Copernical Team
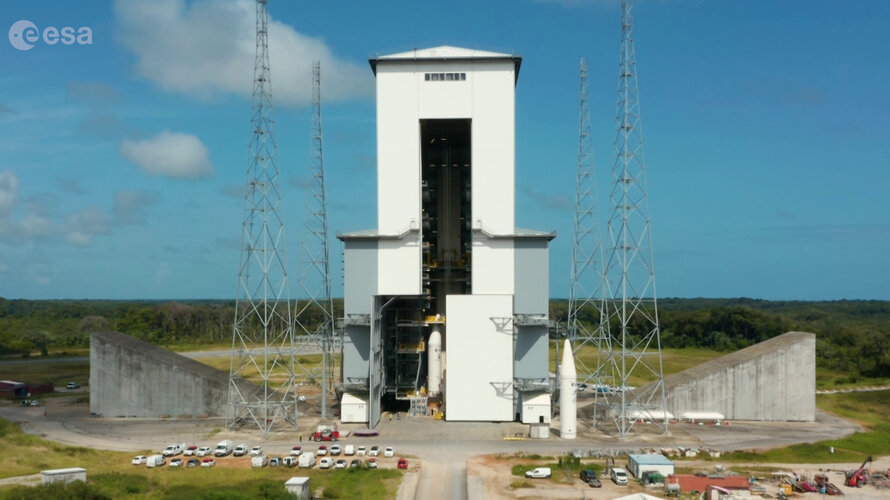
Ariane 6 launch complex – December 2021
 Video:
00:02:15
Video:
00:02:15
Tour the new launch complex for Ariane 6 at Europe's Spaceport in French Guiana.
First, enter the launch vehicle assembly building which is 20 m tall, 112 m long, and 41 m wide, located a kilometre away from the launch zone. It is used for horizontal integration and preparation of the central core of Ariane 6 – its main stage and upper stage – before it is rolled out to the launch zone.
The hydrogen and oxygen storage facilities connect to the launch pad via underground pipes as part of the launch support systems.
The 8200 tonne 90 metre-high mobile
SwRI scientist helps simulate how our solar system formed from rings
 A Southwest Research Institute scientist contributed to a new solar system formation model that explains the existing inner planetary distribution and the asteroid belt between the inner and outer solar system. SwRI's Dr. Rogerio Deienno, who specializes in celestial mechanics and dynamical astronomy, and his colleagues developed a model where three rings of planetesimals, the building blocks fo
A Southwest Research Institute scientist contributed to a new solar system formation model that explains the existing inner planetary distribution and the asteroid belt between the inner and outer solar system. SwRI's Dr. Rogerio Deienno, who specializes in celestial mechanics and dynamical astronomy, and his colleagues developed a model where three rings of planetesimals, the building blocks fo FAST detects coherent interstellar magnetic field with a technique conceived at Arecibo
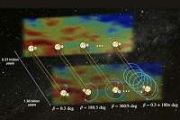
 Magnetic fields are the essential, but often "secret" ingredients of the interstellar medium and the process of making stars. The secrecy shrouding interstellar magnetic fields can be attributed to the lack of experimental probes.
While Michael Faraday was already probing the link between magnetism and electricity with coils in the early 19th century in the basement of the Royal Institutio
Magnetic fields are the essential, but often "secret" ingredients of the interstellar medium and the process of making stars. The secrecy shrouding interstellar magnetic fields can be attributed to the lack of experimental probes.
While Michael Faraday was already probing the link between magnetism and electricity with coils in the early 19th century in the basement of the Royal Institutio Metaverse gets touch of reality at CES
 A jacket equipped with sensors that let wearers feel hugs or even punches in virtual reality was among the innovations giving the metaverse a more realistic edge at the Consumer Electronics Show.
"What is the metaverse if you can't feel it?" asked Jose Fuertes, founder of the Spain-based startup Owo, which made the jacket. "It's just avatars."
The "metaverse" - a parallel universe where
A jacket equipped with sensors that let wearers feel hugs or even punches in virtual reality was among the innovations giving the metaverse a more realistic edge at the Consumer Electronics Show.
"What is the metaverse if you can't feel it?" asked Jose Fuertes, founder of the Spain-based startup Owo, which made the jacket. "It's just avatars."
The "metaverse" - a parallel universe where Tiangong's robotic arm performs well in test
 China's Tiangong space station conducted a test using its robotic arm to reposition the Tianzhou 2 cargo spaceship on Thursday morning, according to the China Manned Space Agency.
In a statement, the agency said that the arm secured the robotic cargo craft early on Thursday morning and began to move it to a new position at 6:12 am. Tianzhou 2 had been connected to the station's Tianhe core
China's Tiangong space station conducted a test using its robotic arm to reposition the Tianzhou 2 cargo spaceship on Thursday morning, according to the China Manned Space Agency.
In a statement, the agency said that the arm secured the robotic cargo craft early on Thursday morning and began to move it to a new position at 6:12 am. Tianzhou 2 had been connected to the station's Tianhe core North Korea says it tested hypersonic missile
 North Korea has successfully tested a hypersonic missile, state media reported Thursday, in the first major weapons test by the nuclear-armed nation this year.
This was the second reported test of what Pyongyang claimed were hypersonic gliding missiles, as it pursues the sophisticated technology despite international sanctions and condemnation.
Hypersonic missiles move far faster and are
North Korea has successfully tested a hypersonic missile, state media reported Thursday, in the first major weapons test by the nuclear-armed nation this year.
This was the second reported test of what Pyongyang claimed were hypersonic gliding missiles, as it pursues the sophisticated technology despite international sanctions and condemnation.
Hypersonic missiles move far faster and are Japan space tourist eyes Mariana Trench trip after ISS
 Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa said Friday his trip into space had given him a new appreciation for Earth, and he now hopes to plunge into the ocean's forbidding Mariana Trench.
Maezawa and his assistant Yozo Hirano spent 12 days on the International Space Station last month, where they documented life in space for one million YouTube subscribers.
Speaking Friday for the first time
Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa said Friday his trip into space had given him a new appreciation for Earth, and he now hopes to plunge into the ocean's forbidding Mariana Trench.
Maezawa and his assistant Yozo Hirano spent 12 days on the International Space Station last month, where they documented life in space for one million YouTube subscribers.
Speaking Friday for the first time New research questions 'whiff of oxygen' in Earth's early history
 Evidence arguing for a "whiff of oxygen" before the Earth's Great Oxygenation Event 2.3 billion years ago are chemical signatures that were probably introduced at a much later time, according to research published in Science Advances.
The result rewinds previous research findings that atmospheric oxygen existed prior to the so-called Great Oxygenation Event-known to researchers as "GOE"- a
Evidence arguing for a "whiff of oxygen" before the Earth's Great Oxygenation Event 2.3 billion years ago are chemical signatures that were probably introduced at a much later time, according to research published in Science Advances.
The result rewinds previous research findings that atmospheric oxygen existed prior to the so-called Great Oxygenation Event-known to researchers as "GOE"- a Debris from failed Russian rocket falls into sea near French Polynesia
 The upper stage of a failed Russian Angara A5 rocket plummeted uncontrolled to Earth, crashing into open sea near French Polynesia.
The U.S. 18th Space Control Squadron confirmed the 4 p.m. Wednesday re-entry
The Persei upper stage was part of a heavy-lift rocket. The debris weighed an estimated 3.5 tons. Astronomer Jonathon McDowell of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophy
The upper stage of a failed Russian Angara A5 rocket plummeted uncontrolled to Earth, crashing into open sea near French Polynesia.
The U.S. 18th Space Control Squadron confirmed the 4 p.m. Wednesday re-entry
The Persei upper stage was part of a heavy-lift rocket. The debris weighed an estimated 3.5 tons. Astronomer Jonathon McDowell of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophy Why the Webb Telescope doesn't have deployment cameras
 As NASA's James Webb Space Telescope makes its way out to its intended orbit, ground teams monitor its vitals using a comprehensive set of sensors located throughout the entire spacecraft. Mechanical, thermal, and electrical sensors provide a wide array of critical information on the current state and performance of Webb while it is in space.
A system of surveillance cameras to watch deplo
As NASA's James Webb Space Telescope makes its way out to its intended orbit, ground teams monitor its vitals using a comprehensive set of sensors located throughout the entire spacecraft. Mechanical, thermal, and electrical sensors provide a wide array of critical information on the current state and performance of Webb while it is in space.
A system of surveillance cameras to watch deplo