Copernical Team
Rocket Lab Announces Neutron Development Update to be Provided on December 2, 2021
 Rocket Lab USA will provide the first major update on the development of the Neutron launch vehicle on December 2, 2021 at 8:00 am EST. The virtual event will be streamed live via Rocket Lab's YouTube channel, which can be accessed at that time at https://youtu.be/A0thW57QeDM.
Join Rocket Lab founder and CEO Peter Beck as he reveals new details about Neutron's unique design, materials, pro
Rocket Lab USA will provide the first major update on the development of the Neutron launch vehicle on December 2, 2021 at 8:00 am EST. The virtual event will be streamed live via Rocket Lab's YouTube channel, which can be accessed at that time at https://youtu.be/A0thW57QeDM.
Join Rocket Lab founder and CEO Peter Beck as he reveals new details about Neutron's unique design, materials, pro Rocket industrial park put into operation in Wuhan
 The China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation Limited (CASIC) said that it completed the construction of an intelligent satellite production line and a rocket industrial park in the central Chinese city of Wuhan.
Located in the Wuhan National Aerospace Industry Base, both the production line and the industrial park went into operation, said Liu Shiquan, general manager of the CASIC.
The China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation Limited (CASIC) said that it completed the construction of an intelligent satellite production line and a rocket industrial park in the central Chinese city of Wuhan.
Located in the Wuhan National Aerospace Industry Base, both the production line and the industrial park went into operation, said Liu Shiquan, general manager of the CASIC. Thales Alenia Space invests in advanced technology for human space flight
 Thales Alenia Space, a joint venture between Thales 67% and Leonardo 33%, has inaugurated a new Friction Stir Welding facility at one of its production sites in Turin, which will double production capacity of pressurized modules, for the production of the future orbiting and surface infrastructures.
The only company in Europe to use this type of processing for pressurized habitation module
Thales Alenia Space, a joint venture between Thales 67% and Leonardo 33%, has inaugurated a new Friction Stir Welding facility at one of its production sites in Turin, which will double production capacity of pressurized modules, for the production of the future orbiting and surface infrastructures.
The only company in Europe to use this type of processing for pressurized habitation module Astroscale space debris removal leaders announce series F raises $109 million
 Astroscale Holdings Inc. ("Astroscale"), the market leader in satellite servicing and long-term orbital sustainability across all orbits, today announced it closed its Series F round with additional funding of U.S. $109 million from a group of new investors led by THE FUND Limited Partnership in Japan, with participation from international investors including Seraphim Space Investment Trust plc
Astroscale Holdings Inc. ("Astroscale"), the market leader in satellite servicing and long-term orbital sustainability across all orbits, today announced it closed its Series F round with additional funding of U.S. $109 million from a group of new investors led by THE FUND Limited Partnership in Japan, with participation from international investors including Seraphim Space Investment Trust plc Testing confirms Webb Telescope on track for targeted Dec 22 lLaunch
 Engineering teams have completed additional testing confirming NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is ready for flight, and launch preparations are resuming toward Webb's target launch date of Wednesday, Dec. 22, at 7:20 a.m. EST.
Additional testing was conducted this week to ensure the observatory's health following an incident that occurred when the release of a clamp band caused a vibrati
Engineering teams have completed additional testing confirming NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is ready for flight, and launch preparations are resuming toward Webb's target launch date of Wednesday, Dec. 22, at 7:20 a.m. EST.
Additional testing was conducted this week to ensure the observatory's health following an incident that occurred when the release of a clamp band caused a vibrati Galileos attached to upper stage as launch draws near
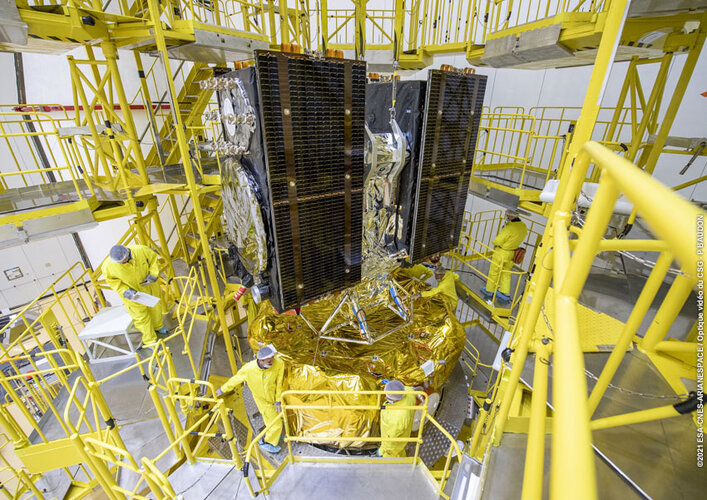 Image:
Galileos attached to upper stage as launch draws near
Image:
Galileos attached to upper stage as launch draws near Galileo satellites in place for launch
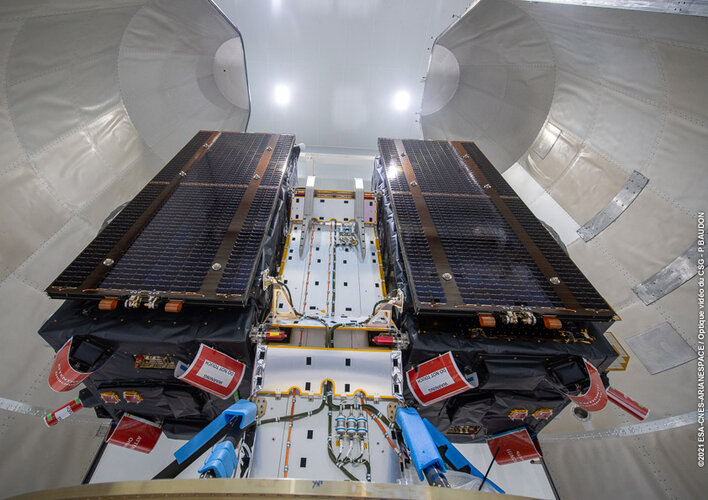

Europe’s next two Galileo satellites have been attached to the dispenser on which they will ride to orbit, and the launcher fairing that will protect them during the first part of the ascent to orbit has been closed around the pair.
Russia launches classified military satellite

Russia on Thursday successfully placed into orbit a military satellite believed to be part of the Kremlin's early warning anti-missile system.
A Soyuz rocket carrying a classified payload blasted off from the Plesetsk cosmodrome in northern Russia in the early hours of Thursday morning, the defence ministry said.
At 0109 GMT a rocket was launched that put a "space apparatus into orbit in the interests of the defence ministry", the ministry said in a statement carried by the Interfax news agency.
It did not provide further details.
According to the Spaceflightnow website, which covers space launches, the launch could be delivering a Tundra satellite.
Russia has previously launched Tundra satellites in 2015, 2017 and 2019, according to Interfax.
Specialist website Russian Space Web said the ground track of Thursday's launch "matched previous missions" delivering satellites for Russia's missile warning system named Kupol or dome.
Unveiled in 2019, Kupol is designed to detect launches of ballistic missiles and track them to their landing site, though its exact configuration is unknown.
In 2018, the US, which suspects Russia of seeking to develop space weapons, said it was alarmed at the "very abnormal behaviour" of a Russian satellite.