
Copernical Team
No toilet for returning SpaceX crew, stuck using diapers

The astronauts who will depart the International Space Station on Sunday will be stuck using diapers on the way home because of their capsule's broken toilet.
NASA astronaut Megan McArthur described the situation Friday as "suboptimal" but manageable. She and her three crewmates will spend 20 hours in their SpaceX capsule, from the time the hatches are closed until Monday morning's planned splashdown.
"Spaceflight is full of lots of little challenges," she said during a news conference from orbit.
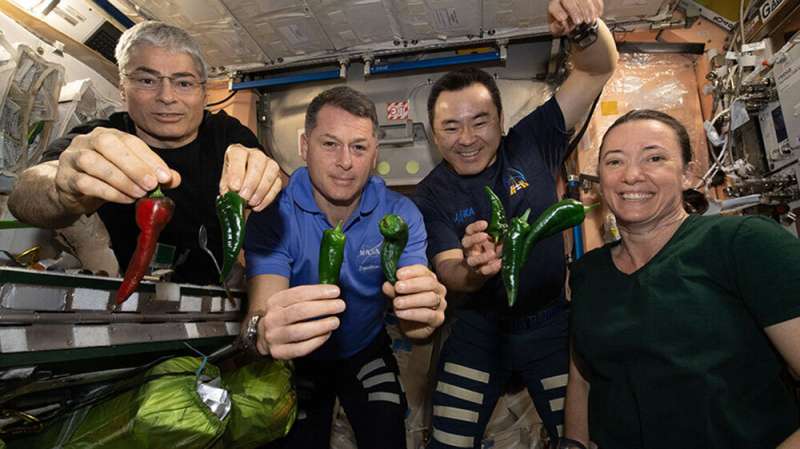
Astronauts to return from space station next week: NASA

Four astronauts are scheduled to return to Earth from the International Space Station early Monday after spending more than six months in space, NASA announced.
The four members of the Crew-2 mission, including a French and a Japanese astronaut, will therefore return to Earth before the arrival of a replacement crew, whose take-off was delayed several times due to unfavorable weather conditions.
NASA said in a statement late Friday that Crew-2 members are due to return to Earth "no earlier than 7:14 am EST (1214 GMT) Monday, Nov. 8, with a splashdown off the coast of Florida."
"As we're preparing to leave, it's kind of a bittersweet feeling, we might never come back to see the ISS, and it's really a magical place," French astronaut Thomas Pesquet said earlier Friday during a press conference from the space station.
New great observatories, including Lynx, recommended as a national priority by decadal survey
The 2020 Decadal Survey for Astronomy and Astrophysics has recommended a new series of three Great Observatories—or space-based telescopes—as a top national priority for the future of space astrophysics.
The Lynx X-Ray Observatory is included as part of this vision. Dozens of scientists and engineers at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian teamed with colleagues around the world to define the observatory's scientific objectives, conceptualize its design and work on key technologies.
Known as the Decadal Survey, the report evaluates astrophysics and astronomy programs and prioritizes them for the next decade of transformative science. Findings from the survey are submitted as recommendations to NASA, the National Science Foundation and the Department of Energy to guide funding requests and allocations for astrophysics over the next 10 years.
"I am pleased to hear that the scientific community endorses a vision for the New Great Observatories that includes Lynx," says Charles Alcock, director of the Center for Astrophysics (CfA). "Lynx will transform our understanding of the cosmos by providing by far the most sensitive X-ray vision into the otherwise invisible universe.
To find life on other planets, NASA rocket team looks to the stars
A NASA sounding rocket will observe a nearby star to learn how starlight affects the atmospheres of exoplanets—key information in the hunt for life outside our solar system.
Last call: fly your payload on first Ariane 6 launch
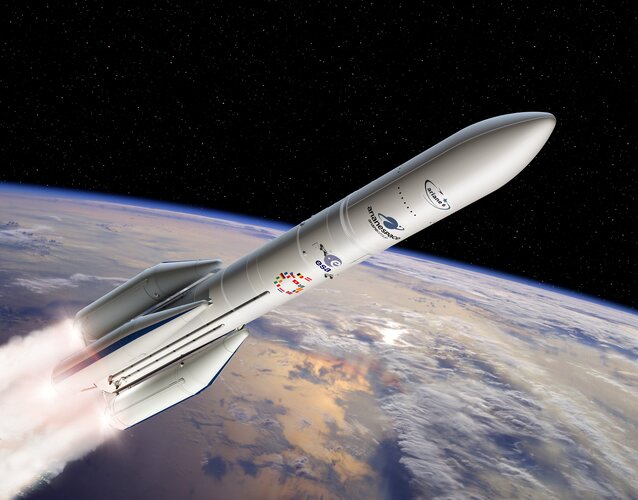

ESA offers an opportunity for payloads and experiments to ride on board the first flight of Ariane 6 planned in 2022. Notice of interest should reach ESA by 15 November.
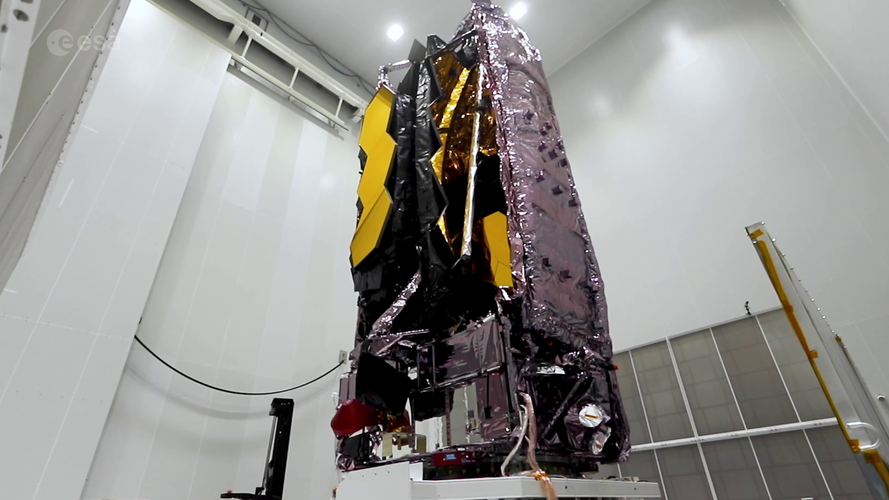
Webb unboxed in cleanroom at Europe’s Spaceport
 Video:
00:01:19
Video:
00:01:19
After its arrival at Pariacabo harbour in French Guiana on 12 October 2021, the James Webb Space Telescope was transported to Europe’s Spaceport and unboxed in the cleanroom. It is now being prepared for its launch on an Ariane 5 rocket in December.
Though the telescope weighs only six tonnes, it is more than 10.5 m high and almost 4.5 m wide when folded. It was shipped in its folded position in a 30 m long container which, with auxiliary equipment, weighed more than 70 tonnes.
After arriving in the harbour, the telescope inside its container
Week in images: 01 - 05 November 2021

Week in images: 01 - 05 November 2021
Discover our week through the lens
Development of the demonstration satellite HIBARI with variable shape attitude control
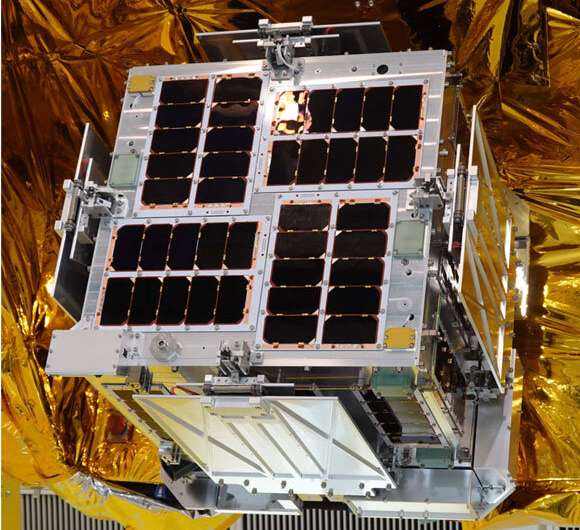

A research team led by Professor Saburo Matunaga of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, School of Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), developed a 50-kg-class technology demonstration microsatellite called HIBARI that denotes "skylark" in English. The purpose of this satellite is the on-orbit demonstration of Variable Shape Attitude Control (VSAC) technology where attitude and orbit are controlled using a variable structure, and the satellite adjusts the attitude via the recoil from the movement of the four movable solar cell paddles. By deploying and retracting the paddles, atmospheric drag can be adjusted and used for orbit control.
HIBARI was selected as a demonstration theme for Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA)'s Innovative Satellite Technology Demonstration (ISTD), and it will be launched on Epsilon-5 sometime after November 2021 from the Uchinoura Space Center. The satellite will be launched into a sun-synchronous orbit at 9:30 Local Sun time at Descending Node with a perigee altitude of 547 km and apogee altitude of 565 km for demonstrating VSAC technology in space.
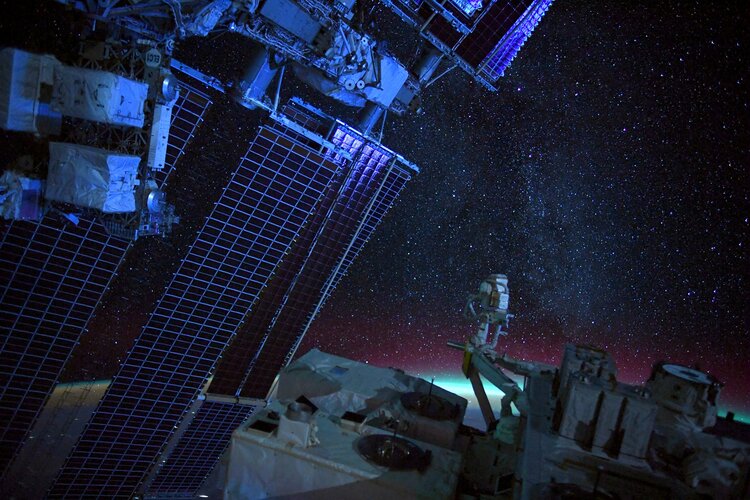
Image: Mind the stars
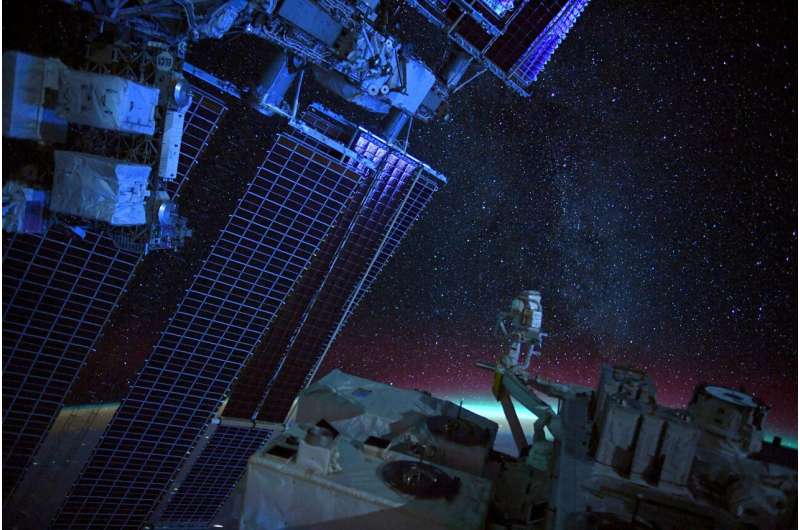

Space can be a cruel mistress, but she is a beautiful one.
As we await the launch of ESA astronaut Matthias Maurer and the return of Thomas Pesquet, let us marvel at the fact that humans live and work in space, an environment so inhospitable to us.
As Thomas nears the end of his six-month mission Alpha on the Space Station, he took this image, noting that living on the International Space Station "really feels like flying on a spaceship into the cosmos… or wait… that's what we do."
While astronauts are often pointing their cameras down to Earth, Thomas looked up for this image. "When you let your eyes adapt to the night, you start seeing millions of stars and it's amazing…there's also a lot of beauty in the cosmos itself, it's just harder to see (and to photograph) at first."
Thanks to collective human intelligence and cooperation, the International Space Station has been a reality for over 20 years, hosting astronauts who run experiments and monitor our planet from above. While launches are quite routine these days, delays happen but that's the space business.
Smart focus on Mars

From panoramas to close-ups, from 3D maps to a wheel selfie, the Earth-bound twin of ESA’s Rosalind Franklin rover is testing the wide range of photo settings that will deliver the greatest science possible during the ExoMars mission on the Red Planet.
