
Copernical Team
William Shatner to be oldest astronaut at 90: How space tourism could affect older people

Is space really the final frontier? William Shatner is set to find out as he boldly goes where no 90-year-old has gone before. Some 55 years after Captain James T Kirk hit our screens in the original Star Trek, Shatner will launch to the edge of space aboard Blue Origin's New Shepard for a ten-minute sub-orbital flight.
Shatner will become the oldest person to go to space, breaking the record set only recently by 82-year-old Wally Funk, who traveled on the New Shepard's first crewed spaceflight in July. Funk was one of the Mercury 13 women who qualified for spaceflight in the 1960s but never flew.
With commercial spaceflight companies now taking older people to space, it's timely to consider the potential physical impact space flight might have on them.
In just a few days in space, the human body starts to adapt. Astronauts' bones start to lose density and their muscles become smaller and weaker because they're not being used to stand up against gravity or to move around.
William Shatner, TV's Capt. Kirk, blasts into space
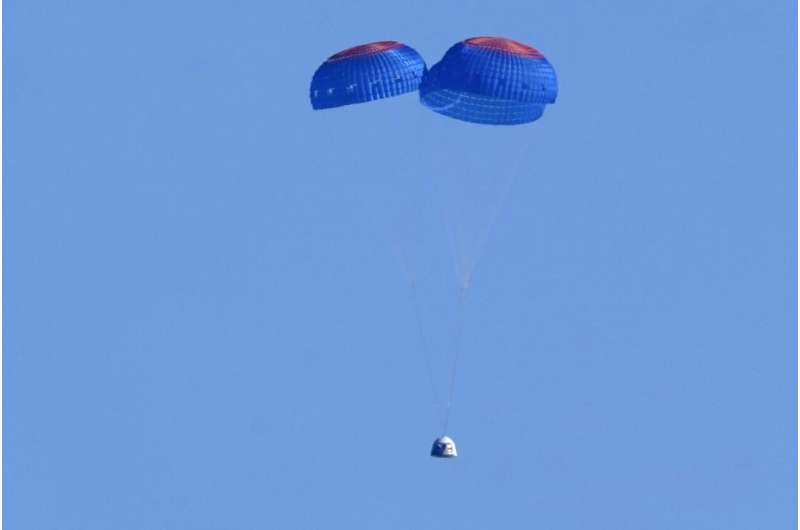

Hollywood's Captain Kirk, 90-year-old William Shatner, blasted into space Wednesday in a convergence of science fiction and science reality, reaching the final frontier aboard a ship built by Jeff Bezos' Blue Origin company.
The "Star Trek" hero and three fellow passengers soared an estimated 66 miles (106 kilometers) over the West Texas desert in the fully automated capsule, then safely parachuted back to Earth in a flight of just over 10 minutes.
Shatner became the oldest person in space, eclipsing the previous record—set by a passenger on a similar jaunt on a Bezos spaceship in July—by eight years.
Euclid Telescope completes space test in Belgium
 Video:
00:00:41
Video:
00:00:41
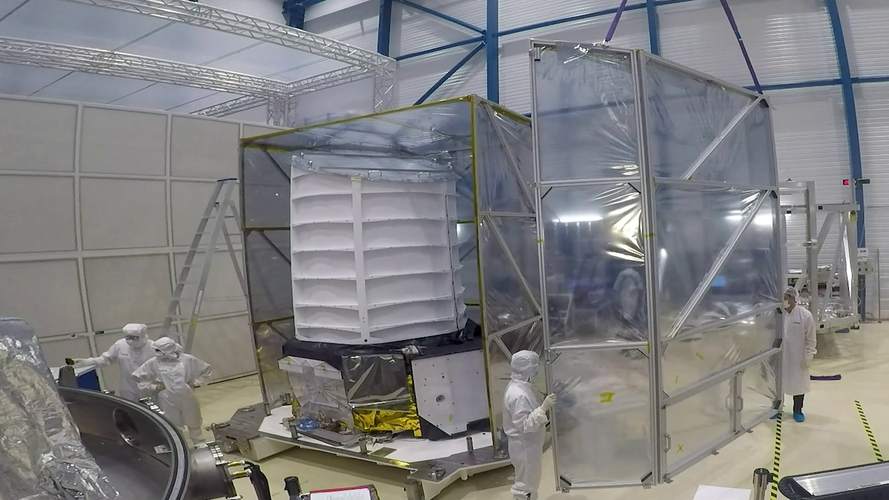
ESA’s Euclid mission aims to investigate dark matter, dark energy and the expanding Universe.
Euclid has reached a new milestone in its development with successful testing of the telescope and instruments showing that it can operate and achieve the required performance in the extreme environment of space.
At Centre Spatial de Liège (CSL) in Belgium, the payload module (containing the telescope and scientific instruments) was packed in a thermal tent, after which it was loaded in a large vacuum tank where it underwent intensive testing.
Euclid experienced simulated space conditions in vacuum with the payload module cooled to -150oC, the
Webb arrives in French Guiana for launch on Ariane 5
 Video:
00:01:54
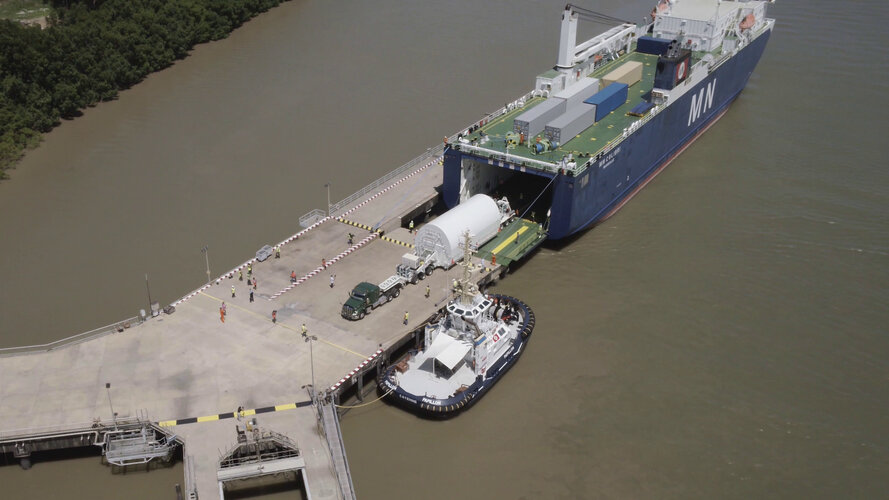
The James Webb Space Telescope arrived in French Guiana on 12 October 2021 ahead its launch on Ariane 5
Video:
00:01:54
The James Webb Space Telescope arrived in French Guiana on 12 October 2021 ahead its launch on Ariane 5 Putting Earth observation into ‘the market perspective’

With a boom in the global market for Earth observation information and data products, participants at this year’s Φ-week conference have been digging deep into the ‘market perspective’. This important topic includes how to gain a better understanding of what governments, industry, the public and other users of Earth observation products and services need and expect to create value for society and the economy.
At your Service Module
 Image:
Image:
The second European Service Module is prepared for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, USA this week at Airbus facilities in Bremen, Germany. Made up of components from ten European countries, ESM-2 will power the first crewed flight to the Moon on the Artemis II mission.
The European Service Modules are a key element of the Orion spacecraft, the first to return humans to the Moon since the 1970s.
Built by the brightest minds in Europe, the module provides propulsion, power and thermal control and will supply astronauts with water and oxygen. The ESM is installed underneath the
Cool tech to almost double deep space data
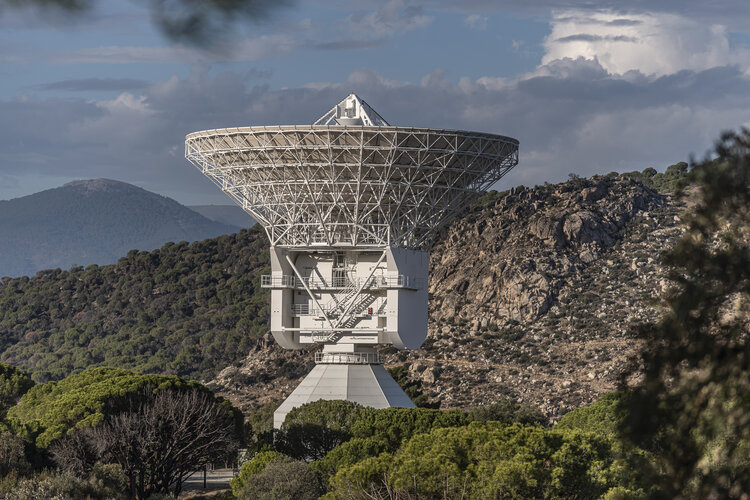

An upgrade to ESA’s three 35-metre deep-space antennas will boost science data return by 40% by cooling the ‘antenna feed’ to just 10 degrees above the lowest temperature possible in the Universe.
Ariane 6 mast gains cryogenic arms
 Image:
Cryogenic arms on the upper part of the Ariane 6 mast on the launch pad connect to the rocket's upper stage and retract at liftoff
Image:
Cryogenic arms on the upper part of the Ariane 6 mast on the launch pad connect to the rocket's upper stage and retract at liftoff Putting the Earth observation into ‘the market perspective’

With a boom in the global market for Earth observation information and data products, participants at this year’s Φ-week conference have been digging deep into the ‘market perspective’. This important topic includes how to gain a better understanding of what governments, industry, the public and other users of Earth observation products and services need and expect to create value for society and the economy.
The future is here: Advanced Manufacturing for space
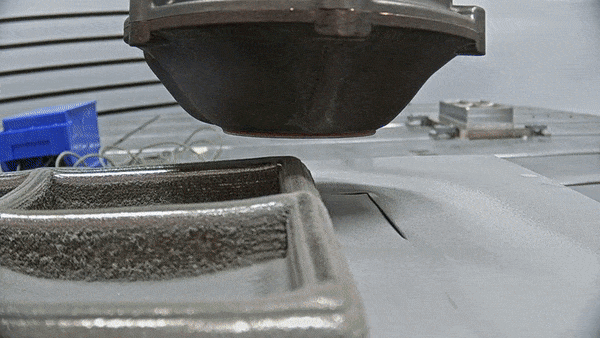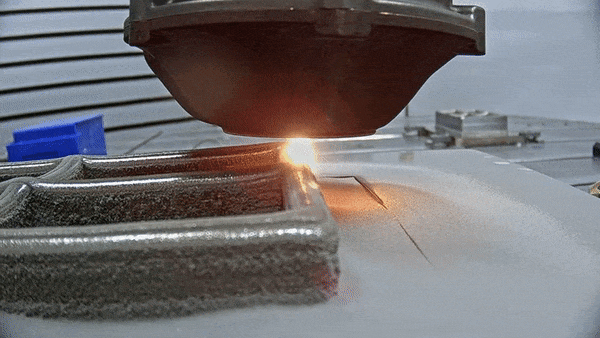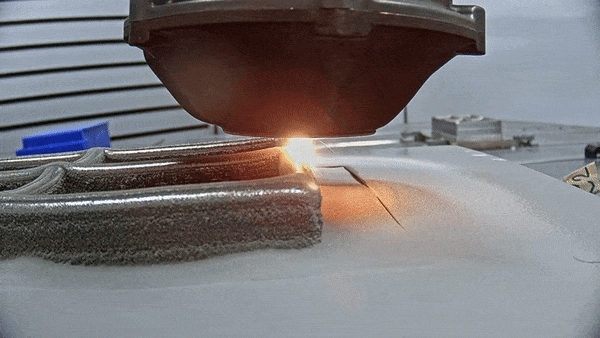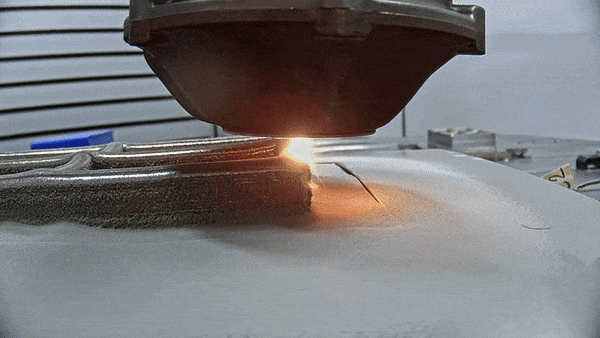
To go to new places in space, or do new things, usually demands innovative technologies, and often novel materials and manufacturing techniques as well. So ESA and NASA have teamed up to support a major international conference on Advanced Manufacturing – bringing together Industry 4.0 with Space 4.0.































