
Copernical Team
Elon Musk had twins with company exec last year: report
 Billionaire tech entrepreneur Elon Musk had twins last year with an executive at one of his companies, online outlet Insider reported Wednesday, citing Texas court documents.
The babies' mother, 36-year-old Canadian Shivon Zilis, is an executive at Neuralink, Musk's brain-implant maker, and has worked at multiple of his other companies, including OpenAI and electric car manufacturer Tesla, I
Billionaire tech entrepreneur Elon Musk had twins last year with an executive at one of his companies, online outlet Insider reported Wednesday, citing Texas court documents.
The babies' mother, 36-year-old Canadian Shivon Zilis, is an executive at Neuralink, Musk's brain-implant maker, and has worked at multiple of his other companies, including OpenAI and electric car manufacturer Tesla, I Boeing subsidiary to build two new Virgin Galactic motherships
 Virgin Galactic confirmed Wednesday it is retaining Boeing subsidiary Aurora Flight Sciences to build two next generation motherships, the company announced on Wednesday.
The agreement calls for the first ship to enter service in 2025, the same year Virgin Galactic's first Delta-class spaceship is expected to begin revenue payload flights.
They represent the spaceflight company's
Virgin Galactic confirmed Wednesday it is retaining Boeing subsidiary Aurora Flight Sciences to build two next generation motherships, the company announced on Wednesday.
The agreement calls for the first ship to enter service in 2025, the same year Virgin Galactic's first Delta-class spaceship is expected to begin revenue payload flights.
They represent the spaceflight company's NASA re-establishes contact with CAPSTONE spacecraft
 NASA has regained communications with its new lunar spacecraft, the space agency confirmed on Wednesday.
"Mission operators have re-established contact with NASA's Cislunar Autonomous Positioning System Technology Operations and Navigation Experiment (CAPSTONE) spacecraft," NASA said in a statement.
It did not immediately provide additional details or updates.
"We have re-
NASA has regained communications with its new lunar spacecraft, the space agency confirmed on Wednesday.
"Mission operators have re-established contact with NASA's Cislunar Autonomous Positioning System Technology Operations and Navigation Experiment (CAPSTONE) spacecraft," NASA said in a statement.
It did not immediately provide additional details or updates.
"We have re- Testing the effect of multicolor lighting on improving people's psychological state
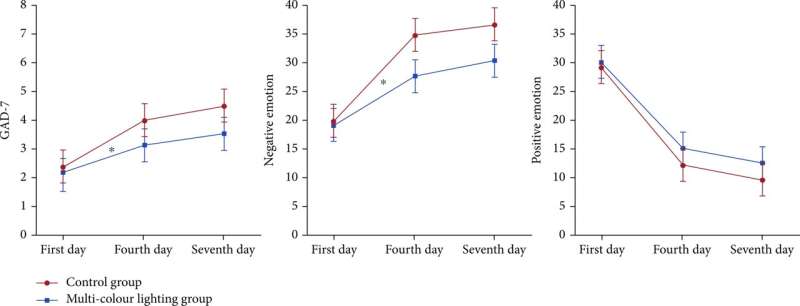
As missions for deep space exploration and space habitats are put on the agenda, astronauts need to withstand being tested by multiple stressors in confined and isolated conditions during such long flights, especially because in deep space exploration, problems such as signal delays make astronauts feel the anxiety of being far away from Earth and the psychological fear of deep space.
According to a series of experiments conducted recently on Earth and during current space missions aboard the International Space Station (ISS), NASA believes that monotony of vision, in particular, aggravates the crew's anxiety, irritability, and depression. Moreover, a large number of studies have also found that crew members on long-term missions on the Antarctic Space Simulation Station are extremely susceptible to psychological problems caused by visual monotony and monochromatic colors.
Contact restored with NASA spacecraft headed to lunar orbit

User Consultation Meeting on Harmony: watch the replay

User Consultation Meeting on Harmony: watch the replay
Follow the discussions on Harmony – the candidate mission for ESA’s tenth Earth Explorer
How to see Webb’s new images
As excitement mounts for the unveiling of Webb’s first full-colour images on Tuesday 12 July, here’s how to participate in the global celebration via ESA’s channels. Choose from watching a livestream, attending an in-person event, or joining our social media activities.
City heat extremes
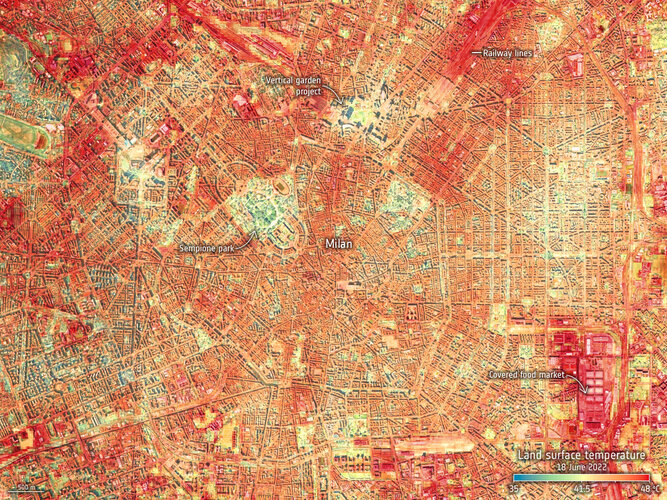
With air temperatures in excess of 10°C above the average for the time of year in parts of Europe, the United States and Asia, June 2022 has gone down as a record breaker. The fear is that these extreme early-season heatwaves are a taste of what could soon be the norm as climate change continues to take hold. For those in cities, the heat dissipates slower creating ‘urban heat islands’, which make everyday life even more of a struggle.
An instrument, carried on the International Space Station, has captured the recent land-surface temperature extremes for
New navigation missions for enhanced satnav and Earth mapping

ESA’s Navigation Directorate – already the design architect of the Galileo satellite navigation system, Europe’s largest satellite constellation – is reaching out to European industry as it plans the development and in-orbit validation of future ‘positioning, navigation and timing’ (PNT) missions into novel orbits.
Rover plus astronaut complete Mount Etna challenge

In a complex role-played version of a mission to the Moon, controllers at ESOC combined with a team of geological scientists and ESA astronaut Thomas Reiter to oversee a rover’s collection of rock samples. Acting as if he were in lunar orbit, the astronaut was in fact based in a hotel room in Catania, Sicily, with the rover 23 km away and 2 600 m uphill on the volcanic flanks of Mount Etna. As Thomas commanded the rover to pick up rocks his hand experienced just what the robot’s gripper felt – an added dimension in remote
































