Displaying items by tag: SBAS
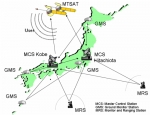
Multi-functional Satellite Augmentation System (MSAS)
Multi-functional Satellite Augmentation System (MSAS) is a Japanese SBAS (Satellite Based Augmentation System), i.e. a satellite navigation system which supports differential GPS (DGPS) designed to supplement the GPS system by reporting (then improving) on the reliability and accuracy of those signals.
A similar service is provided in North America by Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS), and in Europe by European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS).
It is operated by the Japan's Government.
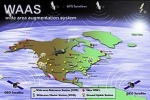
Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS)
The Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) is an air navigation aid developed by the Federal Aviation Administration to augment the Global Positioning System (GPS).
The goal is to improve the GPS signal accuracy, integrity, and availability. Essentially, WAAS is intended to enable aircraft to rely on GPS for all phases of flight, including precision approaches to any airport within its coverage area.
WAAS uses a network of ground-based reference stations, in North America and Hawaii, to measure small variations in the GPS satellites' signals in the western hemisphere. Measurements from the reference stations are routed to master stations, which queue the received Deviation Correction and send the correction messages to geostationary WAAS satellites in a timely manner (every 5 seconds or better). Those satellites broadcast the correction messages back to Earth, where WAAS-enabled GPS receivers use the corrections while computing their positions to improve accuracy.
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) calls this type of system a satellite-based augmentation system (SBAS).
Similar service is provided in Asia, notably Japan, by the Multi-functional Satellite Augmentation System (MSAS), and in Europe by European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS).
EGNOS
The European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS) is a satellite based augmentation system developed by the European Space Agency (ESA), the European Commission and EUROCONTROL.
The EGNOS system provides additional signals to users of satellite navigation services, broadcast through geostationary satellites, guaranteeing the integrity of satellite navigation so that it can be used in support of safety-of-life services such as civil aviation.
It supplements the GPS, GLONASS and Galileo systems by reporting on the reliability and accuracy of the positioning data. The official start of operations was announced by the European Commission on 1 October 2009.
According to specifications, horizontal position accuracy should be better than seven metres. In practice, the horizontal position accuracy is at the metre level. The EGNOS system consists of three geostationary satellites and a network of ground stations.
The system started its initial operations in July 2005, showing outstanding performances in terms of accuracy (better than two metres) and availability (above 99%); and it was certified for use in safety of life applications in March 2011. An EGNOS Data Access Service is also available since July 2012.
Similar service is provided in North America by the Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS), and in Asia, notably Japan, by the Multi-functional Satellite Augmentation System (MSAS).