
Copernical Team
Trading space: ESA bolsters European business
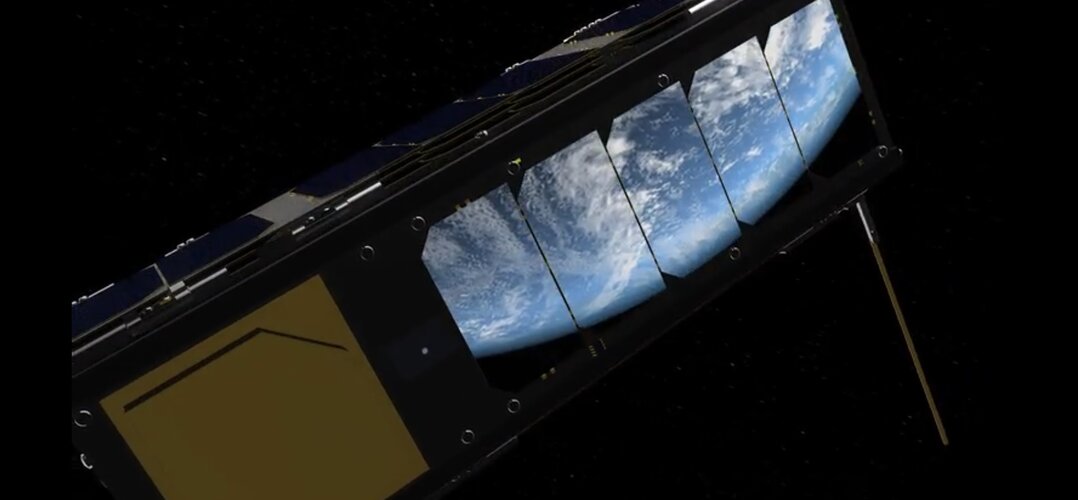

Yesterday, ESA’s orbiting laboratory, OPS-SAT, hosted the first-ever stock trade in space. The successful experiment required developers at Europe’s leading online broker flatexDEGIRO to think far outside of the box and adapt their software to the technical demands and constrained bandwidth found on an orbiting platform at 500 km altitude.
La Palma lava flows into the sea
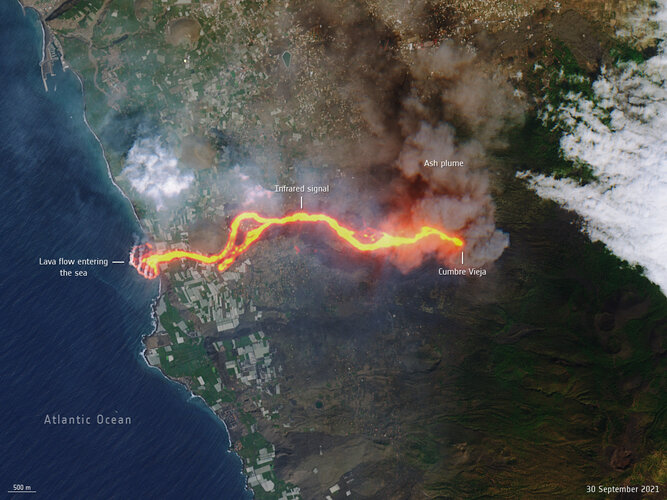 Image:
This image, captured by Copernicus Sentinel-2 on 30 September, shows the flow of lava from the volcano erupting on the Spanish island of La Palma.
Image:
This image, captured by Copernicus Sentinel-2 on 30 September, shows the flow of lava from the volcano erupting on the Spanish island of La Palma. Navigating a very close approach
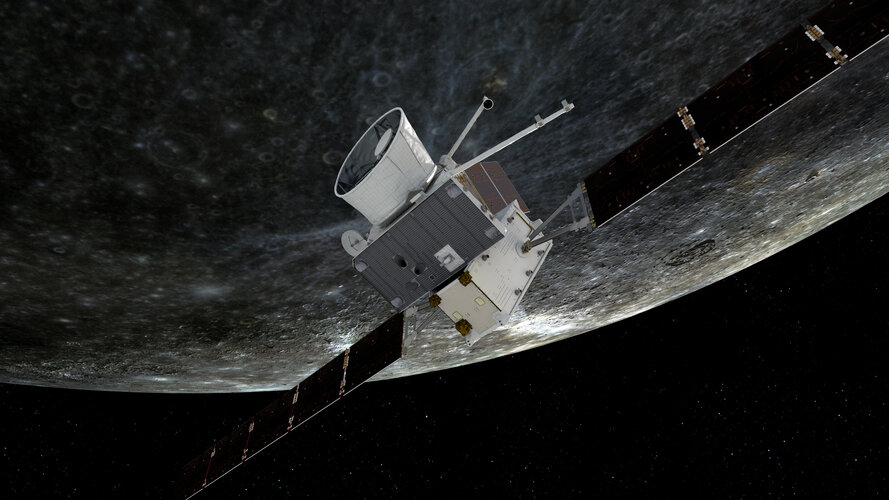

Tonight, BepiColombo will perform the first of six Mercury flybys, each honing the spacecrafts’ trajectory with the ultimate goal of shedding enough energy – after its two years ‘falling’ towards the Sun – to be caught by the innermost planet’s gravity and remain in Mercurial orbit.
Week in images: 27 September - 1 October 2021

Week in images: 27 September - 1 October 2021
Discover our week through the lens
Lorentz test chamber at Sunday's Open Day
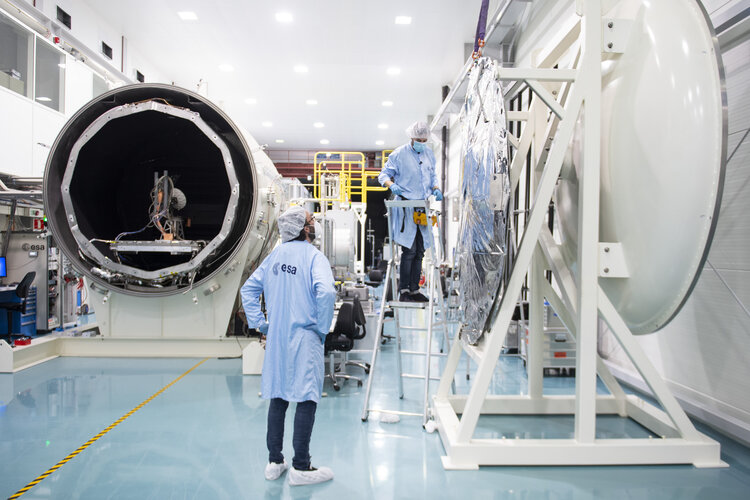 Image:
Lorentz test chamber at Sunday's Open Day
Image:
Lorentz test chamber at Sunday's Open Day Trading spaces: ESA bolsters European business

Yesterday, ESA’s orbiting laboratory, OPS-SAT, hosted the first-ever stock trade in space. The successful experiment required developers at Europe’s leading online broker flatexDEGIRO to think far outside of the box and adapt their software to the technical demands and constrained bandwidth found on an orbiting platform at 500 km altitude.
Open Day online programme
Here is the programme for our virtual ESA Open Day 2021 on Sunday 3 October. Click on the link sent to your email to enter the Live Lobby where your introduction to the Open Day will take place from 1300 CEST. From there, you can choose which talks or events to attend across the various ‘rooms’ listed below. All times listed below are in CEST. (To attend the virtual Open Day you have to register - registrations close at 1200 CEST on Saturday).
Scientists recreate cosmic reactions to unlock astronomical mysteries
 Experiments will give scientists a closer look at how exploding stars create world's heaviest elements. How do the chemical elements, the building blocks of our universe, get built?
This question has been at the core of nuclear physics for the better part of a century. At the beginning of the 20th century, scientists discovered that elements have a central core or nucleus. These nuclei con
Experiments will give scientists a closer look at how exploding stars create world's heaviest elements. How do the chemical elements, the building blocks of our universe, get built?
This question has been at the core of nuclear physics for the better part of a century. At the beginning of the 20th century, scientists discovered that elements have a central core or nucleus. These nuclei con Mercury ahead
 The ESA/JAXA BepiColombo mission to Mercury will make the first of six flybys of its destination planet on 1 October before entering orbit in 2025.
Hot on the heels of its last Venus flyby in August, the spacecraft's next exciting encounter is with Mercury at 23:34 UTC on 1 October (01:34 CEST 2 October). It will swoop by the planet at an altitude of about 200 km, capturing imagery and sci
The ESA/JAXA BepiColombo mission to Mercury will make the first of six flybys of its destination planet on 1 October before entering orbit in 2025.
Hot on the heels of its last Venus flyby in August, the spacecraft's next exciting encounter is with Mercury at 23:34 UTC on 1 October (01:34 CEST 2 October). It will swoop by the planet at an altitude of about 200 km, capturing imagery and sci Study finds photosynthesis in Venus' clouds could support life
 New data analysis has found that the sunlight filtering through Venus' clouds could support Earth-like photosynthesis in the cloud layers and that chemical conditions are potentially amenable to the growth of microorganisms.
Biochemistry Professor Rakesh Mogul is the lead author of the study, Potential for Phototrophy in Venus' Clouds, published online this weekin the journal Astrobiology'
New data analysis has found that the sunlight filtering through Venus' clouds could support Earth-like photosynthesis in the cloud layers and that chemical conditions are potentially amenable to the growth of microorganisms.
Biochemistry Professor Rakesh Mogul is the lead author of the study, Potential for Phototrophy in Venus' Clouds, published online this weekin the journal Astrobiology' 