Copernical Team
First Multiple-Sol Drive
 Perseverance capped its first year on Mars by speeding back around Seitah toward what is expected to be the final sampling location in its crater floor campaign. The drive on Mars was split across three different sols executing instructions planned in a single day on Earth, making this Perseverance's first multiple-sol drive.
Why are we excited about the multiple-sol drive? It creates an o
Perseverance capped its first year on Mars by speeding back around Seitah toward what is expected to be the final sampling location in its crater floor campaign. The drive on Mars was split across three different sols executing instructions planned in a single day on Earth, making this Perseverance's first multiple-sol drive.
Why are we excited about the multiple-sol drive? It creates an o New rocket to be partially reusable
 China's next-generation rocket designed to carry astronauts will be multifunctional and partly reusable, according to a senior rocket scientist.
Wang Xiaojun, president of the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, the country's major maker of carrier rockets, told an international forum in mid-February that the new rocket, which has yet to be named, will have two models.
The fi
China's next-generation rocket designed to carry astronauts will be multifunctional and partly reusable, according to a senior rocket scientist.
Wang Xiaojun, president of the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology, the country's major maker of carrier rockets, told an international forum in mid-February that the new rocket, which has yet to be named, will have two models.
The fi Rocket Lab selects Virginia for Neutron launch pad and manufacturing complex
 Rocket Lab USA, Inc (Nasdaq: RKLB) has selected Wallops Island, Virginia, as the location for its first launch site and extensive manufacturing and operations facilities, for its 8-ton payload class reusable Neutron rocket.
The Neutron Production Complex and launch pad for its Neutron rocket will be located adjacent to and within the NASA Wallops Flight Facility and Mid-Atlantic Regional S
Rocket Lab USA, Inc (Nasdaq: RKLB) has selected Wallops Island, Virginia, as the location for its first launch site and extensive manufacturing and operations facilities, for its 8-ton payload class reusable Neutron rocket.
The Neutron Production Complex and launch pad for its Neutron rocket will be located adjacent to and within the NASA Wallops Flight Facility and Mid-Atlantic Regional S NASA awards SpaceX additional crew flights to Space Station
 NASA has awarded three additional missions to Space Exploration Technologies Corporation (SpaceX) of Hawthorne, California, for crew transportation services to the International Space Station as part of its Commercial Crew Transportation Capability (CCtCap) contract.
The CCtCap modification, following the agency's notice of intent to procure the flights in December 2021, brings the total m
NASA has awarded three additional missions to Space Exploration Technologies Corporation (SpaceX) of Hawthorne, California, for crew transportation services to the International Space Station as part of its Commercial Crew Transportation Capability (CCtCap) contract.
The CCtCap modification, following the agency's notice of intent to procure the flights in December 2021, brings the total m Europe's joint Mars mission with Russia postponed by war

The launch of a joint Europe-Russian mission to Mars this year is now "very unlikely" due to sanctions linked to the war in Ukraine, the European Space Agency said Monday.
NASA exploring ways to keep ISS afloat without Russian help: official

NASA is exploring ways to keep the International Space Station in orbit without Russian help, but doesn't see any immediate signs Moscow is withdrawing from the collaboration following the invasion of Ukraine, a senior official said Monday.
Kathy Lueders, who heads the agency's human spaceflight program, told reporters on a call that operations on the research platform were proceeding "nominally" and "we're not getting any indications at a working level that our counterparts are not committed.
ISS experiments to find solutions for cleaning up orbital debris and repairing damaged satellites

In 2002, the European Space Agency launched Envisat, the largest civilian satellite (at the time) to go to low Earth orbit (LEO).
ULA Atlas V rocket topped off with NOAA's GOES-T satellite
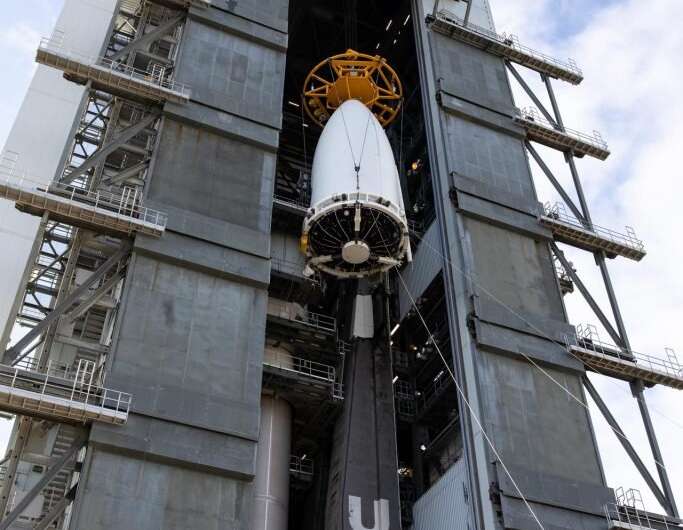

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-T (GOES-T) satellite now officially has its ride.
GOES-T was transported from Astrotech's Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida, to United Launch Alliance's (ULA) nearby Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station's Space Launch Complex 41. It was then mated to the top of the Atlas V 541 rocket, which will carry it into space.
ESA statement regarding cooperation with Russia following a meeting with Member States on 28 February 2022
Press Release N° 6–2022
We deplore the human casualties and tragic consequences of the war in Ukraine. We are giving absolute priority to taking proper decisions, not only for the sake of our workforce involved in the programmes, but in full respect of our European values, which have always fundamentally shaped our approach to international cooperation.
Keeping it fluid(ics) | Cosmic Kiss 360°
 Video:
00:02:58
Video:
00:02:58
Europe’s Columbus laboratory is a hive of activity in this 360° timelapse as ESA astronaut Matthias Maurer works on an experiment called Fluidics and his NASA colleague Raja Chari carries out activity in the Veggie plant habitat.
Developed by French space agency CNES and co-funded by Airbus, the Fluidics experiment investigates how liquids behave in space. It was first run by ESA astronaut Thomas Pesquet in 2017 during his Proxima mission.
Made up of six small, transparent spheres housed in the black centrifuge seen here, the experiment studies two phenomena. The first is ‘sloshing’ or how liquids move in