Copernical Team
Astronomers Detect Signature of Magnetic Field on an Exoplanet
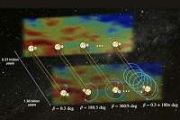
 An international team of astronomers used data from the Hubble Space Telescope to discover the signature of a magnetic field in a planet outside our solar system. The finding, described in a paper in the journal Nature Astronomy, marks the first time such a feature has been seen on an exoplanet.
A magnetic field best explains the observations of an extended region of charged carbon particl
An international team of astronomers used data from the Hubble Space Telescope to discover the signature of a magnetic field in a planet outside our solar system. The finding, described in a paper in the journal Nature Astronomy, marks the first time such a feature has been seen on an exoplanet.
A magnetic field best explains the observations of an extended region of charged carbon particl ESO telescopes help uncover largest group of rogue planets yet
 "We did not know how many to expect and are excited to have found so many," says Nuria Miret-Roig, an astronomer at the Laboratoire d'Astrophysique de Bordeaux, France and the University of Vienna, Austria, and the first author of the new study published in Nature Astronomy.
Rogue planets, lurking far away from any star illuminating them, would normally be impossible to image. However, Mir
"We did not know how many to expect and are excited to have found so many," says Nuria Miret-Roig, an astronomer at the Laboratoire d'Astrophysique de Bordeaux, France and the University of Vienna, Austria, and the first author of the new study published in Nature Astronomy.
Rogue planets, lurking far away from any star illuminating them, would normally be impossible to image. However, Mir Billions of starless planets haunt dark cloud cradles
 In Lovecraftian horror, the Universe is filled with "dark planets" ungraced by the light of a host star. New research shows that reality might be even scarier. An international team composed of French, Japanese, and Spanish astronomers has found about 100 planets floating freely in space rather than orbiting stars. Extrapolating this sample to the rest of the Milky Way Galaxy suggests that there
In Lovecraftian horror, the Universe is filled with "dark planets" ungraced by the light of a host star. New research shows that reality might be even scarier. An international team composed of French, Japanese, and Spanish astronomers has found about 100 planets floating freely in space rather than orbiting stars. Extrapolating this sample to the rest of the Milky Way Galaxy suggests that there Earth and Mars were formed from inner Solar System material
 Earth and Mars were formed from material that largely originated in the inner Solar System; only a few percent of the building blocks of these two planets originated beyond Jupiter's orbit. A group of researchers led by the University of Munster (Germany) report these findings in the journal "Science Advances".
They present the most comprehensive comparison to date of the isotopic composit
Earth and Mars were formed from material that largely originated in the inner Solar System; only a few percent of the building blocks of these two planets originated beyond Jupiter's orbit. A group of researchers led by the University of Munster (Germany) report these findings in the journal "Science Advances".
They present the most comprehensive comparison to date of the isotopic composit NASA Selects New Members for Artemis Rover Science Team
 When NASA's Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, or VIPER, explores and samples the soils at the Moon's South Pole, scientists anticipate it will reveal answers to some of the Moon's enduring mysteries. Where is the water and how much is there? Where did the Moon's water come from? What other resources are there?
What other questions could VIPER answer? NASA sought ideas and re
When NASA's Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, or VIPER, explores and samples the soils at the Moon's South Pole, scientists anticipate it will reveal answers to some of the Moon's enduring mysteries. Where is the water and how much is there? Where did the Moon's water come from? What other resources are there?
What other questions could VIPER answer? NASA sought ideas and re Virgin Orbit and Arqit expand launch agreements
 Virgin Orbit, the responsive launch and space solutions company that has announced a planned business combination with NextGen Acquisition Corp. II, has signed a new launch contract covering two dedicated launches for Arqit Quantum, Inc. a global leader in quantum encryption technology, plus additional commitments.
The two Arqit satellites delivered to Earth orbit by Virgin Orbit's Launche
Virgin Orbit, the responsive launch and space solutions company that has announced a planned business combination with NextGen Acquisition Corp. II, has signed a new launch contract covering two dedicated launches for Arqit Quantum, Inc. a global leader in quantum encryption technology, plus additional commitments.
The two Arqit satellites delivered to Earth orbit by Virgin Orbit's Launche NASA Builds Artemis III Core Stage Forward Skirt
 NASA and Boeing crews have successfully placed the forward skirt for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) Artemis III rocket into the Vertical Assembly Center robotic weld tool for its next phase of production at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans.
The forward skirt sits atop the rocket's core stage, and it will be outfitted with the rocket's flight computers and avionics systems
NASA and Boeing crews have successfully placed the forward skirt for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) Artemis III rocket into the Vertical Assembly Center robotic weld tool for its next phase of production at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans.
The forward skirt sits atop the rocket's core stage, and it will be outfitted with the rocket's flight computers and avionics systems Visual displays in space station culture
 The International Space Station Archaeological Project is the first archaeological study of a human habitat in space. Because of the prohibitive cost of travelling to space, archaeologists have had to think of creative ways to investigate the material culture of the space station. One method is to analyze the thousands of photographs taken of the space station's interior.
Authors Dr. Justi
The International Space Station Archaeological Project is the first archaeological study of a human habitat in space. Because of the prohibitive cost of travelling to space, archaeologists have had to think of creative ways to investigate the material culture of the space station. One method is to analyze the thousands of photographs taken of the space station's interior.
Authors Dr. Justi PLD Space closes a Series B investment round of $28 million
 PLD Space, the Spanish company that leads the space launch business for small satellites in Europe, has just closed a Series B funding round of $28 million.
The operation, led by Arcano Partners, Aciturri and the Centre for the Development of Industrial Technology (CDTI) through the co-investment initiative of Innvierte program, has had the accompaniment of previous company shareholders, w
PLD Space, the Spanish company that leads the space launch business for small satellites in Europe, has just closed a Series B funding round of $28 million.
The operation, led by Arcano Partners, Aciturri and the Centre for the Development of Industrial Technology (CDTI) through the co-investment initiative of Innvierte program, has had the accompaniment of previous company shareholders, w Russia stages 'successful' third launch of new rocket
Russia has conducted a third launch of its new heavy-class Angara rocket, the first developed after the fall of the Soviet Union 30 years ago this month.
Space agency Roscosmos announced late Monday that the next-generation Angara-A5 rocket had been launched with a mock payload from Plesetsk in northern Russia.
It was the third launch of the new rocket after its maiden voyage in 2014.
"Roscosmos congratulates the military-space forces and the entire Russian space industry," the agency said in a statement, calling the launch "successful".
Agency head Dmitry Rogozin welcomed the news on Telegram, writing: "Come on, baby!"
The defence ministry added: "All prelaunch operations and the launch of the Angara-A5 rocket took place properly."
The last launch of the heavy-class Angara rocket took place in December 2020.
Angara rockets—named after a Siberian river flowing out of Lake Baikal—are the first new family of launchers to be built after the collapse of the Soviet Union.
They are designed to replace the Proton rockets that date back to the 1960s and have suffered a series of failures in recent years.
President Vladimir Putin hopes the new launchers will revive Russia's space industry and reduce reliance on other former Soviet countries.