
Copernical Team
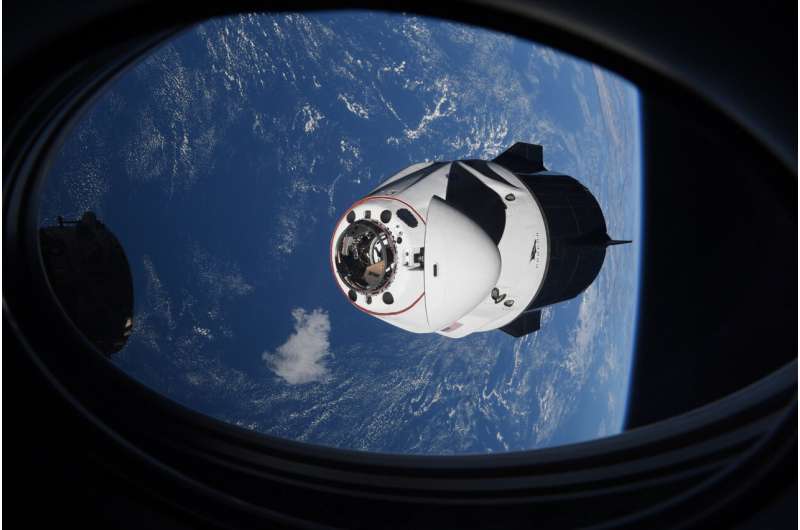
NASA: Space station remains at risk from weapons test debris

Moon lighting: partial lunar eclipse to be longest since 1440
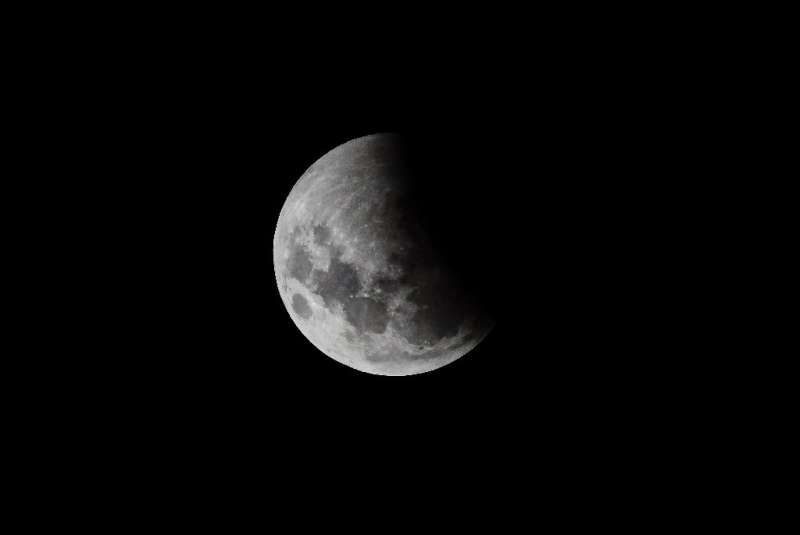

The longest partial lunar eclipse in nearly 600 years, which will bathe the Moon in red, will be visible Thursday and Friday for a big slice of humanity.
The celestial show will see the Moon almost completely cast in shadow as it moves behind the Earth, reddening 99 percent of its face.
The spectacle will be visible for all of North America, as well as parts of South America, Polynesia, Australia and northeast Asia.
Space scientists say sky-watchers in those parts who are blessed with a cloud-free view will see a slight dimming of the Moon from 0602 GMT Friday as it enters Earth's penumbra—the outer shadow.
An hour later it will appear as if someone has taken a giant bite out of the lunar disc as it starts to pass into the umbra—the full shadow.
By 0845 GMT the Moon will appear red, with the most vivid coloring visible at peak eclipse 18 minutes later.
NASA's Laser Communications Relay Demonstration: 6 things you need to know
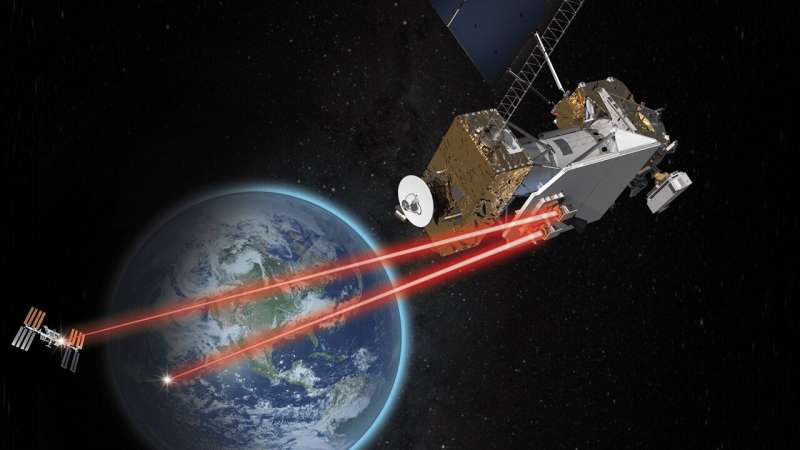

NASA's Laser Communications Relay Demonstration (LCRD) will use laser communications systems to transmit data from space to Earth. Below are six things you need to know about NASA's revolutionary LCRD mission.
1. Laser communications will transform how NASA gets info to and from space
Since the dawn of space exploration, NASA has used radio frequency systems to communicate with astronauts and spacecraft. However, as space missions generate and collect more data, the need for enhanced communications capabilities increases. LCRD leverages the power of laser communications, which uses infrared light rather than radio waves, to encode and transmit information to and from Earth.
Both radio waves and laser infrared light waves are forms of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths at different points on the spectrum. Missions encode their scientific data onto the electromagnetic signals to send back to Earth.
The infrared light used for laser communications differs from radio waves because it occurs at a much higher frequency, allowing engineers to pack more data into each transmission.
Solar Orbiter’s riskiest flyby
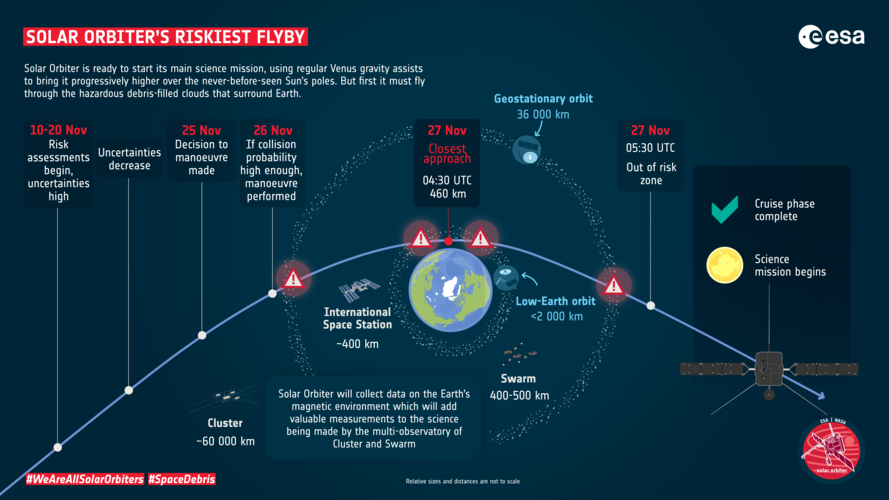 Image:
Solar Orbiter’s riskiest flyby
Image:
Solar Orbiter’s riskiest flyby Transform our inventions into commercial applications

ESA develops a vast array of innovative technologies and applications to make Europe's space endeavours happen. Many of these inventions are protected by patents, resulting in a portfolio of around 580 patents or patent applications. ESA is now offering you the opportunity to find and mature real-world applications of these inventions.
Washington state flooding
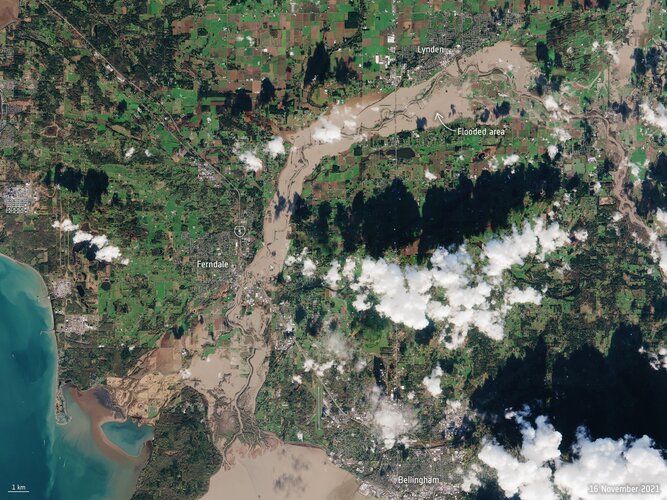 Image:
The US State of Washington is under a state of emergency following days of severe wind and rain leading to extensive flooding in parts of the state. Different satellites in orbit carry different instruments that can provide us with a wealth of complementary information to understand and to
Image:
The US State of Washington is under a state of emergency following days of severe wind and rain leading to extensive flooding in parts of the state. Different satellites in orbit carry different instruments that can provide us with a wealth of complementary information to understand and to Live coverage from the Intermediate Ministerial Meeting

Government ministers in charge of space activities in ESA’s Member States meet on 19 November at an Intermediate Ministerial Meeting in Matosinhos, Portugal. Join us on ESA Web TV for live coverage, including an inflight call with ESA Astronaut Matthias Maurer on the International Space Station.
SpaceX's Musk: 1st Starship test flight to orbit in January

SpaceX founder Elon Musk said Wednesday that his company will attempt to launch its futuristic, bullet-shaped Starship to orbit in January, but he's not betting on success for that first test flight.
"There's a lot of risk associated with this first launch, so I would not say that it is likely to be successful, but we'll make a lot of progress," he said during a virtual meeting organized by the National Academy of Sciences.
Musk said he's confident Starship—launching for the first time atop a mega booster—will successfully reach orbit sometime in 2022. After a dozen or so orbital test flights next year, SpaceX then would start launching valuable satellites and other payloads to orbit on Starships in 2023, he said.
NASA has contracted with SpaceX to use Starship for delivering astronauts to the lunar surface as early as 2025. Musk plans to use the reusable ships to eventually land people on Mars.
The shiny, stainless steel Starship and its first-stage booster—called the Super Heavy—will be the biggest rocket ever to fly, towering 394 feet (120 meters). Liftoff thrust, Musk noted, will be more than double that of NASA's Saturn V rockets that carried astronauts to the moon a half-century ago.
Solar Orbiter returns to Earth
 Video:
00:01:00
Video:
00:01:00
Solar Orbiter’s crucial flyby of Earth on 27 November will place the spacecraft onto the correct orbit for its science phase to begin. But the manoeuvre is not without risk. At closest approach, the spacecraft will be around 460 km above our planet. This is in the Low Earth Orbit zone, where the International Space Station and many other spacecraft can be found. It is also home to a lot of space debris, meaning that there is a small risk of a collision between Solar Orbiter and some space junk. To reach this region, Solar Orbiter will





































