Copernical Team
Testing confirms Webb Telescope on track for targeted Dec 22 lLaunch
 Engineering teams have completed additional testing confirming NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is ready for flight, and launch preparations are resuming toward Webb's target launch date of Wednesday, Dec. 22, at 7:20 a.m. EST.
Additional testing was conducted this week to ensure the observatory's health following an incident that occurred when the release of a clamp band caused a vibrati
Engineering teams have completed additional testing confirming NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is ready for flight, and launch preparations are resuming toward Webb's target launch date of Wednesday, Dec. 22, at 7:20 a.m. EST.
Additional testing was conducted this week to ensure the observatory's health following an incident that occurred when the release of a clamp band caused a vibrati Galileos attached to upper stage as launch draws near
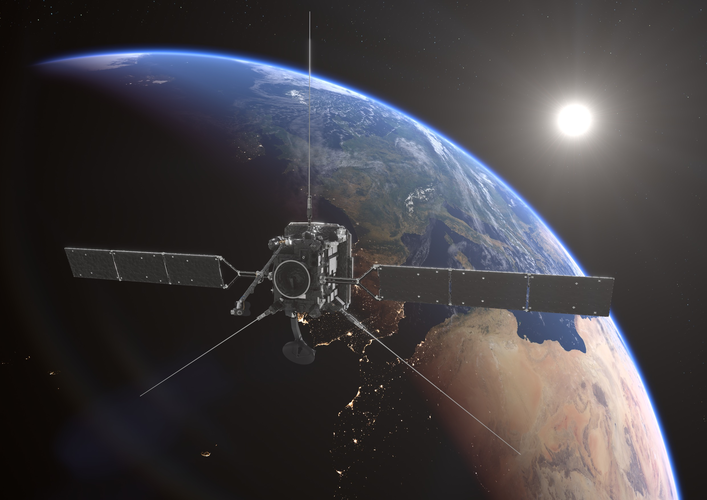
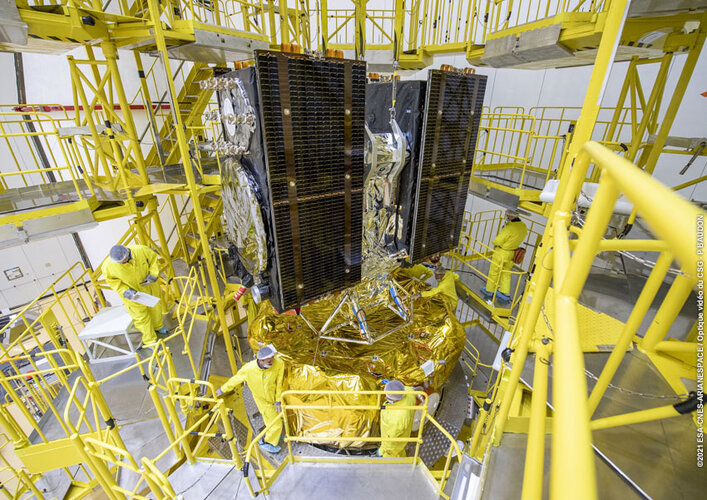 Image:
Galileos attached to upper stage as launch draws near
Image:
Galileos attached to upper stage as launch draws near Galileo satellites in place for launch
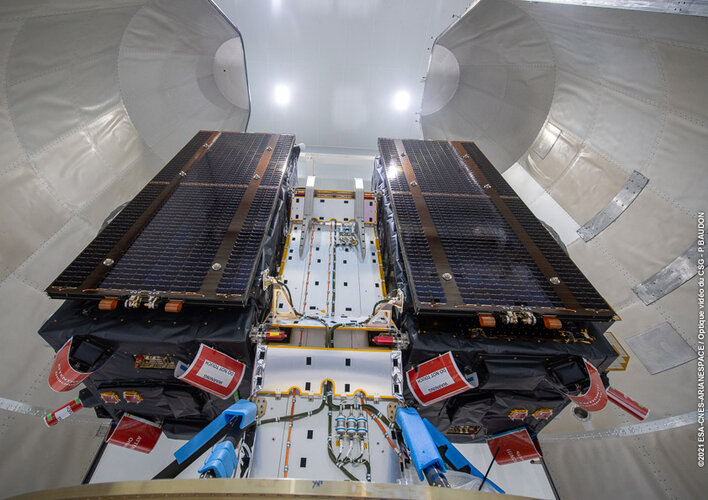

Europe’s next two Galileo satellites have been attached to the dispenser on which they will ride to orbit, and the launcher fairing that will protect them during the first part of the ascent to orbit has been closed around the pair.
Russia launches classified military satellite
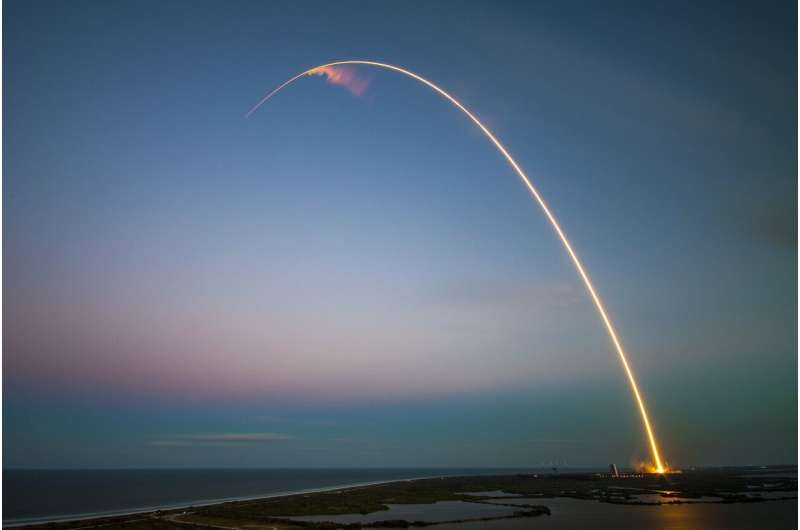

Russia on Thursday successfully placed into orbit a military satellite believed to be part of the Kremlin's early warning anti-missile system.
A Soyuz rocket carrying a classified payload blasted off from the Plesetsk cosmodrome in northern Russia in the early hours of Thursday morning, the defence ministry said.
At 0109 GMT a rocket was launched that put a "space apparatus into orbit in the interests of the defence ministry", the ministry said in a statement carried by the Interfax news agency.
It did not provide further details.
According to the Spaceflightnow website, which covers space launches, the launch could be delivering a Tundra satellite.
Russia has previously launched Tundra satellites in 2015, 2017 and 2019, according to Interfax.
Specialist website Russian Space Web said the ground track of Thursday's launch "matched previous missions" delivering satellites for Russia's missile warning system named Kupol or dome.
Unveiled in 2019, Kupol is designed to detect launches of ballistic missiles and track them to their landing site, though its exact configuration is unknown.
In 2018, the US, which suspects Russia of seeking to develop space weapons, said it was alarmed at the "very abnormal behaviour" of a Russian satellite.
Science with Webb: seeing farther
 Video:
00:01:00
Video:
00:01:00
The James Webb Space Telescope (Webb) is designed to answer fundamental questions about the Universe.
With 100 times more sensitivity than the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, and a mirror which is nearly double the size of ESA’s Herschel Space Observatory, it can detect infrared light generated by galaxies as they formed more than 13.5 billion years ago, in the aftermath of the Big Bang.
For the first time in human history we have the opportunity to directly observe the first stars and galaxies forming in the early Universe. When we observe something that is a million light-years away,
Isolate in Antarctica, for science
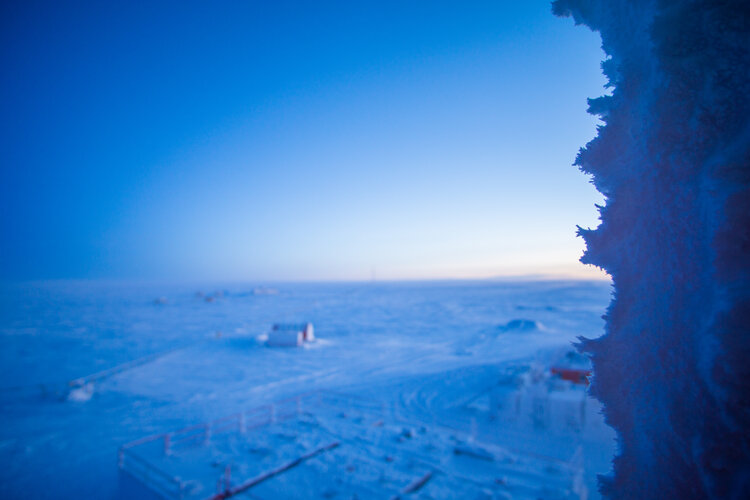 Image:
Image:
Applications are now open for the role of ESA-sponsored research medical doctor at Concordia research station in Antarctica for the 2023 winter over season. Do you have a medical degree, an interest in space exploration and the fortitude to spend almost a year in isolation in the world’s largest desert? Apply today for this unique post.
The blank backdrop
Located at the mountain plateau called Dome C in Antarctica, the French-Italian base is one of only three that is inhabited all year long.
Between the extreme altitude – 3233 m above sea level means the crew experience chronic hypobaric hypoxia or
One in five galaxies in the early universe could still be hidden behind cosmic dust
 Astronomers at the University of Copenhagen's Cosmic Dawn Center have discovered two previously invisible galaxies 29 billion light-years away. Their discovery suggests that up to one in five such distant galaxies remain hidden from our telescopes, camouflaged by cosmic dust. The new knowledge changes perceptions of our universe's evolution since the Big Bang.
Researchers at the University
Astronomers at the University of Copenhagen's Cosmic Dawn Center have discovered two previously invisible galaxies 29 billion light-years away. Their discovery suggests that up to one in five such distant galaxies remain hidden from our telescopes, camouflaged by cosmic dust. The new knowledge changes perceptions of our universe's evolution since the Big Bang.
Researchers at the University NASA awards contract for bed rest studies
 NASA has selected Deutsches Zentrum fur Luft-und Raumfahrt (DLR) of Cologne, Germany, to provide use of its facility to support long-duration bed rest research.
The $49.9 million Bedrest Studies Contract will support a series of bed rest studies at the company's facility in Cologne, Germany. Services also may be required at other NASA centers, contractor or subcontractor locations, or vend
NASA has selected Deutsches Zentrum fur Luft-und Raumfahrt (DLR) of Cologne, Germany, to provide use of its facility to support long-duration bed rest research.
The $49.9 million Bedrest Studies Contract will support a series of bed rest studies at the company's facility in Cologne, Germany. Services also may be required at other NASA centers, contractor or subcontractor locations, or vend