
Copernical Team
NASA-supported solar sail could take science to new heights
 As NASA's exploration continues to push boundaries, a new solar sail concept selected by the agency for development toward a demonstration mission could carry science to new destinations.
The Diffractive Solar Sailing project was selected for Phase III study under the NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) program. Phase III aims to strategically transition NIAC concepts with the highest
As NASA's exploration continues to push boundaries, a new solar sail concept selected by the agency for development toward a demonstration mission could carry science to new destinations.
The Diffractive Solar Sailing project was selected for Phase III study under the NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) program. Phase III aims to strategically transition NIAC concepts with the highest InSight's Final Selfie
 NASA's InSight Mars lander took this final selfie on April 24, 2022, the 1,211th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The lander is covered with far more dust than it was in its first selfie, taken in December 2018, not long after landing - or in its second selfie, composed of images taken in March and April 2019.
The arm needs to move several times in order to capture a full selfie. Becau
NASA's InSight Mars lander took this final selfie on April 24, 2022, the 1,211th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The lander is covered with far more dust than it was in its first selfie, taken in December 2018, not long after landing - or in its second selfie, composed of images taken in March and April 2019.
The arm needs to move several times in order to capture a full selfie. Becau Boeing's Starliner faces one more challenge as it returns to Earth
 Boeing's Starliner capsule is readying to return to Earth on Wednesday in the final step of a key test flight to prove itself worthy of providing rides for NASA astronauts to the International Space Station.
The spaceship is scheduled to autonomously undock at 2:36 pm Eastern Time (1836 GMT) and touch down in New Mexico just over four hours later, at 2249 GMT, wrapping up a six-day mission c
Boeing's Starliner capsule is readying to return to Earth on Wednesday in the final step of a key test flight to prove itself worthy of providing rides for NASA astronauts to the International Space Station.
The spaceship is scheduled to autonomously undock at 2:36 pm Eastern Time (1836 GMT) and touch down in New Mexico just over four hours later, at 2249 GMT, wrapping up a six-day mission c Supporting the Paris Agreement from space

Earth observation is already capable of supporting national climate action, but there are many more opportunities on the horizon, according to discussions today among leading scientists and policymakers at ESA’s Living Planet Symposium being held in Bonn, Germany.
Watch live: Samantha Cristoforetti in-flight call to World Economic Forum (WEF) 2022 in Davos

NASA Awards Contract to National Academy of Sciences
 NASA has awarded a sole-source contract to the National Academy of Sciences of Washington to conduct studies on questions of national importance within the domain of NASA science and technology programs relating to space science, Earth science, and biological and physical science in space.
NASA has awarded a sole-source contract to the National Academy of Sciences of Washington to conduct studies on questions of national importance within the domain of NASA science and technology programs relating to space science, Earth science, and biological and physical science in space. GHGSat joins ESA’s Third Party Mission Programme

GHGSat, a leader in high-resolution greenhouse gas monitoring from space, has officially joined ESA’s prestigious Third Party Mission Programme. Announced today at the Living Planet Symposium currently taking place in Bonn, data from the company’s fleet of commercial satellites will be provided, free of charge, to researchers working in the fields of Earth science and climate change. Users will be able to access greenhouse gas measurements from sites all around the world.
NASA is building a mission that will refuel and repair satellites in orbit
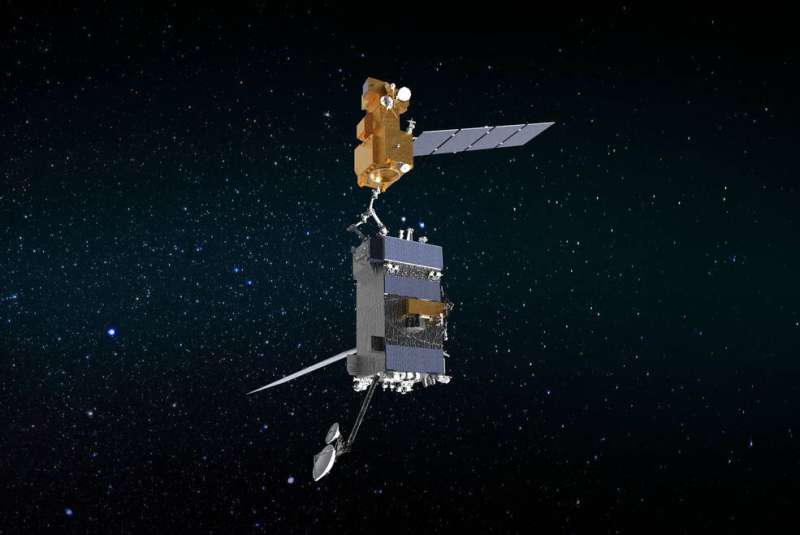

NASA is planning a mission to demonstrate the ability to repair and upgrade satellites in Earth orbit. The mission, called OSAM-1 (On-orbit Servicing, Assembly, and Manufacturing-1), will send a robotic spacecraft equipped with robotic arms and all the tools and equipment needed to fix, refuel or extend satellites' lifespans, even if those satellites were not designed to be serviced on orbit.
The first test flight of OSAM-1 is scheduled for launch no earlier than 2026 and will go to low Earth orbit to rendezvous, grapple and dock with Landsat 7, an Earth observing satellite that has been in orbit since 1999. The mission will conduct a first-of-its-kind refueling demonstration test, then relocate the satellite to a new orbit. While some parts of the mission are autonomous, human tele-operators will conduct much of the procedures and maneuvers remotely from Earth.
NASA says that repairing satellites—instead of just letting defunct spacecraft drift in Earth orbit—helps decrease space debris to create a more sustainable future for space exploration.
Forget about Mars, when will humans be flying to Saturn?

It might be hard to fathom now, but the human exploration of the solar system isn't going to stop at the moon and Mars. Eventually, our descendants will spread throughout the solar system—for those interested in space exploration, the question is only of when rather than if. Answering that question is the focus of a new paper released on arXiv by a group of researchers from the U.S., China, and the Netherlands. Their approach is highly theoretical, but it is likely more accurate than previous estimates, and it gives a reasonable idea of when we could expect to see humans in the outer solar system. The latest they think we could reach the Saturnian system is 2153.
How to even start such a calculation is complicated, so it's best to start at the basics, which in this case involves a bit of calculus. To understand when humans will reach further out in the solar system, the authors needed two variables—distance and time. In this case, distance is defined as the distance from Earth that humans have traveled, and time is defined as having started at the beginning of the space race in 1957 when no human had yet left Earth.
Africa in the spotlight at Living Planet Symposium
We live in uncertain times. The detrimental impacts of climate change are being felt around the world and threatening our future, we are emerging from the global COVID pandemic that halted life as we know it for more than two years, and now the Ukraine crisis is not only a tragedy for those directly affected but its rippling effects are jeopardising energy and food security far and wide. Some nations are able to weather these storms better than others, but a number of countries in Africa, for example, are already on the back foot, particularly when it comes to
