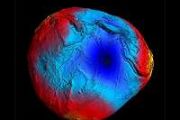
Inflated activity
 Image:
Inflated activity
Image:
Inflated activity China's land-observing satellite starts to take pictures
 A Chinese remote-sensing satellite started to take pictures in its orbit, scientists in charge of the satellite said Friday.
China launched a Long March-4C rocket to place the L-SAR 01A satellite in space on Jan. 26. The satellite, equipped with L-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR), can monitor the geological environment, landslides, and earthquakes.
The radar is now capable of taki
A Chinese remote-sensing satellite started to take pictures in its orbit, scientists in charge of the satellite said Friday.
China launched a Long March-4C rocket to place the L-SAR 01A satellite in space on Jan. 26. The satellite, equipped with L-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR), can monitor the geological environment, landslides, and earthquakes.
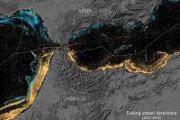
The radar is now capable of taki Satellite imagery gives researchers timeline of when swine waste lagoons were built
 Researchers at North Carolina State University have developed an automated technique that uses satellite imagery to determine when swine waste lagoons were constructed, allowing researchers to determine the extent to which these facilities may have affected environmental quality.
Swine waste lagoons are outdoor basins used to store liquid manure produced by swine farming operations.
Researchers at North Carolina State University have developed an automated technique that uses satellite imagery to determine when swine waste lagoons were constructed, allowing researchers to determine the extent to which these facilities may have affected environmental quality.
Swine waste lagoons are outdoor basins used to store liquid manure produced by swine farming operations. How to look thousands of kilometers deep into the Earth?
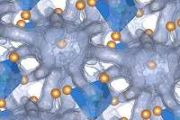
 Researchers led by Sergey Lobanov from the GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences have developed a new method to measure the density of silicon dioxide (SiO2) glass, one of the most important materials in industry and geology, at pressures of up to 110 gigapascals, 1.1 million times higher than normal atmospheric pressure. Instead of employing highly focused X-rays at a synchrotron facility,
Researchers led by Sergey Lobanov from the GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences have developed a new method to measure the density of silicon dioxide (SiO2) glass, one of the most important materials in industry and geology, at pressures of up to 110 gigapascals, 1.1 million times higher than normal atmospheric pressure. Instead of employing highly focused X-rays at a synchrotron facility, Where on Earth did the water come from
 Earth's supply of water is incredibly important for its ability to sustain life, but where did that water come from? Was it present when Earth formed or was it delivered later by meteorites or comets from outer space?
The source of Earth's water has been a longstanding debate and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists think they have the answer - and they found it by look
Earth's supply of water is incredibly important for its ability to sustain life, but where did that water come from? Was it present when Earth formed or was it delivered later by meteorites or comets from outer space?
The source of Earth's water has been a longstanding debate and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists think they have the answer - and they found it by look Kacific and Farmer Charlie team up to boost agricultural output across Pacific
 Kacific Broadband Satellites and Farmer Charlie will bring affordable satellite-powered agricultural information and expertise to farmers in remote and isolated places across South East Asia and the Pacific. The companies have signed an MoU supporting sustainable development and agriculture in small holdings across the region.
Kacific and Farmer Charlie will work together to deliver agricu
Kacific Broadband Satellites and Farmer Charlie will bring affordable satellite-powered agricultural information and expertise to farmers in remote and isolated places across South East Asia and the Pacific. The companies have signed an MoU supporting sustainable development and agriculture in small holdings across the region.
Kacific and Farmer Charlie will work together to deliver agricu