
Copernical Team
Are water plumes spraying from Europa? NASA's Europa Clipper is on the case
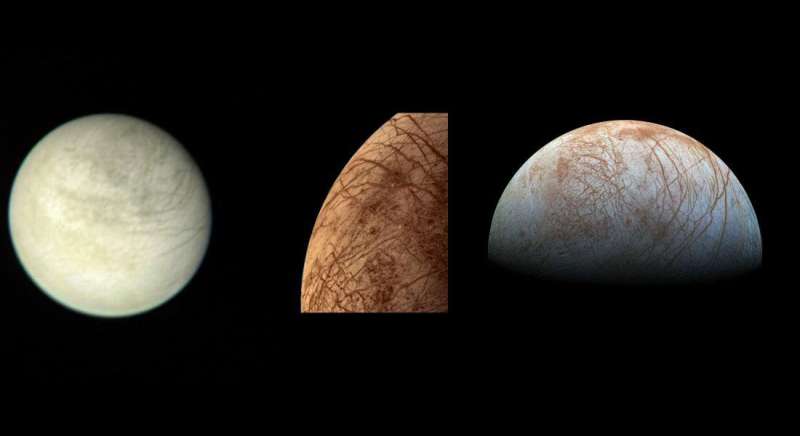

Finding plumes at Europa is an exciting prospect, but scientists warn it'll be tricky, even from up close.
In 2005, images of a brilliant watery plume erupting from the surface of Saturn's moon Enceladus captivated the world. The giant column of vapor, ice particles, and organic molecules spraying from the moon's south polar region suggested that there's a liquid water ocean below Enceladus' ice shell and confirmed the moon is geologically active. The plume also thrust Enceladus and other worlds in the outer solar system, with no atmospheres and far from the heat of the Sun, toward the top of NASA's list of places to search for signs of life.
NASA TV to Air IXPE Prelaunch Activities, Launch
 NASA will provide coverage of the upcoming prelaunch and launch activities for the Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) mission, the first satellite dedicated to measuring the polarization of X-rays from a variety of cosmic sources, such as black holes and neutron stars.
NASA will provide coverage of the upcoming prelaunch and launch activities for the Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) mission, the first satellite dedicated to measuring the polarization of X-rays from a variety of cosmic sources, such as black holes and neutron stars. The Parker Solar Probe is getting pelted by hypervelocity dust. Could it damage the spacecraft?
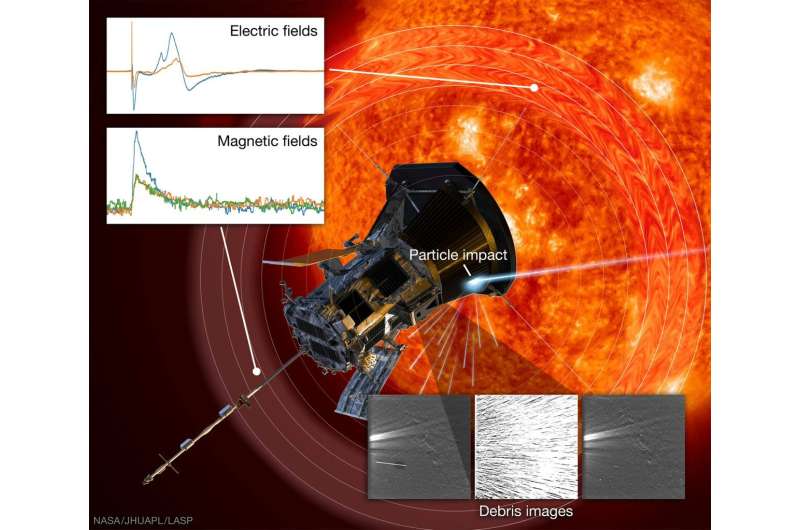
There's a pretty significant disadvantage to going really fast—if you get hit with anything, even if it is small, it can hurt. So when the fastest artificial object ever—the Parker Solar Probe—gets hit by grains of dust that are a fraction the size of a human hair, they still do damage. The question is how much damage, and could we potentially learn anything from how exactly that damage happens? According to new research from scientists at the University of Colorado at Boulder (UCB), the answer to the second question is yes, in fact, we can.
Parker is cruising through the inner solar system on its orbit around the sun at a cool 180 km/s (400,000 mph). But the environment it is traveling through is anything but cool—the probe needs the help of a giant heat shield to ensure that the full force of a star doesn't entirely destroy its innards.
Space junk forces spacewalk delay, too risky for astronauts

Image: ISS captured from the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour
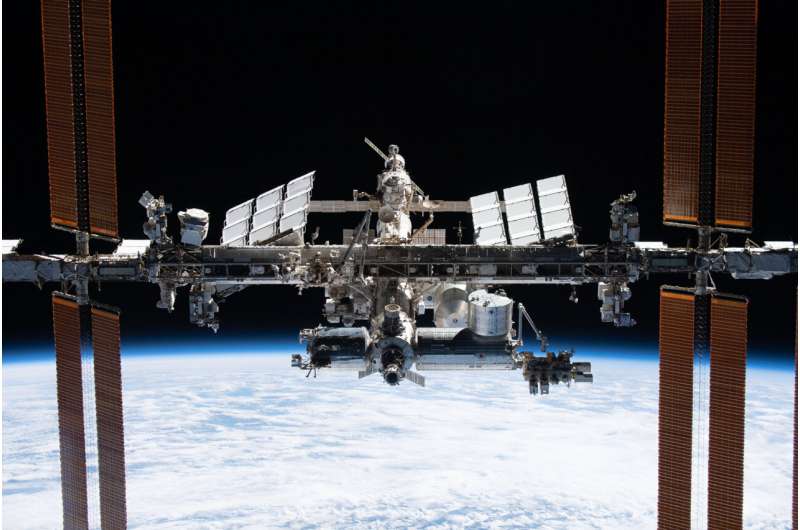

It can be hard to appreciate that a human-made, football-pitch-sized spacecraft is orbiting 400 km above our heads, but there it is.
The jewel of human cooperation and ingenuity that is the International Space Station shines brightly in this image captured by ESA astronaut Thomas Pesquet from the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour.
Crew-2 got this amazing view during a flyaround of the orbiting lab after undocking from the Harmony module on 8 November, before their return to Earth.
Since this image was taken, there has even been a new addition in the form of the Russian Node Module, known as Prichal. The final Russian module planned for the station, it is a spherical node attached to the Russian segment with six docking ports for future Progress and Soyuz arrivals.
A collaboration between five space agencies, the station has become a symbol of peaceful international cooperation for 23 years now. It represents the best of our space engineering capabilities as well as humankind's pursuit of scientific knowledge and exploration.
By any standards, it is an incredible piece of spacecraft engineering. Weighing 420 tons, it travels in low-Earth orbit at more than 27 000 km/hour, circling Earth approximately 16 times every day.
Micro-geostationary satellite wins ESA support
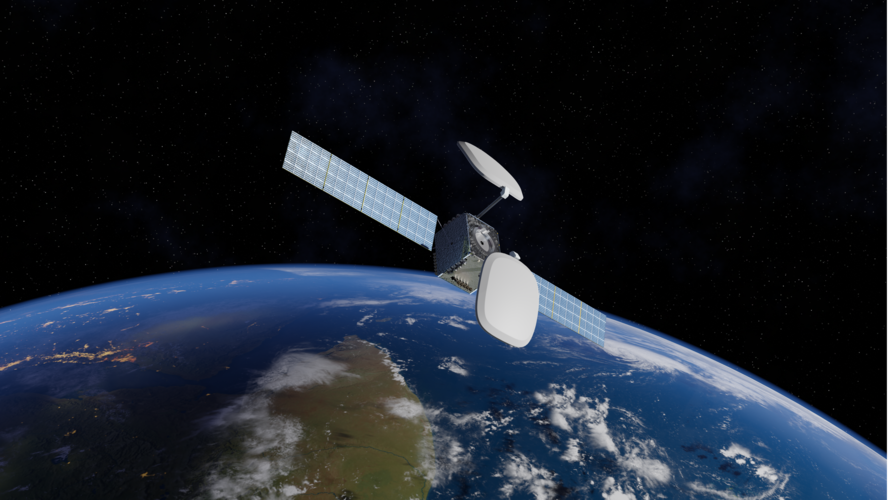

A small European telecommunications satellite intended for launch into geostationary orbit some 36 000 kilometres above the Earth – which can be used as a basis for future satellites – has won support from ESA.
Brain and coat from RUAG Space for Galileo navigation satellites
 On Thursday, December 2 (CET) another two Galileo navigation satellites will be launched from Kourou in French Guiana aboard a Soyuz rocket. This will raise the number of Galileo satellites in orbit from currently 26 to 28. All Galileo satellites use products from RUAG Space, a leading supplier to the space industry.
"We have played an important role in building the European Galileo naviga
On Thursday, December 2 (CET) another two Galileo navigation satellites will be launched from Kourou in French Guiana aboard a Soyuz rocket. This will raise the number of Galileo satellites in orbit from currently 26 to 28. All Galileo satellites use products from RUAG Space, a leading supplier to the space industry.
"We have played an important role in building the European Galileo naviga Kacific enables mobile operators to provide better service to customers
 Kacific Broadband Satellites has introduced the first Ka-band Mobile Backhaul service for Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and telecom operators in Southeast Asia and the Pacific. This will allow operators to extend their network's range in remote and difficult areas and provide them with an effective way of easing congestion in high-demand urban environments.
Mobile Backhaul is part of K
Kacific Broadband Satellites has introduced the first Ka-band Mobile Backhaul service for Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and telecom operators in Southeast Asia and the Pacific. This will allow operators to extend their network's range in remote and difficult areas and provide them with an effective way of easing congestion in high-demand urban environments.
Mobile Backhaul is part of K Knight Sky LLC joins NIC4 to expand critical connectivity solutions for globally
 NIC4, a division of Network Innovations, Inc., announces the acquisition of U.S. government contractor, Knight Sky LLC. The acquisition will effectively combine the expertise of both companies, enhancing the development and delivery of agile, secure and mission critical connectivity solutions for the collective clients of each organization.
NIC4 will complement the existing Knight Sky mana
NIC4, a division of Network Innovations, Inc., announces the acquisition of U.S. government contractor, Knight Sky LLC. The acquisition will effectively combine the expertise of both companies, enhancing the development and delivery of agile, secure and mission critical connectivity solutions for the collective clients of each organization.
NIC4 will complement the existing Knight Sky mana First LoRa message bounced off the moon
 For the first time ever we bounced a LoRa message off the moon on October 5th 2021, using the Dwingeloo radio telescope. This first was achieved by a team consisting of Jan van Muijlwijk (CAMRAS, PA3FXB), Tammo Jan Dijkema (CAMRAS), Frank Zeppenfeldt (ESA, PD0AP) and Thomas Telkamp (Lacuna Space, PA8Z). The signal traveled an amazing distance of 730,360 km, which to our knowledge is the furthest
For the first time ever we bounced a LoRa message off the moon on October 5th 2021, using the Dwingeloo radio telescope. This first was achieved by a team consisting of Jan van Muijlwijk (CAMRAS, PA3FXB), Tammo Jan Dijkema (CAMRAS), Frank Zeppenfeldt (ESA, PD0AP) and Thomas Telkamp (Lacuna Space, PA8Z). The signal traveled an amazing distance of 730,360 km, which to our knowledge is the furthest 