
Copernical Team
Did NASA find a mysterious doorway on Mars? No, but that's no reason to stop looking

For the past 10 years, NASA's Curiosity rover has been trundling around the surface of Mars, taking photos in its quest to understand the history and geology of the red planet and perhaps even find signs of life.
Last week it took a photo which appeared to show a doorway carved into the rock. It's the sort of thing that on Earth might indicate an underground bunker, such as an air-raid shelter.
Seeing is not always believing
At first sight, the picture is totally convincing. At second sight, maybe not. The passage seems to go in only a short way before the steeply descending roof meets the floor.
And then those killjoys at NASA tell us its only about 45 cm high. Still, who said Martians had to be the same height as us? But thengeologists point out several straight-line fractures can be seen in this site, and the "doorway" is where they happen to intersect.
Such a pity. It would have been so exciting if it had been a real doorway.
Swarm unveils magnetic waves deep down
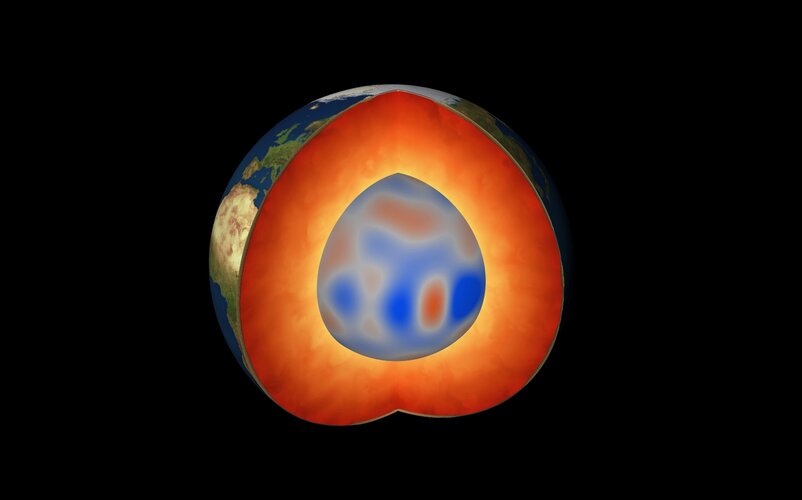
While volcanic eruptions and earthquakes serve as immediate reminders that Earth’s insides are anything but tranquil, there are also other, more elusive, dynamic processes happening deep down below our feet. Using information from ESA’s Swarm satellite mission, scientists have discovered a completely new type of magnetic wave that sweeps across the outermost part of Earth’s outer core every seven years. This fascinating finding, presented today at ESA’s Living Planet Symposium, opens a new window into a world we can never see.
Living Planet Symposium kicks off
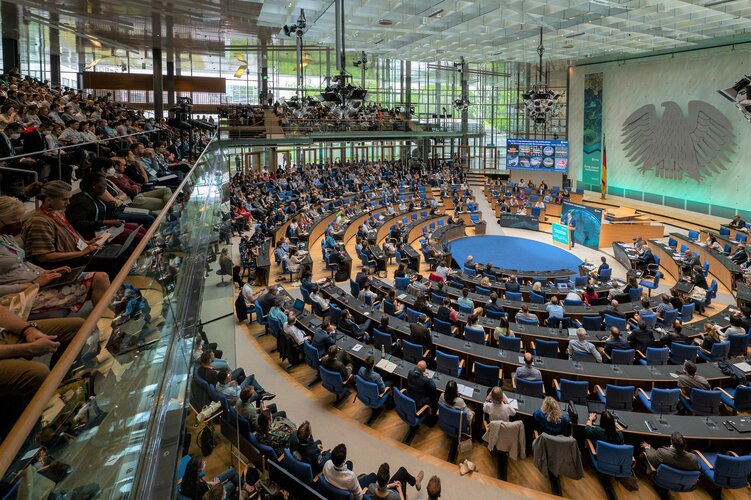

ESA’s Living Planet Symposium has opened with a flourish with over 4000 participants including scientists, academics, space industry representatives, institutional stakeholders, data users, students and citizens gathered to discuss the latest findings on our changing planet, as well as advances in satellite technologies, new opportunities in the commercial world, and ESA’s plans for the future.
NASA's ECOSTRESS detects 'heat islands' in extreme Indian heat wave
 A relentless heat wave has blanketed India and Pakistan since mid-March, causing dozens of deaths, fires, increased air pollution, and reduced crop yields. Weather forecasts show no prospect of relief any time soon. NASA's Ecosystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station instrument (ECOSTRESS) has been measuring these temperatures from space, at the highest spatial resolution
A relentless heat wave has blanketed India and Pakistan since mid-March, causing dozens of deaths, fires, increased air pollution, and reduced crop yields. Weather forecasts show no prospect of relief any time soon. NASA's Ecosystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station instrument (ECOSTRESS) has been measuring these temperatures from space, at the highest spatial resolution Kongsberg Defence and Aerospace orders three surveillance satellites from NanoAvionics
 Norway's Kongsberg Defence and Aerospace (Kongsberg) has placed an order for three microsatellites with Lithuanian mission integrator NanoAvionics for a space-based maritime surveillance mission covering the North Sea area. All three satellites will be based on NanoAvionics's largest satellite bus so far, the MP42 microsatellite bus.
The surveillance payload will consist of instrumentation
Norway's Kongsberg Defence and Aerospace (Kongsberg) has placed an order for three microsatellites with Lithuanian mission integrator NanoAvionics for a space-based maritime surveillance mission covering the North Sea area. All three satellites will be based on NanoAvionics's largest satellite bus so far, the MP42 microsatellite bus.
The surveillance payload will consist of instrumentation Charting a safe course through a highly uncertain environment
 An autonomous spacecraft exploring the far-flung regions of the universe descends through the atmosphere of a remote exoplanet. The vehicle, and the researchers who programmed it, don't know much about this environment.
With so much uncertainty, how can the spacecraft plot a trajectory that will keep it from being squashed by some randomly moving obstacle or blown off course by sudden, gal
An autonomous spacecraft exploring the far-flung regions of the universe descends through the atmosphere of a remote exoplanet. The vehicle, and the researchers who programmed it, don't know much about this environment.
With so much uncertainty, how can the spacecraft plot a trajectory that will keep it from being squashed by some randomly moving obstacle or blown off course by sudden, gal Fly me to the Moon: US, Japan aim for lunar landing
 Japan and the United States said Monday they want to put the first Japanese astronaut on the Moon as the allies deepen cooperation on space projects.
No non-American has ever touched down on the lunar surface, and Japan has previously said it hopes to achieve a Moon landing by the end of this decade.
President Joe Biden, after his first face-to-face meeting with Japan's Prime Minister Fu
Japan and the United States said Monday they want to put the first Japanese astronaut on the Moon as the allies deepen cooperation on space projects.
No non-American has ever touched down on the lunar surface, and Japan has previously said it hopes to achieve a Moon landing by the end of this decade.
President Joe Biden, after his first face-to-face meeting with Japan's Prime Minister Fu Live now: Living Planet Symposium

Live now: Living Planet Symposium
Watch the Opening Session live from Bonn
Self-cleaning spacecraft surfaces to combat microbes
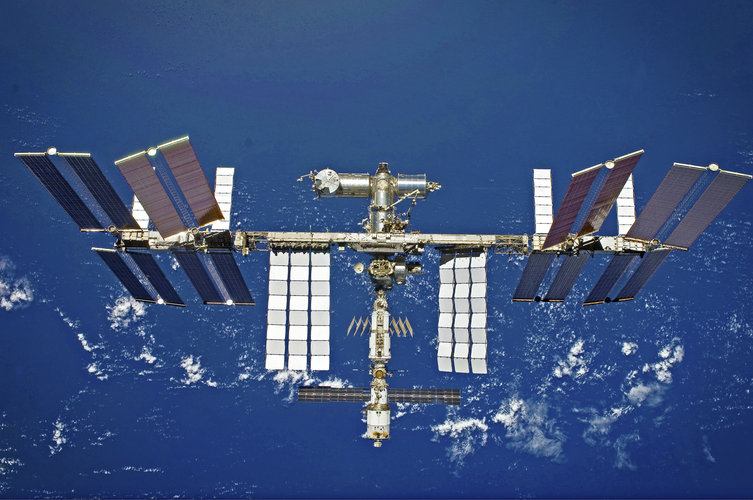

Astronauts live and work in orbit along with teaming populations of microorganisms, which could present a serious threat to health – and even the structural integrity of spacecraft. To help combat such invisible stowaways, an ESA-led project is developing microbe-killing coatings suitable for use within spacecraft cabins.
Satellites and drones can help save pollinators
 Satellites and drones can provide key information to protect pollinators, researchers say.
Their study examines new ways of using these technologies to track the availability of flowers, and says this could be combined with behavioural studies to see the world through the eyes of insects.
The flowers available to insects vary from day to day and place to place, and human activity is
Satellites and drones can provide key information to protect pollinators, researchers say.
Their study examines new ways of using these technologies to track the availability of flowers, and says this could be combined with behavioural studies to see the world through the eyes of insects.
The flowers available to insects vary from day to day and place to place, and human activity is 