
Copernical Team
Scientists use seasons to find water for future Mars astronauts
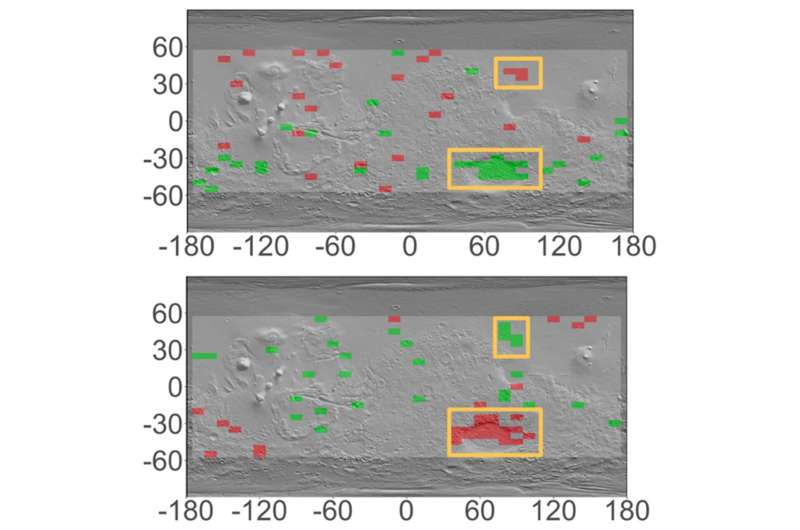
Exotic mix in China's delivery of moon rocks
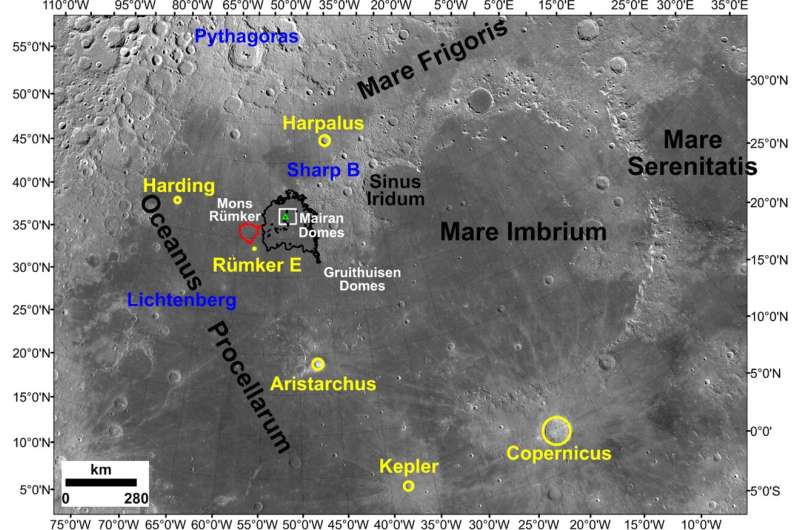
On 16 December 2020 the Chang'e-5 mission, China's first sample return mission to the Moon, successfully delivered to Earth nearly two kilograms of rocky fragments and dust from our celestial companion. Chang'e-5 landed on an area of the Moon not sampled by the NASA Apollo or the Soviet Luna missions nearly 50 years ago, and retrieved fragments of the youngest lunar rocks ever brought back for analysis in laboratories on Earth.
Wildfire Map wins top prize at App Camp
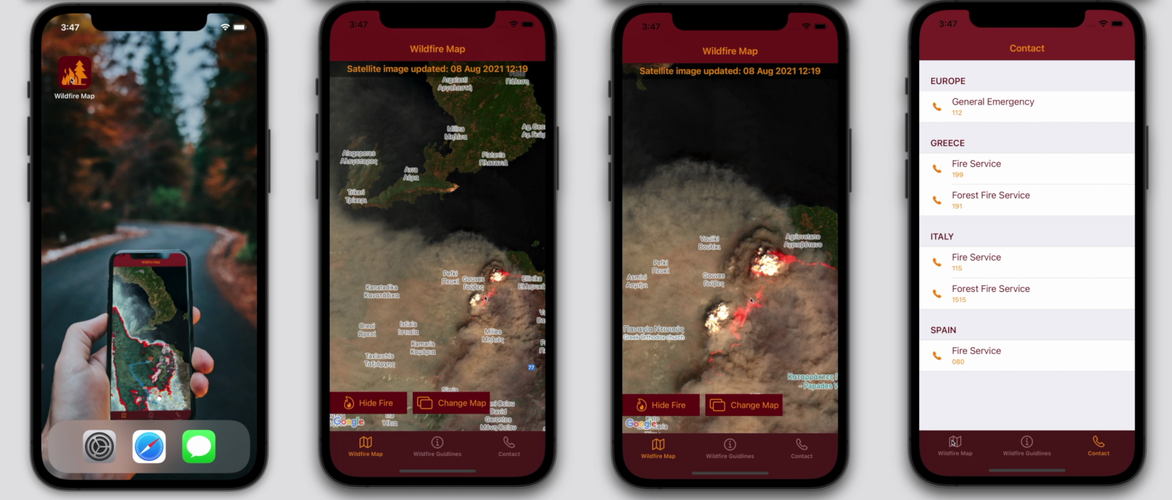
An app that uses satellite data to show the location and impact of wildfires took home the top prize at this year’s Space App Camp.
Week in images: 20 - 24 September 2021
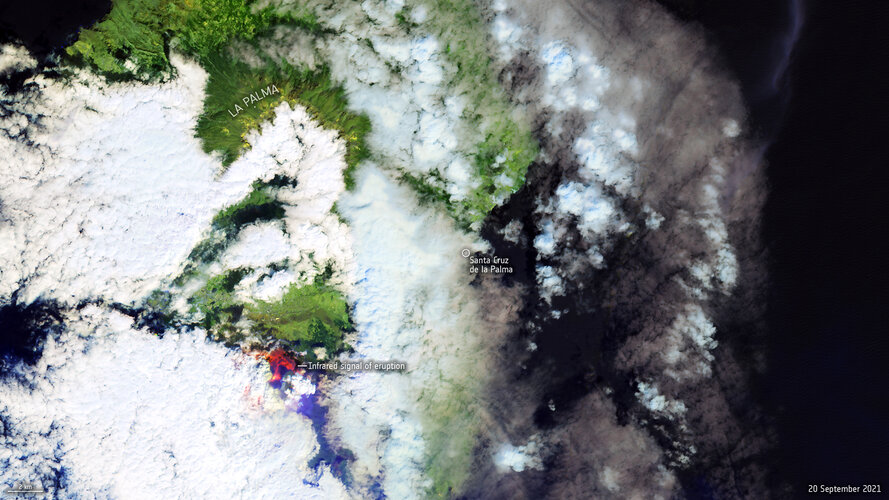

Week in images: 20 - 24 September 2021
Discover our week through the lens
For reasons by Vivaldi
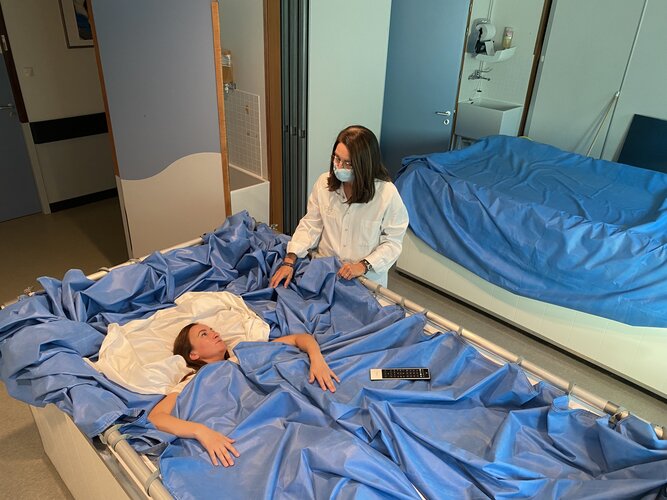 Image:
Image:
A female volunteer gets comfortable in her waterbed, as the dry immersion study to recreate some of the effects of spaceflight on the body kicks off this week in Toulouse, France. Called Vivaldi, or Validation of the Dry Immersion, the campaign features all female-participants in a European first.
Immersion begins when water covers the subject above the thorax, immobilised with legs and trunk covered with a cotton sheet. Only the arms and head remain free outside the tarp.
As a result, the body experiences ‘supportlessness’ – something close to what astronauts feel while floating on the International Space Station.
In weightlessness,
Layered history
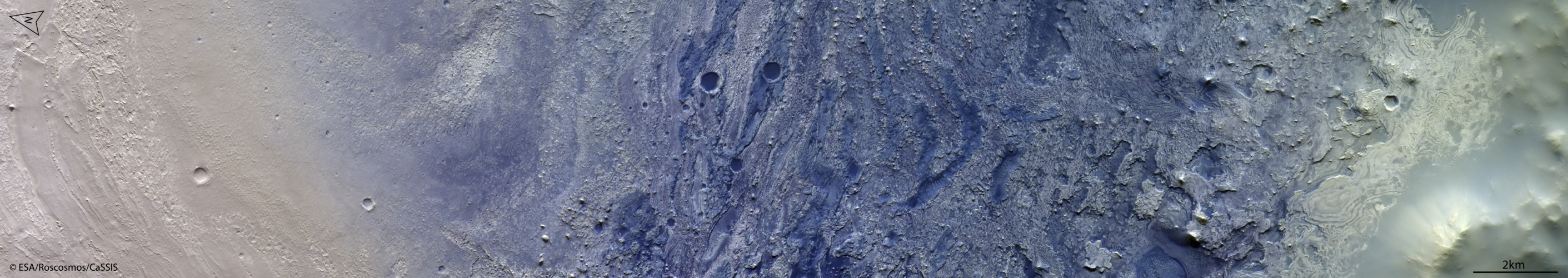 Image:
Layered history
Image:
Layered history How to weigh a quasar
 Astronomers of the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy have, for the first time, successfully tested a new method for determining the masses of extreme black holes in quasars. This method is called spectroastrometry and is based on the measurement of radiation emitted by gas in the vicinity of supermassive black holes.
This measurement simultaneously determines the rotational velocity of th
Astronomers of the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy have, for the first time, successfully tested a new method for determining the masses of extreme black holes in quasars. This method is called spectroastrometry and is based on the measurement of radiation emitted by gas in the vicinity of supermassive black holes.
This measurement simultaneously determines the rotational velocity of th Exolaunch to facilitate launch of Lunasonde's Gossamer Satellite Constellation
 Lunasonde, a startup that focuses on subsurface imaging from space, and Exolaunch, a global leader in rideshare launch, deployment and integration services for small satellites, announce the launch agreements to fly a portion of the Gossamer satellite constellation to a sun-synchronous orbit aboard SpaceX's Falcon 9 Transporter missions in 2022.
Though resources such as water and minerals
Lunasonde, a startup that focuses on subsurface imaging from space, and Exolaunch, a global leader in rideshare launch, deployment and integration services for small satellites, announce the launch agreements to fly a portion of the Gossamer satellite constellation to a sun-synchronous orbit aboard SpaceX's Falcon 9 Transporter missions in 2022.
Though resources such as water and minerals The Biomass satellite and disappearing 'football fields'
 Forests, especially tropical rainforests, are guardians against climate change. But our forests are burning. They are withering and dwindling. Our guardians are themselves threatened by climate change. A new European Space Agency (ESA) satellite mission, currently being built by Airbus, is set to investigate exactly how our forests are faring. The name says it all: Biomass.
Our forests and
Forests, especially tropical rainforests, are guardians against climate change. But our forests are burning. They are withering and dwindling. Our guardians are themselves threatened by climate change. A new European Space Agency (ESA) satellite mission, currently being built by Airbus, is set to investigate exactly how our forests are faring. The name says it all: Biomass.
Our forests and SpaceX satellite signals used like GPS to pinpoint location on Earth
 Engineering researchers have developed a method to use signals broadcast by Starlink internet service satellites to accurately locate a position here on Earth, much like GPS does. It is the first time the Starlink system has been harnessed by researchers outside SpaceX for navigation.
The Starlink satellites, sent into orbit by Elon Musk's SpaceX, are designed to provide broadband internet
Engineering researchers have developed a method to use signals broadcast by Starlink internet service satellites to accurately locate a position here on Earth, much like GPS does. It is the first time the Starlink system has been harnessed by researchers outside SpaceX for navigation.
The Starlink satellites, sent into orbit by Elon Musk's SpaceX, are designed to provide broadband internet 































