
Copernical Team
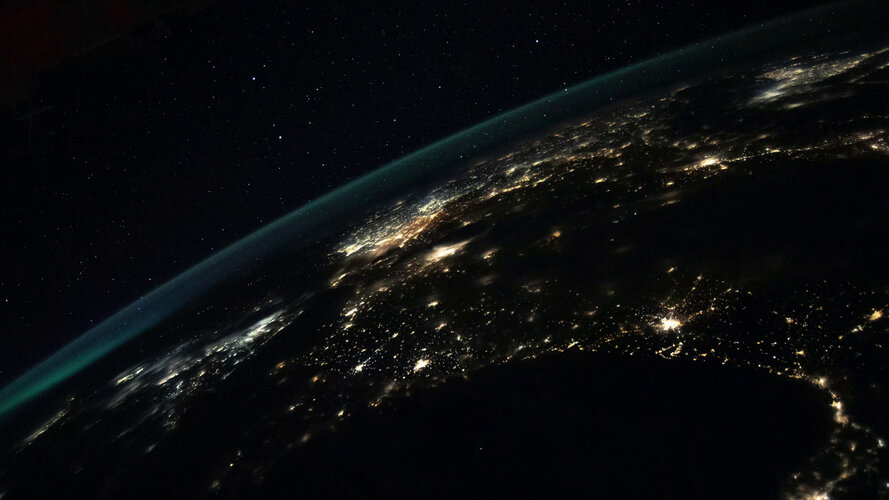
Europe night timelapse
 Video:
00:01:11
Video:
00:01:11
Timelapse video made during ESA astronaut Thomas Pesquet’s second mission to the International Space Station, “Alpha”. The camera is setup to take pictures at intervals of two a second, and the pictures are then edited into this video that plays at 25 pictures a second. The video is around 12 times faster than real speed.
Thomas shared this video on social media with the caption:
“Timelapse Tuesday: Approaching Europe at night, the Madeira islands seem to act as beacons that Portugal and Spain are on the horizon under the green hue of our atmosphere. The voyage continues over a
Tiger Team solves mystery of Euclid’s galaxy speed camera
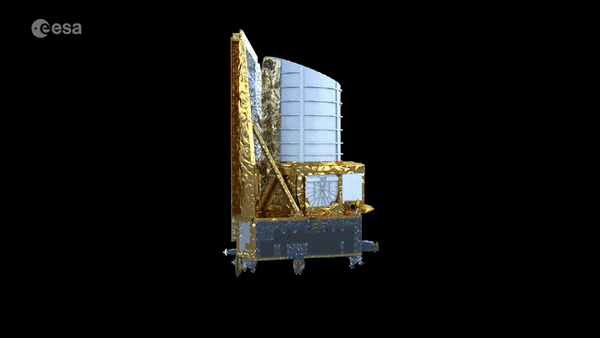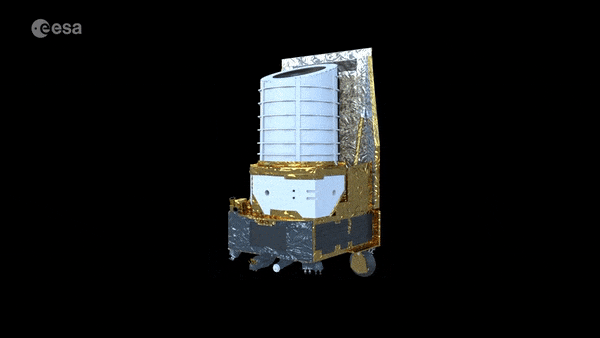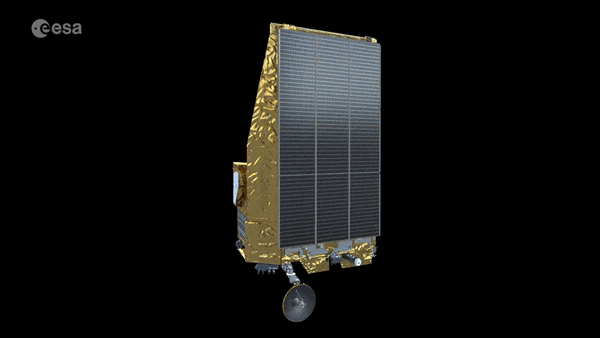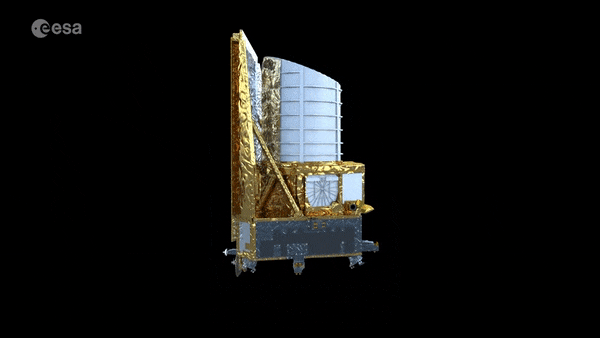
When tested in space-like conditions, the instrument on ESA’s Euclid space telescope set to measure the velocities of fast-receding galaxies abruptly stopped operating. Blindsided, the mission team feared it might take weeks or even months of extra time to uncover the reason why. Then a newly-convened ESA Tiger Team came to their assistance, pinpointing the cause and keeping Euclid on its set launch schedule.
Euclid telescope ready for extreme space environment
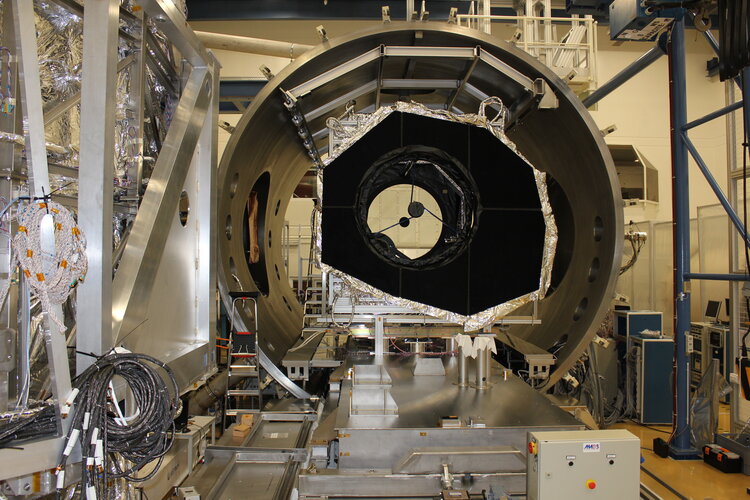
ESA’s Euclid mission has reached a new milestone in its development with successful testing of the telescope and instruments showing that it can operate and achieve the required performance in the extreme environment of space.
China launches high-resolution Earth-observation satellite
 China launched a Kuaizhou 1A carrier rocket to place a high-resolution Earth-observation satellite in space on Monday afternoon, according to China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation.
The State-owned space contractor said in a statement the solid-propellant rocket blasted off at 2:19 pm at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in northwestern China and soon deployed the satellite - J
China launched a Kuaizhou 1A carrier rocket to place a high-resolution Earth-observation satellite in space on Monday afternoon, according to China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation.
The State-owned space contractor said in a statement the solid-propellant rocket blasted off at 2:19 pm at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in northwestern China and soon deployed the satellite - J NASA drought research shows value of both climate mitigation and adaptation
 Seasonal summer rains have done little to offset drought conditions gripping the western United States, with California and Nevada seeing record July heat and moderate-to-exceptional drought according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Now, new NASA research is showing how drought in the region is expected to change in the future, providing stakeholders with crucial i
Seasonal summer rains have done little to offset drought conditions gripping the western United States, with California and Nevada seeing record July heat and moderate-to-exceptional drought according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Now, new NASA research is showing how drought in the region is expected to change in the future, providing stakeholders with crucial i Isotropic Systems secures funding to develop multi-link antenna through to product launch in 2022
 Isotropic Systems, a leading developer of transformational broadband terminal technologies, announces that it has raised over $37 million in an equity financing round, which fully funds the development of its game-changing multi-link antennas through to product launch in 2022.
The round is led by Seraphim Space Investment Trust PLC - the world's first listed space tech fund - in the first
Isotropic Systems, a leading developer of transformational broadband terminal technologies, announces that it has raised over $37 million in an equity financing round, which fully funds the development of its game-changing multi-link antennas through to product launch in 2022.
The round is led by Seraphim Space Investment Trust PLC - the world's first listed space tech fund - in the first Airbus backs Dereum Labs to collaborate on lunar resources extraction
 Airbus has signed a memorandum of understanding with the Mexican Space Agency (AEM) and the Mexican start-up Dereum Labs to collaborate on the technologies needed for lunar resources extraction. This will lead to the creation of a new Mexican In-Situ Resources Utilisation (ISRU) Programme for lunar extraction and help develop the necessary industrial ecosystem for this technology in-country.
Airbus has signed a memorandum of understanding with the Mexican Space Agency (AEM) and the Mexican start-up Dereum Labs to collaborate on the technologies needed for lunar resources extraction. This will lead to the creation of a new Mexican In-Situ Resources Utilisation (ISRU) Programme for lunar extraction and help develop the necessary industrial ecosystem for this technology in-country. Asteroid sample brought back to Earth gets a close-up look at Brown
 In December 2020, Japan's Hayabusa2 spacecraft swung by Earth to drop off a cache of rock samples taken from a near-Earth asteroid called Ryugu. Asteroids like Ryugu are thought to represent the ancient building blocks of the solar system, and scientists have been eager to get a closer look at the returned samples.
Last week, the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency shipped one of the sam
In December 2020, Japan's Hayabusa2 spacecraft swung by Earth to drop off a cache of rock samples taken from a near-Earth asteroid called Ryugu. Asteroids like Ryugu are thought to represent the ancient building blocks of the solar system, and scientists have been eager to get a closer look at the returned samples.
Last week, the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency shipped one of the sam Soyuz docks to new Nauka module port at ISS
 The Soyuz MS-18 spacecraft that first launched and arrived to the International Space Station April 9 has now successfully relocated with its crew aboard from the station's Earth-facing Rassvet module to the "Nauka" Multipurpose Laboratory Module. The spacecraft carrying Russian cosmonauts Oleg Novitskiy, commander of the Soyuz, and Pyotr Dubrov along with NASA astronaut Mark Vande Hei, docked a
The Soyuz MS-18 spacecraft that first launched and arrived to the International Space Station April 9 has now successfully relocated with its crew aboard from the station's Earth-facing Rassvet module to the "Nauka" Multipurpose Laboratory Module. The spacecraft carrying Russian cosmonauts Oleg Novitskiy, commander of the Soyuz, and Pyotr Dubrov along with NASA astronaut Mark Vande Hei, docked a Spin test a success, but Ingenuity Flight 14 delayed until after conjunction
 It's been an eventful several Martian days, or sols, since our last blog post, so we wanted to provide everyone with an update on where things stand on Mars. In our last post, we explained that we were getting ready to begin flying with a higher rotor speed to compensate for decreasing atmospheric density caused by seasonal changes on Mars.
Increasing the rotor speed is a significant chang
It's been an eventful several Martian days, or sols, since our last blog post, so we wanted to provide everyone with an update on where things stand on Mars. In our last post, we explained that we were getting ready to begin flying with a higher rotor speed to compensate for decreasing atmospheric density caused by seasonal changes on Mars.
Increasing the rotor speed is a significant chang 